What Is ELB?
Elastic Load Balance (ELB) automatically distributes incoming traffic across multiple backend servers based on the routing policies you configure. ELB expands the service capabilities of your applications and improves their availability by eliminating single points of failure (SPOFs).
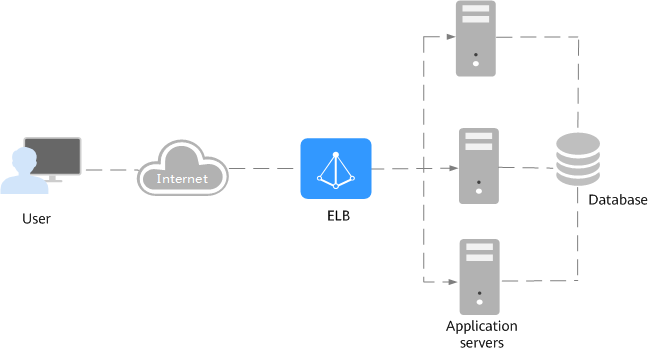
In the following figure, ELB distributes incoming traffic to three application servers, and each server processes one third of the requests. ELB checks the health of backend servers and distributes traffic only to servers that are running normally, improving the availability of applications.
ELB Components
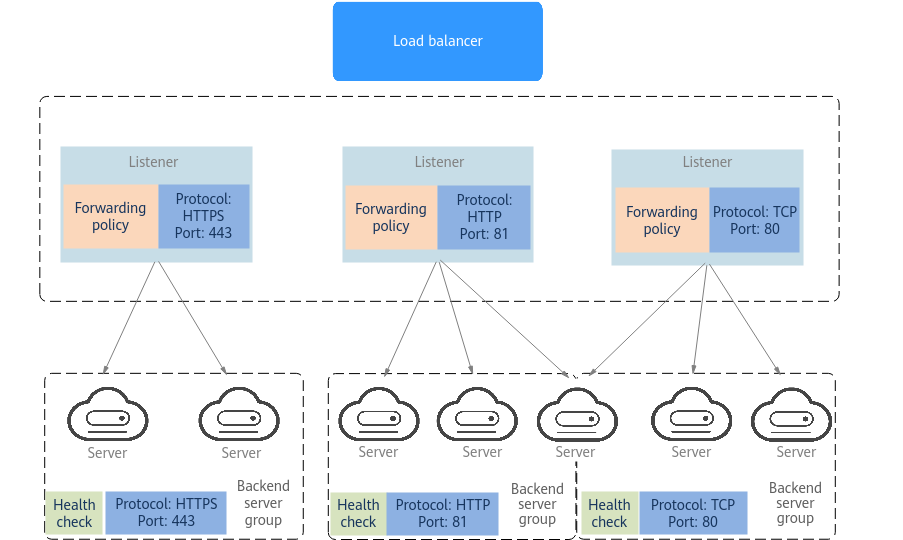
ELB consists of the components as shown in the figure below.
|
Load balancer |
Distributes incoming traffic across backend servers in one or more availability zones (AZs). |
|---|---|
|
Listener |
Uses the protocol and port you specify to check requests from clients and route the requests to associated backend servers based on the routing policies and forwarding policies you configure. You can add one or more listeners to a load balancer. |
|
Backend server group |
Contains one or more backend servers to receive requests routed by the listener. A backend server can be a cloud server, supplementary network interface, or IP address. |
|
Backend server |
Processes requests from the associated load balancer. When you add a listener to a load balancer, you can create or select a backend server group to receive requests from the load balancer by using the port and protocol you specify for the backend server group and the load balancing algorithm you select. |
Accessing ELB
You can use either of the following methods to access ELB:
- APIs
You can call APIs to access ELB. For details, see the Elastic Load Balance API Reference.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






