Migrating Data from Oracle to CSS
Scenario
Cloud Search Service provides users with structured and unstructured data search, statistics, and report capabilities. This section describes how to use CDM to migrate data from the Oracle database to Cloud Search Service. The procedure is as follows:
Prerequisites
- You have subscribed to Cloud Search Service and obtained the IP address and port number of the Cloud Search Service cluster.
- You have obtained the IP address, name, username, and password of the Oracle database.
- If the Oracle database is deployed on an on-premises data center or a third-party cloud, ensure that an IP address that can be accessed from the public network has been configured for the Oracle database, or the VPN or Direct Connect between the on-premises data center and Huawei Cloud has been established.
- You have uploaded the Oracle database driver on the page.
Creating a CDM Cluster and Binding an EIP to the Cluster
- If CDM is used an independent service, create a CDM cluster by following the instructions in Creating a CDM Cluster. If CDM is used as a module of DataArts Studio, create a CDM cluster by following the instructions in Creating a CDM Cluster.
The key configurations are as follows:
- The flavor of the CDM cluster is selected based on the amount of data to be migrated. Generally, cdm.medium meets the requirements for most migration scenarios.
- The CDM and Cloud Search Service clusters must be in the same VPC. In addition, it is recommended that the CDM cluster be in the same subnet and security group as the Cloud Search Service cluster.
- If the same subnet and security group cannot be used for security purposes, ensure that a security group rule has been configured to allow the CDM cluster to access the Cloud Search Service cluster.
- After the CDM cluster is created, on the Cluster Management page, click Bind EIP in the Operation column to bind an EIP to the cluster. The CDM cluster uses the EIP to access the Oracle data source.
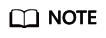
If SSL encryption is configured for the access channel of a local data source, CDM cannot connect to the data source using the EIP.
Creating a Cloud Search Service Link
- Click Job Management in the Operation column of the CDM cluster. On the displayed page, click the Links tab and then Create Link. The Select Connector page is displayed.
Figure 1 Selecting a connector
- Select Cloud Search Service and click Next. On the page that is displayed, configure the CSS link parameters.
- Name: Enter a custom link name, for example, csslink.
- Elasticsearch Server List: Enter the IP address and port number of the Cloud Search Service cluster (cluster later than 5.x). The format is ip:port. Use semicolons to separate multiple addresses. For example, 192.168.0.1:9200;192.168.0.2:9200.
- Username and Password: Enter the username and password used for logging in to the Cloud Search Service cluster. The user must have the read and write permissions on the database.
Figure 2 Creating a CSS link
- Click Save. The Link Management page is displayed.
Creating an Oracle Link
- Click Job Management in the Operation column of the CDM cluster. On the displayed page, click the Links tab and then Create Link. The Select Connector page is displayed.
Figure 3 Selecting a connector type

- Select Oracle and click Next to configure parameters for the Oracle link.
- Name: Enter a custom link name, for example, oracle_link.
- Database Server and Port: Enter the address and port number of the Oracle server.
- Database Name: Enter the name of the Oracle database whose data is to be exported.
- Username and Password: Enter the username and password used for logging in to the Oracle database. The user must have the permission to read the Oracle metadata.
- Click Save. The Link Management page is displayed.
Creating a Migration Job
- Choose to create a job for exporting data from the Oracle database to Cloud Search Service.
Figure 4 Creating a job for migrating data from Oracle to Cloud Search Service

- Job Name: Enter a unique name.
- Source Job Configuration
- Source Link Name: Select the oracle_link link created in Creating an Oracle Link.
- Schema/Tablespace: Enter the name of the database whose data is to be migrated.
- Table Name: Enter the name of the table to be migrated.
- Retain the default values of the optional parameters in Show Advanced Attributes.
- Destination Job Configuration
- Destination Link Name: Select the csslink link created in Creating a Cloud Search Service Link.
- Index: Select the Elasticsearch index of the data to be written. You can also enter a new index. CDM automatically creates the index on Cloud Search Service.
- Type: Select the Elasticsearch type of the data to be written. You can enter a new type. CDM automatically creates a type at the migration destination.
- Retain the default values of the optional parameters in Show Advanced Attributes.
- Click Next. The Map Field page is displayed. CDM automatically matches the source and destination fields. See Figure 5.
- If the field mapping is incorrect, you can drag the fields to adjust the mapping.
- If the type is automatically created at the migration destination, you need to configure the type and name of each field.
- CDM supports field conversion during the migration. For details, see Converting Fields.
- Click Next and set task parameters. Generally, retain the default values of all parameters.
In this step, you can configure the following optional functions:
- Retry If Failed: Determine whether to automatically retry the job if it fails. Retain the default value Never.
- Group: Select the group to which the job belongs. The default group is DEFAULT. On the Job Management page, jobs can be displayed, started, or exported by group.
- Schedule Execution: Determine whether to automatically execute the job at a scheduled time. Retain the default value No in this example.
- Concurrent Extractors: Enter the number of concurrent extractors. An appropriate value improves migration efficiency. For details, see Performance Tuning. Retain the default value 1.
- Write Dirty Data: Specify this parameter if data that fails to be processed or filtered out during job execution needs to be written to OBS for future viewing. Before writing dirty data, create an OBS link on the CDM console. Retain the default value No so that dirty data is not recorded.
Figure 6 Configuring the task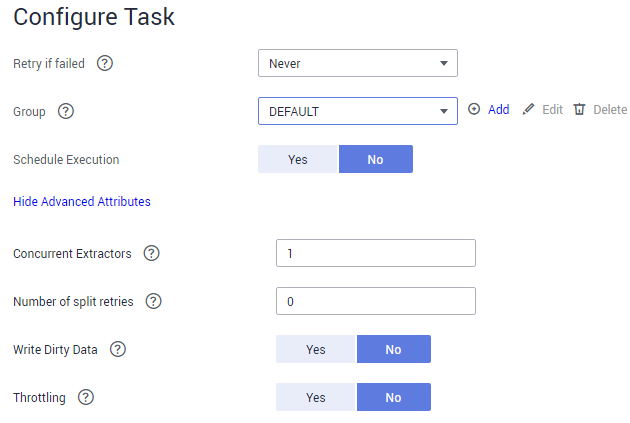
- Click Save and Run. The Job Management page is displayed, on which you can view the job execution progress and result.
- After the job is successfully executed, in the Operation column of the job, click Historical Record to view the job's historical execution records and read/write statistics.
On the Historical Record page, click Log to view the job logs.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.







