(Optional) Step 8: Creating a Log Storage Pipeline
This topic describes how to create a log storage location (pipeline) in SecMaster for log storage and analysis.
This step is required when you transfer security logs from non-Huawei Cloud systems to SecMaster. Skip this step if you only need to transfer Huawei Cloud logs to a third-party system or product.
Creating a Log Storage Pipeline
- Log in to the SecMaster console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Workspaces > Management. In the workspace list, click the name of the target workspace.
Figure 1 Workspace management page

- In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
Figure 2 Accessing the Security Analysis tab
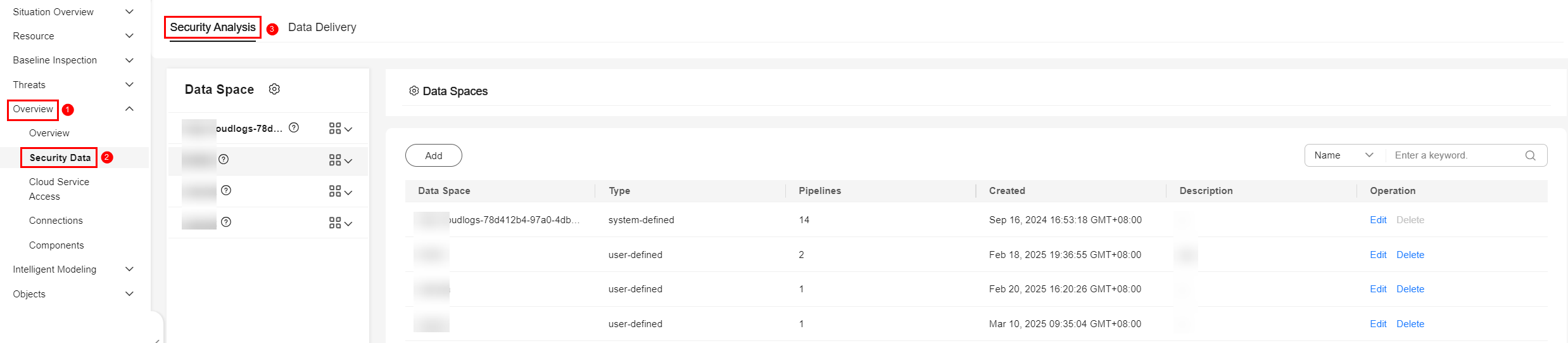
- Create a data space.
- In the upper left corner of the data space list, click Add. The Add Data Space panel is displayed on the right.
Figure 3 Add Data Space

- On the Add Data Space panel, set the parameters for the new data space.
Table 1 Parameters for adding a data space Parameter
Description
Data Space
Enter a data space name. The name must meet the following requirements:
- The name can contain 5 to 63 characters.
- The value can contain letters, numbers, and hyphens (-). The name cannot start or end with a hyphen (-) or contain consecutive hyphens (-).
- The name cannot be the same as any other data space name on Huawei Cloud.
Description
(Optional) Remarks of the data space.
- Click OK.
- In the upper left corner of the data space list, click Add. The Add Data Space panel is displayed on the right.
- In the data space navigation tree on the left, click
 on the right of the data space name created in 4 and select Create Pipeline.
Figure 4 Creating a pipeline
on the right of the data space name created in 4 and select Create Pipeline.
Figure 4 Creating a pipeline
- On the Create Pipeline page, configure pipeline parameters. For details about the parameters, see Table 2.
Table 2 Creating a pipeline Parameter
Description
Data Space
Data space to which the pipeline belongs, which is generated by the system by default.
Pipeline Name
Name of the pipeline. The name must meet the following requirements:
- The name can contain 5 to 63 characters.
- The value can contain letters, numbers, and hyphens (-). The name cannot start or end with a hyphen (-) or contain consecutive hyphens (-).
- The name must be unique in the data space.
Shards
The number of shards of the pipeline. The value ranges from 1 to 64.
An index can potentially store a large amount of data that exceeds the hardware limits of a single node. To solve this problem, Elasticsearch subdivides your index into multiple pieces called shards. When creating an index, you can specify the number of shards as required. Each shard is in itself a fully-functional and independent "index" that can be hosted on any node in the cluster.
Lifecycle
Life cycle of data in the pipeline. The value ranges from 7 to 180.
Description
Remarks on the pipeline. This parameter is optional.
- Click OK
After the pipeline is created, you can click the data space name to view the created pipeline.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.






