Reading Data from MySQL CDC and Writing Data to GaussDB(DWS)

This guide provides reference for Flink 1.12 only.
Description
Change Data Capture (CDC) can synchronize incremental changes from the source database to one or more destinations. During data synchronization, CDC processes data, for example, grouping (GROUP BY) and joining multiple tables (JOIN).
This example creates a MySQL CDC source table to monitor MySQL data changes and insert the changed data into a GaussDB(DWS) database.
Prerequisites
- You have created an RDS for MySQL instance. In this example, the RDS for MySQL database version is 8.0.
- You have created a GaussDB(DWS) instance.
Overall Process
Step 1: Create an Elastic Resource Pool and Create Queues Within It
Step 2: Create an RDS for MySQL Database and Table
Step 3: Create a GaussDB(DWS) Database and Table
Step 1: Create an Elastic Resource Pool and Create Queues Within It
The CIDR block of a new queue cannot overlap with the CIDR blocks of DMS Kafka and RDS for MySQL instances. Otherwise, datasource connections will fail to be created.
- Log in to the DLI management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Resources > Resource Pool.
- On the displayed page, click Buy Resource Pool in the upper right corner.
- On the displayed page, set the parameters.
In this example, we will buy the resource pool in the CN East-Shanghai2 region. Table 1 describes the parameters.
Table 1 Parameter descriptions Parameter
Description
Example Value
Region
Select a region where you want to buy the elastic resource pool.
CN East-Shanghai2
Project
Project uniquely preset by the system for each region
Default
Name
Name of the elastic resource pool
dli_resource_pool
Specifications
Specifications of the elastic resource pool
Standard
CU Range
The maximum and minimum CUs allowed for the elastic resource pool
64-64
CIDR Block
CIDR block the elastic resource pool belongs to. If you use an enhanced datasource connection, this CIDR block cannot overlap that of the data source. Once set, this CIDR block cannot be changed.
172.16.0.0/19
Enterprise Project
Select an enterprise project for the elastic resource pool.
default
- Click Buy.
- Click Submit.
- In the elastic resource pool list, locate the pool you just created and click Add Queue in the Operation column.
- Set the basic parameters listed below.
Table 2 Basic parameters for adding a queue Parameter
Description
Example Value
Name
Name of the queue to add
dli_queue_01
Type
Type of the queue
- To execute SQL jobs, select For SQL.
- To execute Flink or Spark jobs, select For general purpose.
For SQL jobs, select For SQL.
For other scenarios, select For general purpose.
Engine
SQL queue engine. The options are Spark and HetuEngine.
Spark
Enterprise Project
Select an enterprise project.
default
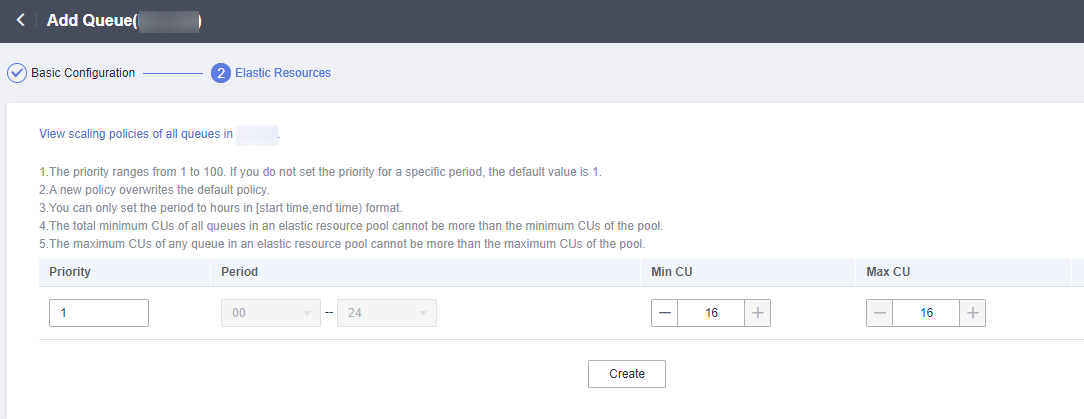
- Click Next and configure scaling policies for the queue.
Click Create to add a scaling policy with varying priority, period, minimum CUs, and maximum CUs.
Figure 2 shows the scaling policy configured in this example.Table 3 Scaling policy parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Priority
Priority of the scaling policy in the current elastic resource pool. A larger value indicates a higher priority. In this example, only one scaling policy is configured, so its priority is set to 1 by default.
1
Period
The first scaling policy is the default policy, and its Period parameter configuration cannot be deleted or modified.
The period for the scaling policy is from 00 to 24.
00–24
Min CU
Minimum number of CUs allowed by the scaling policy
16
Max CU
Maximum number of CUs allowed by the scaling policy
64
- Click OK.
