Application Scenarios
Prerequisites
All the custom keys mentioned in this section are symmetric keys. For details about symmetric keys and asymmetric keys, see Key Types.
Small Data Encryption and Decryption
You can use the online tool on the KMS console or call KMS APIs to directly encrypt or decrypt a small amount of data, such as passwords, certificates, or phone numbers. Currently, a maximum of 4 KB of data can be encrypted or decrypted in this way.
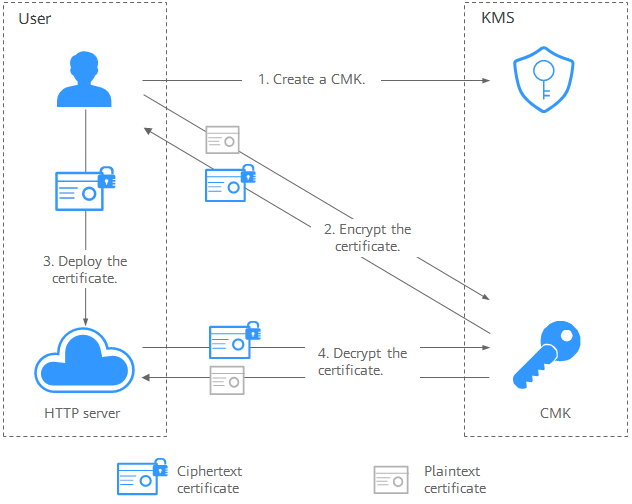
Figure 1 shows an example about how to call the APIs to encrypt and decrypt an HTTPS certificate.
- Create a CMK on KMS.
- Call the encrypt-data API of KMS and use the CMK to encrypt the plaintext certificate.
- Deploy the certificate onto a server.
- The server calls the decrypt-data API of KMS to decrypt the ciphertext certificate.
Large Data Encryption and Decryption
If you want to encrypt or decrypt large volumes of data, such as pictures, videos, and database files, you can use the envelope encryption method, where the data does not need to be transferred over the network.
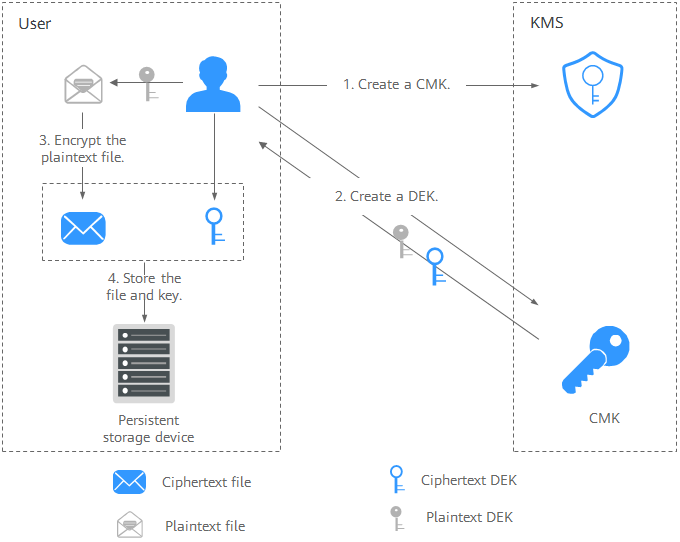
- Figure 2 illustrates the process for encrypting a local file.
The procedure is as follows:
- Create a CMK on KMS.
- Call the create-datakey API of KMS to create a DEK. Then you get a plaintext DEK and a ciphertext DEK. The ciphertext DEK is generated when you use a CMK to encrypt the plaintext DEK.
- Use the plaintext DEK to encrypt the file. A ciphertext file is generated.
- Save the ciphertext DEK and the ciphertext file together in a persistent storage device or a storage service.
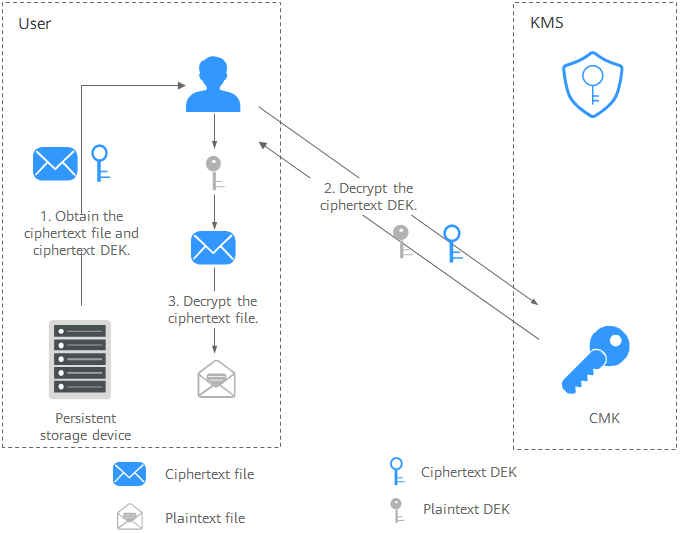
- Figure 3 illustrates the process for decrypting a local file.
The procedure is as follows:
- Obtain the ciphertext DEK and file from the persistent storage device or the storage service.
- Call the decrypt-datakey API of KMS and use the corresponding CMK (the one used for encrypting the DEK) to decrypt the ciphertext DEK. Then you get the plaintext DEK.
If the CMK is deleted, the decryption fails. Therefore, properly keep your CMKs.
- Use the plaintext DEK to decrypt the ciphertext file.
Helpful Links
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.