Connecting to a DB Instance from a Linux ECS
You can connect to your DB instance using a Linux ECS installed with a PostgreSQL client over a public network.
You can use the PostgreSQL client psql to connect to your DB instance over a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connection. SSL encrypts connections to your DB instance, making in-transit data more secure.
SSL is enabled by default when you create an RDS for PostgreSQL DB instance and cannot be disabled after the instance is created.
Step 1: Buy an ECS
- Log in to the management console and check whether there is an ECS available.
- Buy an ECS and select Linux (for example, CentOS) as its OS.
To download a PostgreSQL client to the ECS, bind an EIP to the ECS.
For details about how to purchase a Linux ECS, see "Purchasing an ECS" in Elastic Cloud Server User Guide.
- On the ECS Information page, view the region and VPC of the ECS.
- On the Basic Information page of the RDS for PostgreSQL instance, view the region and VPC of the DB instance.
Step 2: Test Connectivity and Install a PostgreSQL Client
- Log in to the ECS. For details, see "Login Using VNC" in the Elastic Cloud Server User Guide.
- On the Instances page, click the DB instance name.
- Choose Connectivity & Security from the navigation pane. In the Connection Information area, obtain the EIP and database port of the DB instance.
If no EIP has been bound to the DB instance, see Binding an EIP.
- On the ECS, check whether the EIP and database port of the DB instance can be connected.
- If yes, network connectivity is normal.
- If no, check the security group rules.
- If in the security group of the ECS, there is no outbound rule with Destination set to 0.0.0.0/0 and Protocol & Port set to All, add an outbound rule for the EIP and port of the DB instance.
- If in the security group of the DB instance, there is no inbound rule with Source set to 0.0.0.0/0 and Protocol & Port set to All, add an inbound rule for the private IP address and port of the ECS. For details, see Configuring Security Group Rules.
- Open the client installation page.
PostgreSQL provides client installation methods for different OSs on its official website.
The following describes how to install a PostgreSQL 12 client in CentOS.
- Select a DB engine version, OS, and OS architecture, and run the following commands on the ECS to install a PostgreSQL client:
sudo yum install -y https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm sudo yum install -y postgresql12-server
Figure 1 Installing a client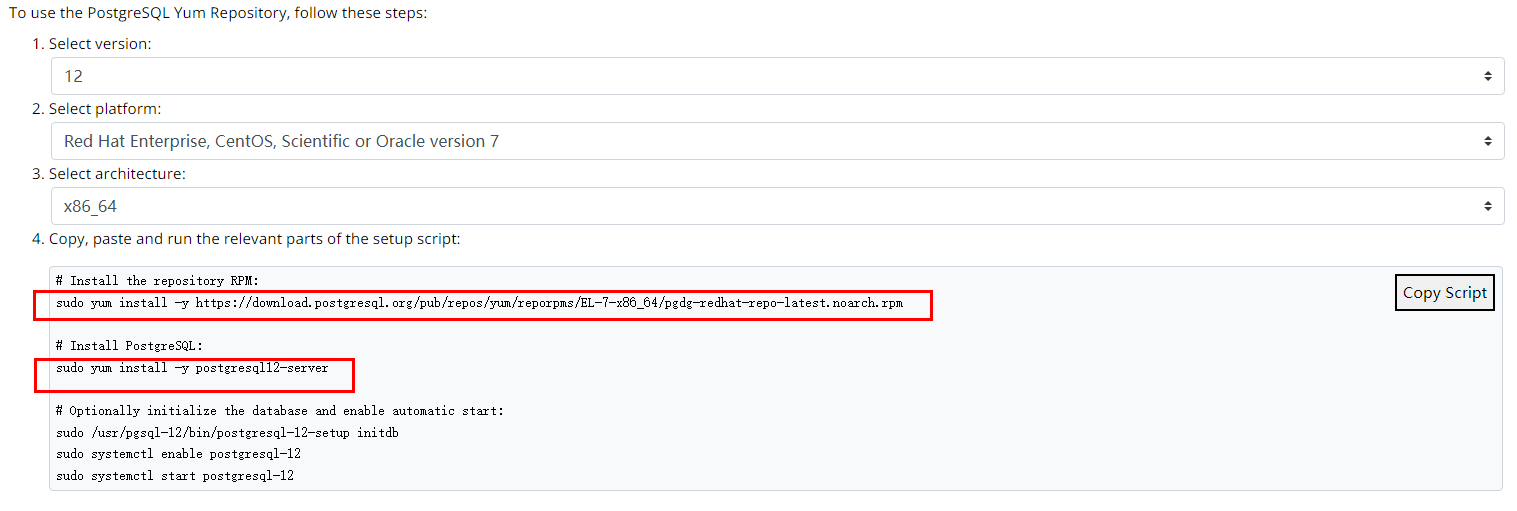
- Select a DB engine version that is consistent with that of your RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
- Select an OS that is consistent with that of the ECS.
- Select an OS architecture that is consistent with that of the ECS.