Step 2: Create an RDS for MySQL Database and Table
- Log in to the RDS console. On the displayed page, locate the desired RDS for MySQL instance, click More in its Operation column, and select Log In.
- In the login dialog box that appears, enter the username and password and click Log In.
- On the Databases page, click Create Database. In the displayed dialog box, enter testrdsdb as the database name and retain default values of rest parameters. Then, click OK.
- In the Operation column of row where the created database locates, click SQL Window and enter the following statement to create a table:
CREATE TABLE mysqlcdc ( `order_id` VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL, `order_channel` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL, `order_time` VARCHAR(32), `pay_amount` DOUBLE, `real_pay` DOUBLE, `pay_time` VARCHAR(32), `user_id` VARCHAR(32), `user_name` VARCHAR(32), `area_id` VARCHAR(32) ) ENGINE = InnoDB DEFAULT CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4;
Step 3: Create a GaussDB(DWS) Database and Table
- Connect to the created GaussDB(DWS) cluster.
- Connect to the default database gaussdb of a GaussDB(DWS) cluster.
gsql -d gaussdb -h Connection address of the GaussDB(DWS) cluster -U dbadmin -p 8000 -W password -r
- gaussdb: Default database of the GaussDB(DWS) cluster
- Connection address of the GaussDB(DWS) cluster: If a public network address is used for connection, set this parameter to the public network IP address or domain name. If a private network address is used for connection, set this parameter to the private network IP address or domain name. If an ELB is used for connection, set this parameter to the ELB address.
- dbadmin: Default administrator username used during cluster creation
- -W: Default password of the administrator
- Run the following command to create the testdwsdb database:
CREATE DATABASE testdwsdb;
- Run the following command to exit the gaussdb database and connect to testdwsdb:
\q gsql -d testdwsdb -h Connection address of the GaussDB(DWS) cluster -U dbadmin -p 8000 -W password -r
- Run the following commands to create a table:
create schema test; set current_schema= test; drop table if exists dwsresult; CREATE TABLE dwsresult ( car_id VARCHAR, car_owner VARCHAR, car_age INTEGER , average_speed FLOAT8, total_miles FLOAT8 );
Step 4: Create an Enhanced Datasource Connection
- Connecting DLI to RDS
- Go to the RDS console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Instances. On the displayed page, click the name of the desired RDS instance. Basic information of the instance is displayed.
- In the Connection Information pane, obtain the floating IP address, database port, VPC, and subnet.
- Click the security group name. On the displayed page, click the Inbound Rules tab and add a rule to allow access from DLI queues. For example, if the CIDR block of the queue is 10.0.0.0/16, set Priority to 1, Action to Allow, Protocol to TCP, Type to IPv4, Source to 10.0.0.0/16, and click OK.
- Log in to the DLI management console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Datasource Connections. On the displayed page, click Create in the Enhanced tab.
- In the displayed dialog box, set the following parameters: For details, see the following section:
- Connection Name: Enter a name for the enhanced datasource connection. For this example, enter dli_rds.
- Resource Pool: Select the elastic resource pool created in Step 1: Create an Elastic Resource Pool and Create Queues Within It.
- VPC: Select the VPC of the RDS instance.
- Subnet: Select the subnet of RDS instance.
- Set other parameters as you need.
Click OK. Click the name of the created datasource connection to view its status. You can perform subsequent steps only after the connection status changes to Active.
- Choose Resources > Queue Management from the navigation pane, locate the queue you created in Step 1: Create an Elastic Resource Pool and Create Queues Within It. In the Operation column, click More > Test Address Connectivity.
- In the displayed dialog box, enter floating IP address:database port of the RDS instance you have obtained in 2 in the Address box and click Test to check whether the database is reachable.
- Connecting DLI to GaussDB(DWS)
- On the GaussDB(DWS) management console, choose Clusters. On the displayed page, click the name of the created GaussDB(DWS) cluster to view basic information.
- On the Basic Information tab, locate the Database Attributes pane and obtain the private IP address and port number of the instance. In the Network pane, obtain VPC and subnet information.
- Click the security group name. On the displayed page, click the Inbound Rules tab and add a rule to allow access from DLI queues. For example, if the CIDR block of the queue is 10.0.0.0/16, set Priority to 1, Action to Allow, Protocol to TCP, Type to IPv4, Source to 10.0.0.0/16, and click OK.
- Check whether the RDS instance and GaussDB(DWS) instance are in the same VPC and subnet.
- Log in to the DLI management console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Datasource Connections. On the displayed page, click Create in the Enhanced tab.
- In the displayed dialog box, set the following parameters: For details, see the following section:
- Connection Name: Enter a name for the enhanced datasource connection. For this example, enter dli_dws.
