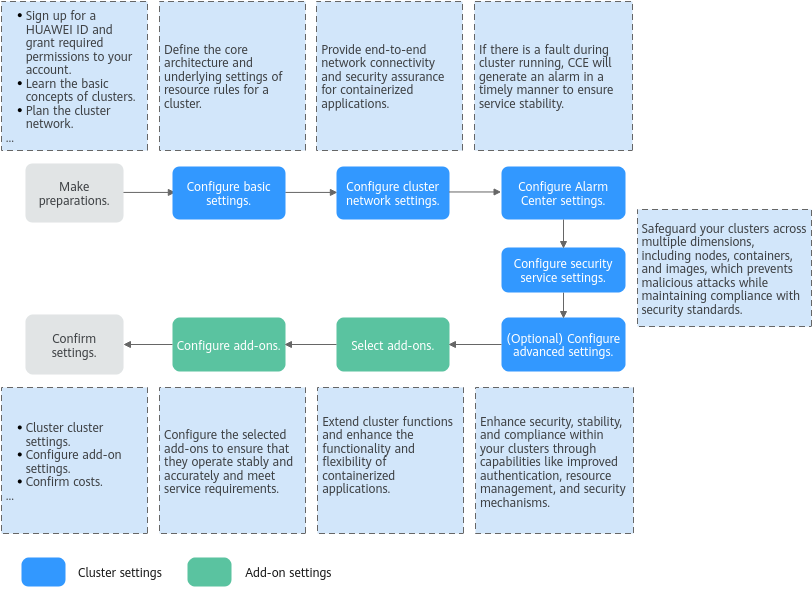
Buying a CCE Standard/Turbo Cluster
CCE standard and Turbo clusters provide enterprise-class Kubernetes cluster hosting service that supports full lifecycle management of containerized applications. They offer a highly scalable, high-performance solution for deploying and managing cloud native applications. On the CCE console, you can easily create CCE standard and Turbo clusters. After a cluster is created, CCE hosts the master nodes. You only need to create worker nodes. In this way, you can implement cost-effective O&M and efficient service deployment. For details about how to buy a cluster, see Figure 1.
Before purchasing a CCE standard or Turbo cluster, you are advised to learn about What Is CCE? Networking Overview, and Planning CIDR Blocks for a Cluster.
Preparations
- Before you start, sign up for a HUAWEI ID. For details, see Signing up for a HUAWEI ID and Enabling Huawei Cloud Services.
- If you are using CCE for the first time, grant required permissions to your account in advance.
Step 1: Configure Basic Settings
Basic settings define the core architecture and underlying resource rules of a cluster, providing a framework for cluster running and resource allocation.
- Log in to the CCE console. In the upper left corner of the page, click
 and select a region for your cluster. The closer the selected region is to the region where resources are deployed, the lower the network latency and the faster the access.
and select a region for your cluster. The closer the selected region is to the region where resources are deployed, the lower the network latency and the faster the access.
After confirming the region, click Buy Cluster. If you use CCE for the first time, you need to create an agency following instructions.
- Configure the basic settings of the cluster. For details, see Table 1.
Table 1 Basic settings of a cluster (applicable to standard and Turbo clusters) Parameter
Description
Modifiable After Cluster Creation
Type
Select CCE Standard Cluster or CCE Turbo Cluster as required.
- CCE standard clusters provide highly reliable and secure containers for commercial use.
- CCE Turbo clusters use the high-performance cloud native network. Such clusters provide cloud native hybrid scheduling, achieving higher resource utilization and wider scenario coverage.
For details, see cluster types.
No
Billing Mode
Select a billing mode as required.- Yearly/Monthly: a prepaid billing mode. Resources will be billed based on the service duration. This cost-effective mode is ideal when the duration of resource usage is predictable.
If you choose this billing mode, configure the required duration and determine whether to automatically renew the subscription. (If you purchase a monthly subscription, the automatic renewal period is one month. If you purchase a yearly subscription, the automatic renewal period is one year.)
