Overview
Supported Regions
The supported regions are subject to those available on the management console.
Scenario
To meet business development requirements, enterprise A needs to implement communication between its on-premises data center and its VPC. In this case, enterprise A can use the VPN service to create connections between the on-premises data center and the VPC.
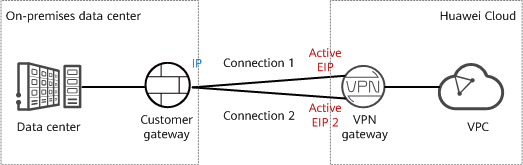
- If the on-premises data center has only one customer gateway and this gateway can be configured with only one IP address, it is recommended that the VPN gateway use the active-active mode. Figure 1 shows the networking.
In active-active mode, if connection 1 is faulty, traffic is automatically switched to connection 2 for transmission, without affecting enterprise services.
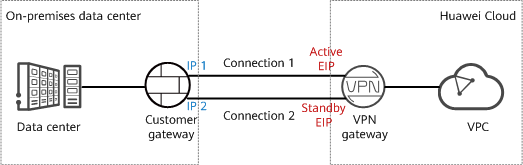
- If the on-premises data center has two customer gateways or has only one customer gateway that can be configured with two IP addresses, it is recommended that the VPN gateway use the active/standby mode. Figure 2 shows the networking.
In active/standby mode, connection 1 is the active link and connection 2 is the standby link. By default, traffic is transmitted only through the active link. If the active link fails, traffic is automatically switched to the standby link, without affecting enterprise services. After the active link recovers, traffic is switched back to the active link.
Limitations and Constraints
- The customer gateway device must support standard IKE and IPsec protocols.
- The interconnection subnets of the on-premises data center neither overlap with those of the VPC nor contain 100.64.0.0/10 or 214.0.0.0/8.
If the VPC uses Direct Cloud or Cloud Connect connections to communicate with other VPCs, the on-premises data center subnets cannot overlap with those of these VPCs.
Data Plan
|
Category |
Item |
Data |
|---|---|---|
|
VPC |
Subnet that needs to access the on-premises data center |
192.168.0.0/16 |
|
VPN gateway |
Interconnection subnet |
This subnet is used for communication between the VPN gateway and VPC. Ensure that the selected interconnection subnet has four or more assignable IP addresses. 192.168.2.0/24 |
|
HA mode |
Active-active |
|
|
EIP |
EIPs are automatically generated when you buy them. By default, a VPN gateway uses two EIPs. In this example, the EIPs are as follows:
|
|
|
VPN connection |
Tunnel interface addresses under Connection 1's Configuration |
The IP addresses are used to establish an IPsec tunnel between a VPN gateway and a customer gateway. At the two ends of the IPsec tunnel, the configured local and remote tunnel interface addresses must be reversed.
|
|
Tunnel interface addresses under Connection 2's Configuration |
|
|
|
On-premises data center |
Subnet that needs to access the VPC |
172.16.0.0/16 |
|
Customer gateway |
Gateway IP address |
The gateway IP address is assigned by a carrier. In this example, the gateway IP address is: 22.xx.xx.22 |
Operation Process
Figure 3 shows the process of using the VPN service to enable communication between an on-premises data center and a VPC.
|
No. |
Step |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Bind two EIPs to the VPN gateway. If you have purchased EIPs, you can directly bind them to the VPN gateway. |
|
|
2 |
Configure the VPN device in the on-premises data center as the customer gateway. |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
5 |
Log in to an ECS and run the ping command to verify the network connectivity. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.