- Resource Pool: Select the elastic resource pool created in Step 1: Create an Elastic Resource Pool and Create Queues Within It.
- VPC: Select the VPC of the GaussDB(DWS) instance.
- Subnet: Select the subnet of GaussDB(DWS) instance.
- Set other parameters as you need.
Click OK. Click the name of the created datasource connection to view its status. You can perform subsequent steps only after the connection status changes to Active.
- Choose Resources > Queue Management from the navigation pane, locate the queue you created in Step 1: Create an Elastic Resource Pool and Create Queues Within It. In the Operation column, click More > Test Address Connectivity.
- In the displayed dialog box, enter floating IP address:database port of the GaussDB(DWS) instance you have obtained in 2 in the Address box and click Test to check whether the database is reachable.
Step 5: Run a Job
- On the DLI management console, choose Job Management > Flink Jobs. On the Flink Jobs page, click Create Job.
- In the Create Job dialog box, set Type to Flink OpenSource SQL and Name to FlinkCDCMySQLDWS. Click OK.
- On the job editing page, set the following parameters and retain the default values of other parameters.
- Queue: Select the queue created in Step 1: Create an Elastic Resource Pool and Create Queues Within It.
- Flink Version: Select 1.12.
- Save Job Log: Enable this function.
- OBS Bucket: Select an OBS bucket for storing job logs and grant access permissions of the OBS bucket as prompted.
- Enable Checkpointing: Enable this function.
- Enter a SQL statement in the editing pane. The following is an example. Modify the parameters in bold as you need.

In this example, the syntax version of Flink OpenSource SQL is 1.12. In this example, the data source is Kafka and the result data is written to Elasticsearch.
create table mysqlCdcSource( order_id string, order_channel string, order_time string, pay_amount double, real_pay double, pay_time string, user_id string, user_name string, area_id STRING ) with ( 'connector' = 'mysql-cdc', 'hostname' = ' 192.168.12.148',--IP address of the RDS for MySQL instance 'port'= ' 3306',--Port number of the RDS for MySQL instance 'pwd_auth_name'= 'xxxxx', -- Name of the datasource authentication of the password type created on DLI. If datasource authentication is used, you do not need to set the username and password for the job. 'database-name' = ' testrdsdb',--Database name of the RDS for MySQL instance 'table-name' = ' mysqlcdc'--Name of the target table in the database ); create table dwsSink( order_channel string, pay_amount double, real_pay double, primary key(order_channel) not enforced ) with ( 'connector' = 'gaussdb', 'driver' = 'com.huawei.gauss200.jdbc.Driver', 'url'='jdbc:gaussdb://192.168.168.16:8000/testdwsdb ', ---192.168.168.16:8000 indicates the internal IP address and port of the GaussDB(DWS) instance. testdwsdb indicates the name of the created GaussDB(DWS) database. 'table-name' = ' test\".\"dwsresult', ---test indicates the schema of the created GaussDB(DWS) table, and dwsresult indicates the GaussDB(DWS) table name. 'pwd_auth_name'= 'xxxxx', -- Name of the datasource authentication of the password type created on DLI. If datasource authentication is used, you do not need to set the username and password for the job. 'write.mode' = 'insert' ); insert into dwsSink select order_channel, sum(pay_amount),sum(real_pay) from mysqlCdcSource group by order_channel;
- Click Check Semantic and ensure that the SQL statement passes the check. Click Save. Click Start, confirm the job parameters, and click Start Now to execute the job. Wait until the job status changes to Running.
Step 6: Send Data and Query Results
- Log in to the RDS console. On the displayed page, locate the desired RDS for MySQL instance, click More in its Operation column, and select Log In.
- In the login dialog box that appears, enter the username and password and click Log In.
- In the Operation column of row where the created database locates, click SQL Window and enter the following statement to create a table and insert data to the table:
insert into mysqlcdc values ('202103241000000001','webShop','2021-03-24 10:00:00','100.00','100.00','2021-03-24 10:02:03','0001','Alice','330106'), ('202103241206060001','appShop','2021-03-24 12:06:06','200.00','180.00','2021-03-24 16:10:06','0002','Jason','330106'), ('202103241403000001','webShop','2021-03-24 14:03:00','300.00','100.00','2021-03-24 10:02:03','0003','Lily','330106'), ('202103241636060001','appShop','2021-03-24 16:36:06','200.00','150.00','2021-03-24 16:10:06','0001','Henry','330106'); - .
- Connect to the default database testdwsdb of a GaussDB(DWS) cluster.
gsql -d testdwsdb -h Connection address of the GaussDB(DWS) cluster -U dbadmin -p 8000 -W password -r
- Run the following statements to query table data:
select * from test.dwsresult;
The query result is as follows:order_channel pay_amount real_pay appShop 400.0 330.0 webShop 400.0 200.0
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.