- Pay-per-use: a postpaid billing mode. It is suitable for scenarios where resources will be billed based on usage frequency and duration. You can provision or delete resources at any time.
Yes
Cluster Name
Enter a cluster name. Cluster names under the same account must be unique.
Enter 4 to 128 characters. Start with a lowercase letter and do not end with a hyphen (-). Only lowercase letters, digits, and hyphens (-) are allowed.
Yes
Enterprise Project
This parameter is available only for enterprise users who have enabled an enterprise project.
After an enterprise project is selected, clusters and their security groups will be created in that project. To manage clusters and other resources like nodes, load balancers, and node security groups, you can use the Enterprise Project Management Service (EPS).
Yes
Cluster Version
Select a Kubernetes version. The latest commercial version is recommended, and it provides you with more stable, reliable features.
Yes
Cluster Scale
Select a cluster scale as required. This parameter controls the maximum number of worker nodes that a cluster can manage.
Yes
The cluster that has been created can only be scaled out. For details, see Changing a Cluster Scale.
Master Nodes
Select the number of master nodes. The master nodes are automatically hosted by CCE and deployed with Kubernetes cluster management components such as kube-apiserver, kube-controller-manager, and kube-scheduler.
- Multiple: Three master nodes will be created for high cluster availability.
- Single: Only one master node will be created in your cluster.
NOTE:
If more than half of the master nodes in a CCE cluster are faulty, the cluster cannot function properly.
You can also select AZs for deploying the master nodes of a specific cluster. By default, AZs are allocated automatically for the master nodes.- Automatic: Master nodes are randomly distributed in different AZs for cluster DR. If there are not enough AZs available, CCE will prioritize assigning nodes in AZs with enough resources to ensure cluster creation. However, this may result in AZ-level DR not being guaranteed.
- Custom: Master nodes are deployed in specific AZs.
If there is one master node in a cluster, you can select one AZ for the master node. If there are multiple master nodes in a cluster, you can select multiple AZs for the master nodes.
- AZ: Master nodes are deployed in different AZs for cluster DR.
- Host: Master nodes are deployed on different hosts in the same AZ for cluster DR.
- Custom: Master nodes are deployed in the AZs you specified.
No
After the cluster is created, the number of master nodes and the AZs where they are deployed cannot be changed.
Step 2: Configure Network Settings
Network configuration follows a hierarchical management system. It ensures end-to-end network connectivity and security assurance for containerized applications through collaborative configuration of the cluster networks, container networks, and Service networks.
- Cluster network: handles communication between nodes, transmitting pod and Service traffic while ensuring cluster infrastructure connectivity and security.
- Container network: assigns each pod an independent IP address, enabling direct container communication and cross-node communication.
- Service network: establishes a stable access entry, supports load balancing, and optimizes traffic management for Services within a cluster.
Before configuring the network settings, you are advised to learn the concepts and relationships of the three types of networks. For details, see Networking Overview.
- Configure cluster network settings. For details, see Table 2.
Table 2 Cluster network settings Parameter
Description
Modifiable After Cluster Creation
VPC
Select a VPC for a cluster.
If no VPC is available, click Create VPC to create one. After the VPC is created, click the refresh icon. For details about how to create a VPC, see Creating a VPC and Subnet.
No
Default Node Subnet
Select a subnet. Once selected, all nodes in the cluster will automatically use the IP addresses assigned within that subnet. However, during node or node pool creation, the subnet settings can be reconfigured.
No
Default Node Security Group
Select the security group automatically generated by CCE or select an existing one.
The default node security group must allow traffic from certain ports to ensure normal communication. Otherwise, the node cannot be created.
Yes
- Configure container network parameters. For details, see Table 3.
Table 3 Container network settings Parameter
Description
Modifiable After Cluster Creation
Network Model
The network model used by the container network in a cluster.- Tunnel network: applies to large clusters (with up to 2000 nodes) and scenarios that do not demand high performance such as web applications and data middle- and back-end services with low access traffic.
