Single-Node Redis
This section describes single-node DCS Redis instances.

Single-node instances only have one master node, and can be vulnerable of data reliability when a physical server is faulty. Exercise caution. You are not advised to use them in production environments. DCS Service Level Agreement does not apply to single-node instances.
Features
- Low-cost and suitable for development and testing
Single-node instances are 40% cheaper than master/standby DCS instances, suitable for setting up development or testing environments.
- Data not persisted
Data persistence is not ensured through one master node for single-node instances. The data cannot be backed up.
Architecture
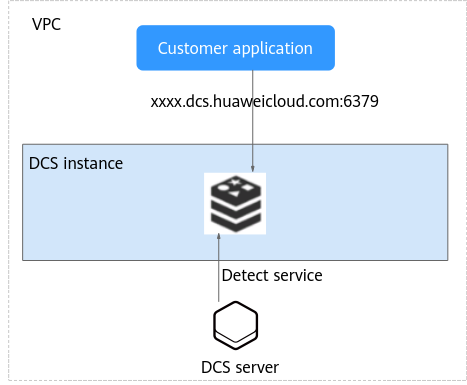
Figure 1 shows the architecture of a single-node DCS Redis instance.

- For Redis 4.0 and later, you can specify a port or use the default port 6379. In the following architecture, port 6379 is used. If you have customized a port, replace 6379 with the actual port.
- The major version of a DCS Redis 4.0 or later instance cannot be upgraded. For example, a single-node DCS Redis 4.0 instance cannot be upgraded to a single-node DCS Redis 5.0 one. If your service requires the features of higher Redis versions, create a DCS Redis instance of a higher version and then migrate data from the old instance to the new one.
Architecture description:
- VPC
The VPC where all nodes of the instance run.
- Application
The client of the instance, which is the application running on an Elastic Cloud Server (ECS).
DCS Redis instances are compatible with Redis, and can be accessed through open-source clients. For examples of accessing DCS instances with different programming languages, see instance access instructions.
- DCS instance
A single-node DCS instance, which has only one node and runs one Redis process.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.