Figure 2 Installing the RPM package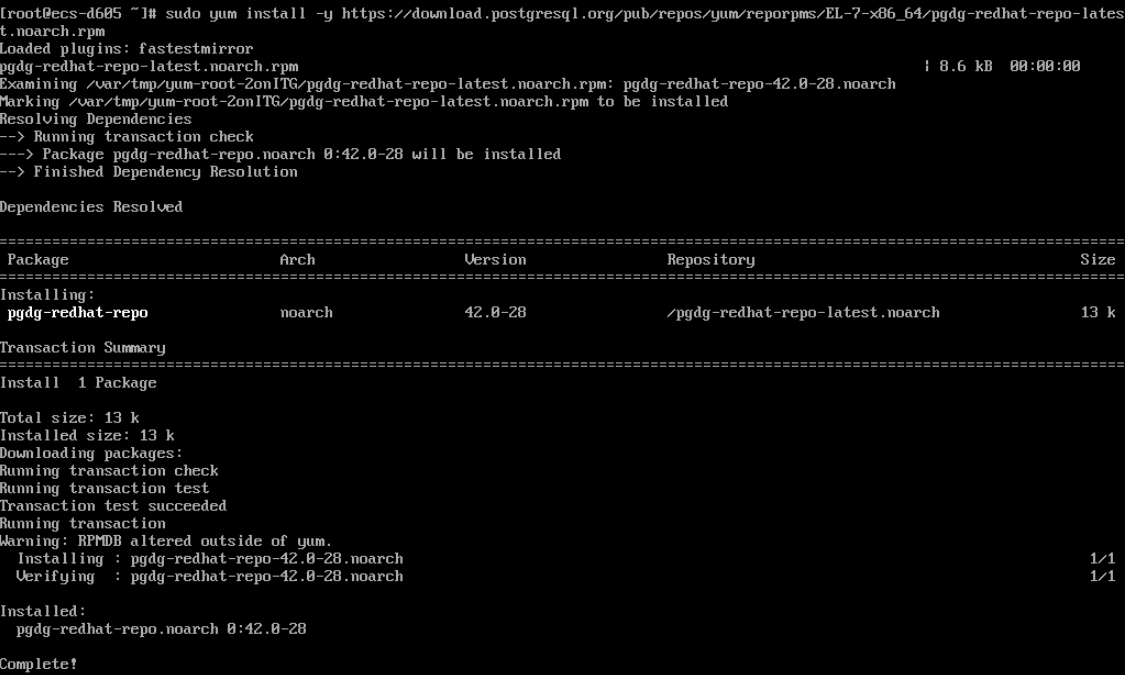 Figure 3 Client installed
Figure 3 Client installed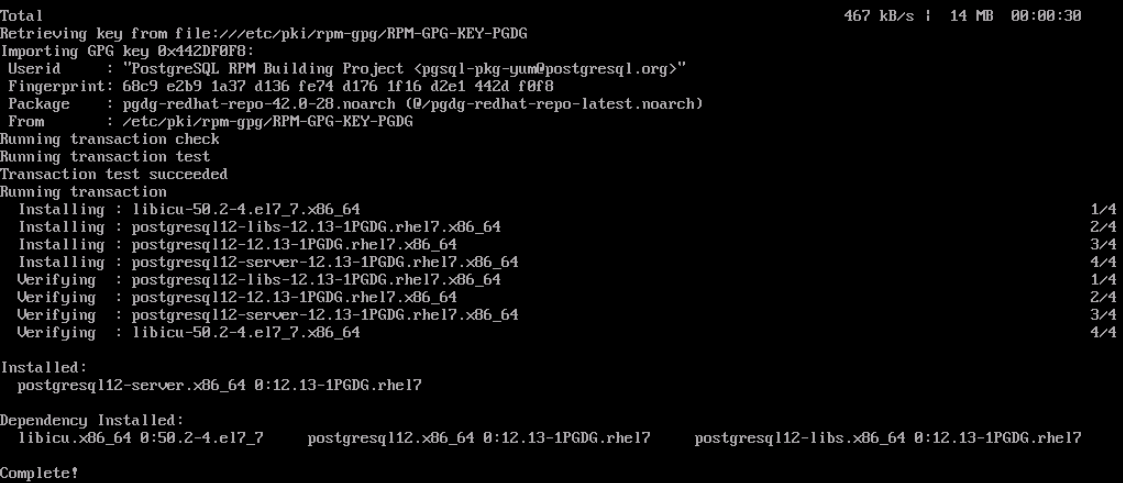
Step 3: Connect to the DB Instance Using Commands (SSL Connection)
- On the Instances page, click the DB instance name.
- In the navigation pane, choose Connectivity & Security.
- In the Connection Information area, click
 next to the SSL field to download Certificate Download.zip, and extract the root certificate ca.pem and bundle ca-bundle.pem from the package.
next to the SSL field to download Certificate Download.zip, and extract the root certificate ca.pem and bundle ca-bundle.pem from the package. - Upload ca.pem to the ECS.
- Run the following command on the ECS to connect to the DB instance:
psql --no-readline -h <host> -p <port> "dbname=<database> user=<user> sslmode=verify-ca sslrootcert=<ca-file-directory>"
Example:
psql --no-readline -h 192.168.0.44 -p 5432 "dbname=postgres user=root sslmode=verify-ca sslrootcert=/root/ca.pem"
Table 1 Parameter description Parameter
Description
<host>
EIP obtained in 3.
<port>
Database port obtained in 3. The default value is 5432.
<database>
Name of the database to be connected. The default database name is postgres.
<user>
Administrator account root.
<ca-file-directory>
Directory of the CA certificate used for the SSL connection. This certificate should be stored in the directory where the command is executed.
sslmode
SSL connection mode. Set it to verify-ca to use a CA to check whether the service is trusted.
- Enter the password of the database account as prompted.
Password:
If the following information is displayed, the connection is successful.SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.2, cipher: ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384, bits: 256, compression: off)
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






