Container Cluster Protection Overview
HSS can check for non-compliance baseline issues, vulnerabilities, and malicious files when a container image is started and report alarms on or block container startup that has not been unauthorized or may incur high risks.
You can configure container cluster protection policies to block images with vulnerabilities, malicious files, non-compliant baselines, or other threats, hardening cluster security.
Constraints
- Container cluster protection is available only in the HSS container edition.
- The cluster version is 1.20 or later.
- In a CCE cluster, to operate and protect resource objects, you need to obtain either of the following operation permissions:
- IAM permissions: Tenant Administrator or CCE Administrator.
- Namespace permissions (authorized by Kubernetes RBAC): O&M permissions.
Process of Using Container Cluster Protection
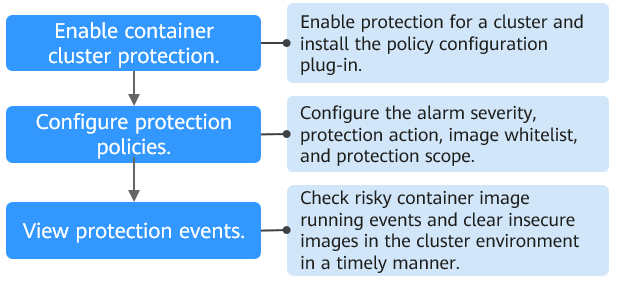
|
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Enable protection for a cluster to protect its workloads and critical data. When protection is enabled, HSS automatically installs the policy management plug-in on the cluster. |
|
|
Configure the severity of baseline, vulnerability, and malicious file risks that trigger alarms; container cluster protection scope; image whitelist; and actions to be taken on alarms. |
|
|
On the HSS console, you can view unauthorized or high-risk container image running events that are reported or blocked, and check and clear insecure container images in a timely manner. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