- VPC network: applies to small clusters (with 1000 nodes or fewer) and scenarios that demand high performance such as AI and big data computing.
For more details about their differences, see Overview.
No
Container CIDR Block
CIDR block used by containers. This parameter determines the maximum number of containers in the cluster.
No
After a cluster using a VPC network is created, you can add container CIDR blocks to the cluster but cannot modify or delete the existing ones.
Pod IP Addresses Reserved for Each Node (supported by clusters using the VPC networks)
The number of pod IP addresses that can be allocated on each node (alpha.cce/fixPoolMask). This parameter determines the maximum number of pods that can be created on each node.
In a container network, each pod is assigned a unique IP address. If the number of pod IP addresses reserved for each node is insufficient, pods cannot be created. For details, see Number of Allocatable Pod IP Addresses on a Node.
No
- Configure Service network parameters. For details, see Table 4.
Table 4 Service network settings Parameter
Description
Modifiable After Cluster Creation
Service CIDR Block
Configure an IP address range for the ClusterIP Services in a cluster. This parameter controls the maximum number of ClusterIP Services in a cluster. ClusterIP Services enable communication between containers in a cluster. The Service CIDR block cannot overlap with the node subnet or container CIDR block.
No
Request Forwarding
Configure load balancing and route forwarding of Service traffic in a cluster. IPVS and iptables are supported. For details, see Comparing iptables and IPVS.
- iptables: the traditional kube-proxy mode. It applies to the scenario where the number of Services is small or a large number of short connections are concurrently sent on the client. IPv6 clusters do not support iptables.
- IPVS: allows higher throughput and faster forwarding. It is suitable for large clusters or when there are a large number of Services.
No
- Configure cluster network settings. For details, see Table 5.
Table 5 Cluster network settings Parameter
Description
Modifiable After Cluster Creation
VPC
Select a VPC for a cluster.
If no VPC is available, click Create VPC to create one. After the VPC is created, click the refresh icon. For details about how to create a VPC, see Creating a VPC and Subnet.
No
Default Node Subnet
Select a subnet. Once selected, all nodes in the cluster will automatically use the IP addresses assigned within that subnet. However, during node or node pool creation, the subnet settings can be reconfigured.
No
Default Node Security Group
Select the security group automatically generated by CCE or select an existing one.
The default node security group must allow traffic from certain ports to ensure normal communication. Otherwise, the node cannot be created.
Yes
- Configure container network parameters. For details, see Table 6.
Table 6 Container network settings Parameter
Description
Modifiable After Cluster Creation
Network Model
The network model used by the container network in a cluster. Only Cloud Native Network 2.0 is supported.
For more details about this network model, see Overview.
No
Pod Subnet
Select the subnet to which the pod belongs. If no subnet is available, click Create Subnet to create one. The pod subnet determines the maximum number of containers in a cluster. You can add pod subnets after a cluster is created.
Yes
Default Security Group
Select the security group automatically generated by CCE or select an existing one. This parameter controls inbound and outbound traffic to prevent unauthorized access.
The default security group of containers must allow access from specified ports to ensure proper communication between containers in the cluster.
Yes
- Configure Service network parameters. For details, see Table 7.
Table 7 Service network settings Parameter
Description
Modifiable After Cluster Creation
Service CIDR Block
Configure an IP address range for the ClusterIP Services in a cluster. This parameter controls the maximum number of ClusterIP Services in a cluster. ClusterIP Services enable communication between containers in a cluster. The Service CIDR block cannot overlap with the node subnet or container CIDR block.
No
Request Forwarding
Configure load balancing and route forwarding of Service traffic in a cluster. IPVS and iptables are supported. For details, see Comparing iptables and IPVS.
- iptables: the traditional kube-proxy mode. It applies to the scenario where the number of Services is small or a large number of short connections are concurrently sent on the client. IPv6 clusters do not support iptables.
- IPVS: allows higher throughput and faster forwarding. It is suitable for large clusters or when there are a large number of Services.
