Connecting to an Instance with SSL
If SSL is enabled, data will be encrypted before transmission for enhanced security.
The following demo shows how to access and use a RabbitMQ instance in a VPC, assuming that the RabbitMQ client is deployed in an ECS.
RabbitMQ instances are compatible with the open-source RabbitMQ protocol. To access a RabbitMQ instance in your service code, see the tutorials for different languages at https://www.rabbitmq.com/getstarted.html.
Prerequisites
- A RabbitMQ instance has been created following the instructions in Step 2: Create a RabbitMQ Instance, and the username and password used to create the instance have been obtained.
- The Instance Address (Private Network) or Instance Address (Public Network) of the instance has been recorded from the instance details.
- An ECS has been created, and its VPC, subnet, and security group configurations are the same as those of the RabbitMQ instance.
- You have installed the JDK and configured the environment variables. For details, see Step 1: Prepare the Environment.
Accessing the Instance Using CLI
- Run the following command to download RabbitMQ-Tutorial-SSL.zip:
$ wget https://dms-demo.obs.cn-north-1.myhuaweicloud.com/RabbitMQ-Tutorial.zip
- Run the following command to decompress RabbitMQ-Tutorial-SSL.zip:
$ unzip RabbitMQ-Tutorial-SSL.zip
- Run the following command to navigate to the RabbitMQ-Tutorial-SSL directory, which contains the precompiled JAR file:
$ cd RabbitMQ-Tutorial-SSL
- Create messages using the sample project.
$ java -cp .:rabbitmq-tutorial-sll.jar Send host port user password
host indicates the connection address for accessing the instance. port is the listening port of the instance, which is 5671 by default. user and password indicate the username and password used for accessing the instance.
Figure 1 Sample project for message creation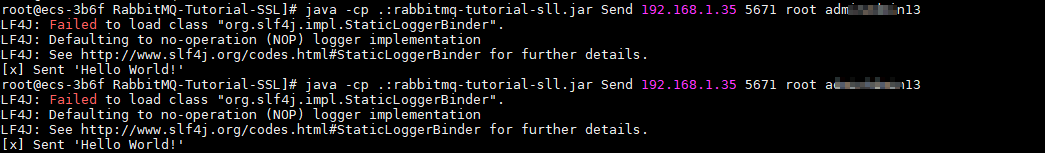
Press Ctrl+C to exit.
- Retrieve messages using the sample project.
$ java -cp .:rabbitmq-tutorial-sll.jar Recv host port user password
host indicates the connection address for accessing the instance. port is the listening port of the instance, which is 5671 by default. user and password indicate the username and password used for accessing the instance.
Figure 2 Sample project for message retrieval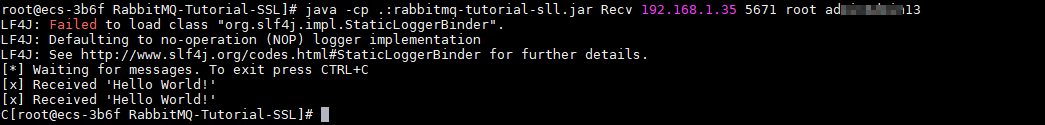
To stop retrieving messages, press Ctrl+C to exit.
Java Sample Code
Accessing an instance and creating messages
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost(host);
factory.setPort(port);
factory.setUsername(user);
factory.setPassword(password);
factory.useSslProtocol();
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
String message = "Hello World!";
channel.basicPublish("", QUEUE_NAME, null, message.getBytes("UTF-8"));
System.out.println(" [x] Sent '" + message + "'");
channel.close();
connection.close();
Accessing an instance and retrieving messages
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost(host);
factory.setPort(port);
factory.setUsername(user);
factory.setPassword(password);
factory.useSslProtocol();
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
System.out.println(" [*] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C");
Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel)
{
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties,
byte[] body)
throws IOException
{
String message = new String(body, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(" [x] Received '" + message + "'");
}
};
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, true, consumer);
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.









