Constraints
Database audit is subject to certain constraints.
Supported Database Types
Database audit supports databases on the cloud, on-premises, or on other clouds (the network connection between the database and the audit instance must be normal). For databases on the cloud, the following types of databases are supported:
- Relational Database Service (RDS)
- Databases on Elastic Cloud Servers (ECSs)
- Databases on Bare Metal Servers (BMSs)
Databases That Do Not Need Agents
Databases of some types and versions can be audited without using agents, as shown in Table 1.
|
Type |
Supported Edition |
|---|---|
|
GaussDB(for MySQL) |
All editions are supported by default. |
|
RDS for SQLServer |
All editions are supported by default. |
|
RDS for MySQL |
|
|
GaussDB(DWS) |
|
|
PostgreSQL
NOTICE:
If the size of an SQL statement exceeds 4 KB, the SQL statement will be truncated during auditing. As a result, the SQL statement is incomplete. |
|
|
RDS for MariaDB |
All editions are supported by default. |
Databases That Need Agents
Database audit supports the following database types and versions, as shown in Table 2.
|
Database Type |
Edition |
|---|---|
|
MySQL |
|
|
Oracle |
|
|
PostgreSQL |
|
|
SQL Server |
|
|
GaussDB(for MySQL) |
8.0 |
|
DWS |
|
|
DAMENG |
DM8 |
|
KINGBASE |
V8 |
|
SHENTONG |
V7.0 |
|
GBase 8a |
V8.5 |
|
GBase 8s |
V8.8_3.3.0 |
|
Gbase XDM Cluster |
V8.0 |
|
Greenplum |
V6.0 |
|
HighGo |
V6.0 |
|
GaussDB |
|
|
MongoDB |
V5.0 |
|
DDS |
4.0 |
|
Hbase (Supported by CTS instance 23.02.27.182148 and later versions) |
|
|
Hive |
|
|
MariaDB |
10.6 |
|
TDSQL |
10.3.17.3.0 |
|
Vastbase |
G100 V2.2 |
|
TiDB |
|
Supported OSs
- For more information, see Table 3.
Table 3 Supported Linux OS versions System Name
System version
CentOS
- CentOS 7.0 (64bit)
- CentOS 7.1 (64bit)
- CentOS 7.2 (64bit)
- CentOS 7.3 (64bit)
- CentOS 7.4 (64bit)
- CentOS 7.5 (64bit)
- CentOS 7.6 (64bit)
- CentOS 7.8 (64bit)
- CentOS 7.9 (64bit)
- CentOS 8.0 (64bit)
- CentOS 8.1 (64bit)
- CentOS 8.2 (64bit)
Debian
- Debian 7.5.0 (64bit)
- Debian 8.2.0 (64bit)
- Debian 8.8.0 (64bit)
- Debian 9.0.0 (64bit)
- Debian 10.0.0 (64bit)
Fedora
- Fedora 24 (64bit)
- Fedora 25 (64bit)
- Fedora 29 (64bit)
- Fedora 30 (64bit)
OpenSUSE
- SUSE 13 (64bit)
- SUSE 15 (64bit)
- SUSE 42 (64bit)
SUSE
- SUSE 11 SP4 (64bit)
- SUSE 12 SP1 (64bit)
- SUSE 12 SP2 (64bit)
Ubuntu
- Ubuntu 14.04 (64bit)
- Ubuntu 16.04 (64bit)
- Ubuntu 18.04 (64bit)
- Ubuntu 20.04 (64-bit)
EulerOS
- Euler 2.2 (64bit)
- Euler 2.3 (64bit)
- Euler 2.5 (64bit)
OpenEuler
- OpenEuler 20.03 (64bit)
Oracle Linux
- Oracle Linux 6.9 (64bit)
- Oracle Linux 7.4 (64bit)
Red Hat
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.4 (64bit)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.6 (64bit)
NeoKylin
- NeoKylin 7.0 (64bit)
Kylin
- Kylin Linux Advanced Server release V10 (64bit)
Uniontech OS
- Uniontech OS Server 20 Enterprise (64bit)
Huawei Cloud Euler
- Huawei Cloud Euler 2.0 (64bit)
KylinSec
- KylinSec 3.4 (64bit)
Anolis OS
- 7.9 (64bit)
- 8.4 (64bit)
- 8.6 (64bit)
- The following Windows OSs are supported:
- Windows Server 2008 R2 (64bit)
- Windows Server 2012 R2 (64bit)
- Windows Server 2016 (64bit)
- Windows Server 2019 (64bit)
- Windows 7 (64bit)
- Windows 10 (64bit)
The DBSS agent depends on Npcap. If the message "Npcap not found, please install Npcap first" is displayed when you install the DBSS agent, first install Npcap and then the DBSS agent.
Download Npcap before installing the DBSS agent.Figure 1 Npcap not found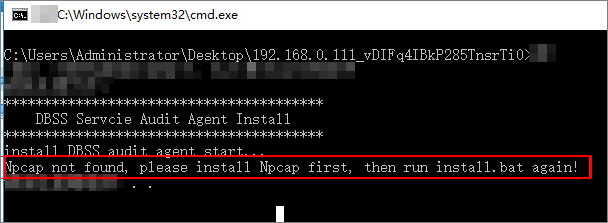
Other Constraints
- No. The database to be audited and the database audit instance you purchased must be in the same region.
- The Windows agent does not support IPv6 database audit.
- If SSL is enabled for a database, the database cannot be audited. To use database audit, disable SSL first. For details, see How Do I Disable SSL for a Database?
- Ensure the VPC of the database audit instance is the same as that of the node (application side or database side) where you plan to install the database audit agent. Otherwise, the instance will be unable to connect to the agent or perform audit. For more information, see How Do I Determine Where to Install an Agent?
- In some SQL Server databases, complex declare statements, select functions, and symbol statements that cannot be identified by the system may fail to be parsed.
- SQL request result recording is supported only for SQL Server, PostgreSQL, and MySQL databases. (The result set storage function must be enabled. This function is disabled by default. For details, see Configuring Privacy Data Protection Rules.)
- When agent-free GaussDB and RDS for MariaDB databases are audited, database logs of some fields and scenarios are not recorded. Therefore, DBSS cannot be audited.
Databases and Versions That Can Be Managed by Database Encryption
After adding data assets (databases) to the system, you can identify sensitive data in the databases and encrypt, decrypt, and mask sensitive information.
Database encryption supports the following database types and versions, as shown in Table 4.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