No
Step 4: Enable Security Service
CCE offers a comprehensive security service that safeguards clusters. Through capabilities like runtime monitoring and vulnerability detection, it ensures the security of clusters across multiple dimensions, including nodes, containers, and images, proactively preventing malicious attacks while maintaining compliance with security standards. This function is in the initial rollout stage. For details about the regions where this function is available, see the console.
(Optional) Step 5: Configure Advanced Settings
Advanced settings extend and strengthen previous settings, enhancing security, stability, and compliance within clusters. This is achieved through capabilities like improved authentication, resource management, and security mechanisms.
|
Parameter |
Description |
Modifiable After Cluster Creation |
|---|---|---|
|
IAM Authentication |
CCE clusters support IAM authentication. You can call IAM authenticated APIs to access CCE clusters. |
No |
|
Certificate Authentication |
Certificate authentication is used for identity authentication and access control. It ensures that only authorized users or services can access specific cluster.
|
No |
|
CPU Management |
CPU management policies allow precise control over CPU allocation for pods. For details, see CPU Policy.
|
Yes |
|
Overload Control |
After this function is enabled, concurrent requests will be dynamically controlled based on the resource demands received by master nodes, ensuring stable running of the master nodes and the cluster. For details, see Enabling Overload Control for a Cluster. |
Yes |
|
Cluster Deletion Protection |
After this function is enabled, you will not be able to delete or unsubscribe from clusters on CCE. This option is a measure to prevent accidental deletion of clusters through the console or APIs. You can modify the function status in Settings after creating it. |
Yes |
|
Time Zone |
The cluster's scheduled tasks and nodes are subject to the chosen time zone. |
× |
|
Resource Tag |
Adding tags to resources allows for customized classification and organization. A maximum of 20 resource tags can be added. You can create predefined tags on the TMS console. These tags are available to all resources that support tags. You can use these tags to improve the tag creation and resource migration efficiency. |
Yes |
|
Description |
Cluster description helps users and administrators quickly understand the basic settings, status, and usage of a cluster. The description can contain a maximum of 200 characters. |
Yes |
Step 6: Select Add-ons
CCE provides a variety of add-ons to extend cluster functions and enhance the functionality and flexibility of containerized applications. You can select add-ons as required. Some basic add-ons are set as mandatory by default. If non-basic add-ons are not installed during cluster creation, they can still be added later on the Add-ons page after the cluster is created.
- Click Next: Select Add-on. On the page displayed, select the add-ons to be installed during cluster creation.
- Select basic add-ons to ensure the proper running of the cluster. For details, see Table 9.
Table 9 Basic add-ons Add-on
Description
CCE Container Network (Yangtse CNI)
This add-on provides network connectivity, Internet access, and security isolation for pods in a cluster. It is the basic cluster add-on.
CCE Container Storage (Everest)
This add-on (CCE Container Storage (Everest)) is installed by default. It is a cloud native container storage system based on CSI and supports cloud storage services such as EVS.
CoreDNS
This add-on (CoreDNS) is installed by default. It provides DNS resolution for your cluster and can be used to access the in-cloud DNS server.
NodeLocal DNSCache
(Optional) After you select this option, CCE will automatically install NodeLocal DNSCache. NodeLocal DNSCache improves cluster DNS performance by running a DNS cache proxy on cluster nodes.
Volcano Scheduler
(Optional) After you select this option, CCE will automatically install Volcano Scheduler and set the default scheduler of the cluster to Volcano. This will enable you to access advanced scheduling capabilities for batch computing and high-performance computing.
- Select the observability add-ons to experience the full observability function. For details, see Table 9.
Table 10 Observability add-ons Add-on
Description
Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring
(Optional) After you select this option, CCE will automatically install Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring. Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring collects monitoring metrics for your cluster and reports the metrics to AOM. The agent mode does not support HPA based on custom Prometheus statements. If related functions are required, install this add-on manually after the cluster is created.
Collecting basic metrics is free of charge. Collecting custom metrics is billed by AOM. For details, see Pricing Details. For details, see Monitoring Custom Metrics Using Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring.
Cloud Native Log Collection
(Optional) After you select this option, CCE will automatically install Cloud Native Log Collection. Cloud Native Log Collection helps report logs to LTS. After the cluster is created, you are allowed to obtain and manage collection rules on the Logging page of the CCE cluster console.
LTS does not charge you for creating log groups and offers a free quota for you to collect logs every month. You pay only for the log volume exceeding the quota. For details, see Price Calculator.
CCE Node Problem Detector
(Optional) After you select this option, CCE will automatically install CCE Node Problem Detector to detect faults and isolate nodes for prompt cluster troubleshooting.
Step 7: Configure Add-ons
Configure the selected add-ons to ensure they operate stably and accurately and meet service requirements.
- Click Next: Configure Add-on.
- Configure the basic add-ons. For details, see Table 11.
Table 11 Basic add-on settings Add-on
Description
CCE Container Network (Yangtse CNI)
This add-on is unconfigurable.
CCE Container Storage (Everest)
This add-on is unconfigurable. After the cluster is created, you can go to Add-ons to modify the settings.
CoreDNS
This add-on is unconfigurable. After the cluster is created, you can go to Add-ons to modify the settings.
NodeLocal DNSCache
This add-on is unconfigurable. After the cluster is created, you can go to Add-ons to modify the settings.
Volcano Scheduler
This add-on is unconfigurable. After the cluster is created, you can go to Add-ons to modify the settings.
- Configure the observability add-ons. For details, see Table 12.
Table 12 Observability add-on settings Add-on
Description
Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring
Select an AOM instance for Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring to report metrics. If no AOM instance is available, click Creating Instance to create one.
Collecting basic metrics is free of charge. Collecting custom metrics is billed by AOM. For details, see Pricing Details. For details, see Monitoring Custom Metrics Using Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring.
Cloud Native Log Collection
Select the logs to be collected. If enabled, a log group named k8s-log-{clusterId} will be automatically created, and a log stream will be created for each selected log type.
- Container log: Standard output logs of containers are collected. The corresponding log stream is named in the format of stdout-{Cluster ID}.
- Kubernetes Events: Kubernetes logs are collected. The corresponding log stream is named in the format of event-{Cluster ID}.
- Kubernetes Audit Logs: Audit logs of the master nodes are collected. The log streams are named in the format of audit-{Cluster ID}.
- Control Plane Logs: Logs from critical components such as kube-apiserver, kube-controller-manage, and kube-scheduler that run on the master nodes are collected. The log streams are named in the format of kube-apiserver-{Cluster ID}, kube-controller-manage-{Cluster ID}, and kube-scheduler-{Cluster ID}, respectively.
If log collection is disabled, choose Logging in the navigation pane of the cluster console after the cluster is created and enable this option.
LTS does not charge you for creating log groups and offers a free quota for you to collect logs every month. You pay only for the log volume exceeding the quota. For details, see Price Calculator. For details about how to collect custom metrics, see Collecting Container Logs Using the Cloud Native Log Collection Add-on.
CCE Node Problem Detector
This add-on is unconfigurable. After the cluster is created, you can go to Add-ons to modify the settings.
Step 8: Confirm Settings
Click Next: Confirm Settings. The cluster resource list is displayed. Confirm the information and click Submit.
It takes about 5 to 10 minutes to create a cluster. You can click Back to Cluster List to perform other operations on the cluster or click Go to Cluster Events to view the cluster details.
Helpful Links
- Accessing a cluster: You can use kubectl to access a cluster and perform cluster management tasks on the CLI. For details, see Accessing a Cluster Using kubectl and Connecting to Multiple Clusters Using kubectl.
- Adding a node: After a cluster is created, you can add nodes to the cluster. For details, see Creating a Node.
- Managing a cluster: After a cluster is created, you can configure resource scheduling policies, security control rules, and lifecycle management to meet service requirements. For details, see Cluster Management Overview.
- If a cluster fails to be created, rectify the fault by referring to Why Can't I Create a CCE Cluster?
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.