Migrating Data from a Third-Party Elasticsearch Cluster to Huawei Cloud Using Backup and Restoration
You can use backup and restoration to migrate data from a third-party Elasticsearch cluster to a Huawei Cloud Elasticsearch cluster.
Scenarios
Data migration between a third-party Elasticsearch cluster and a Huawei Cloud Elasticsearch cluster through backup and restoration depends on storage repositories. Typical application scenarios include:
- Changing the service provider: An enterprise currently using a third-party Elasticsearch service wishes to switch to Huawei Cloud for reasons such as cost, performance, or other strategic considerations.
- Cluster merge: Data scattered across different third-party Elasticsearch clusters can be migrated to Huawei Cloud Elasticsearch clusters for centralized management, enabling more efficient data analysis and querying.
- Cross-version migration: Data is migrated from a third-party Elasticsearch cluster of an earlier version to a Huawei Cloud Elasticsearch cluster of a later version.
- Unified technology stack: For a simplified, unified technology stack, companies that are already using some services on Huawei Cloud may choose to migrate their in-house built Elasticsearch clusters to Huawei Cloud.
Solution Architecture
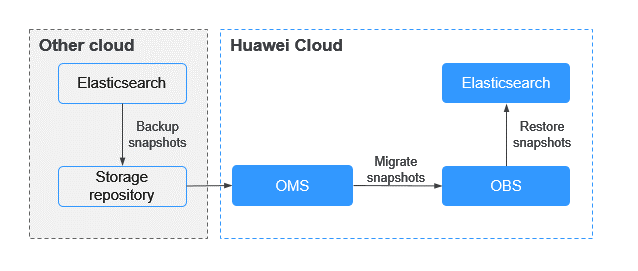
Figure 1 shows the process of migrating a third-party Elasticsearch cluster (source cluster) to Huawei Cloud Elasticsearch cluster (destination cluster).
- Back up third-party Elasticsearch data to a third-party shared repository.
- Use OMS to migrate data from the shared repository to Huawei Cloud OBS.
- Use Huawei Cloud OBS to restore data to a Huawei Cloud Elasticsearch cluster.
Advantages
- Easy to use and manage: The snapshot and restoration APIs provided by Elasticsearch are easy to use and manage, and can be used to automate some of the tasks.
- Suitable for large-scale data migration: Snapshots can be used to migrate GB, TB, or even PB of data.
- Controllable restoration process: During data restoration, you can restore specific indexes or all indexes and specify the cluster status to be restored.
Impact on Performance
This migration method works by copying data directly from the storage layer. It does not rely on any external Elasticsearch APIs. Hence it significantly reduces any impact on the performance of the source cluster. For latency-insensitive workloads, the impact is negligible.
Constraints
- The version of the destination cluster must not be earlier than that of the source cluster. For details, see Snapshot version compatibility.
- This method does not support incremental data synchronization. You need to pause data update before starting to back up data.
- Snapshots can be migrated only when public access is enabled for third-party storage repositories.
Prerequisites
- The source and destination Elasticsearch clusters are available.
- The OBS bucket (esbak) for storing snapshots has been created. The OBS bucket and the destination Elasticsearch cluster in CSS are in the same Region, and the Storage Class is Standard.
Procedure
- Log in to the third-party cloud that hosts the Elasticsearch cluster you want to migrate and create a shared storage repository that supports the S3 protocol.
For example, log in to Alibaba Cloud, access the OSS service, and create a directory named patent-esbak. Or log in to Tencent Cloud, access the COS service, and create a directory named patent-esbak.
- Create a snapshot backup repository in the third-party Elasticsearch cluster to store Elasticsearch snapshot data.
For example, create a backup repository named my_backup in Elasticsearch and associate it with the OSS repository.
PUT _snapshot/my_backup { # Repository type. "type": "oss", "settings": { # # Private network domain name of the repository in step 1. "endpoint": "http://oss-xxx.example.com", # User ID and password of the repository. Hard-coded or plaintext access keys (AK/SK) are risky. For security purposes, encrypt your access keys and store them in the configuration file or environment variables. In this example, access keys are stored in the environment variables for identity authentication. Before running the code in this example, configure the AK and SK in environment variables. "access_key_id": "ak", "secret_access_key": "sk", # Bucket name of the repository created in step 1. "bucket": "patent-esbak", # # Whether to enable snapshot file compression. "compress": false, # If the size of the uploaded snapshot data exceeds the value of this parameter, the data will be uploaded as blocks to the repository. "chunk_size": "1g", # Start position of the repository. The default value is the root directory. "base_path": "snapshot/" } } - Create a snapshot in the third-party Elasticsearch cluster.
- Create a snapshot for all indexes.
For example, create a snapshot named snapshot_1.
PUT _snapshot/my_backup/snapshot_1?wait_for_completion=true
- Create a snapshot for specified indexes.
For example, create a snapshot named snapshot_test that contains indexes patent_analyse and patent.
PUT _snapshot/my_backup/snapshot_test { "indices": "patent_analyse,patent" }
- Create a snapshot for all indexes.
- View the snapshot creation progress in the third-party Elasticsearch cluster.
- Run the following command to view information about all snapshots:
GET _snapshot/my_backup/_all
- Run the following command to view information about snapshot_1:
GET _snapshot/my_backup/snapshot_1
- Run the following command to view information about all snapshots:
- Use the Object Storage Migration Service (OMS) to migrate the snapshot data from the repository to the OBS bucket esbak.
OMS supports data migration from multiple cloud vendors to OBS. For details, see .

When creating a migration task on OMS, set Object Metadata to Migrate. Otherwise, data migration may be abnormal.
- Log in to the Kibana console of a CSS Elasticsearch cluster.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > Elasticsearch.
- In the cluster list, find the target cluster, and click Kibana in the Operation column to log in to the Kibana console.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Dev Tools.
The left part of the console is the command input box, and the triangle icon in its upper-right corner is the execution button. The right part shows the execution result.
- Create a repository in the CSS Elasticsearch cluster and associate it with OBS. This repository will be used for restoring the snapshots of the third-party Elasticsearch cluster.
For example, create a repository named my_backup_all in the CSS Elasticsearch cluster and associate it with the OBS bucket esbak.
PUT _snapshot/my_backup_all/ { "type" : "obs", "settings" : { # Private network domain name of OBS "endpoint" : "obs.xxx.example.com", "region" : "xxx", # Username and password for accessing OBS. Hard-coded or plaintext access keys (AK/SK) are risky. For security purposes, encrypt your access keys and store them in the configuration file or environment variables. In this example, access keys are stored in the environment variables for identity authentication. Before running the code in this example, configure the AK and SK in environment variables. "access_key": "ak", "secret_key": "sk", # OBS bucket name, which must be the same as the destination OBS bucket name in the previous step. "bucket" : "esbak", "compress" : "false", "chunk_size" : "1g", #Note that there is no slash (/) after snapshot. "base_path" : "snapshot", "max_restore_bytes_per_sec": "100mb", "max_snapshot_bytes_per_sec": "100mb" } } - Restore snapshot data to the CSS Elasticsearch cluster.
- Check information about all snapshots.
GET _snapshot
- Restore data using snapshots.
- Restore all the indexes from a snapshot. For example, to restore all the indexes from snapshot_1, run the following command:
POST _snapshot/my_backup_all/snapshot_1/_restore?wait_for_completion=true
- Restores some indexes from a snapshot. For example, in the snapshot named snapshot_1, restore only the indexes that do not start with a period (.).
POST _snapshot/my_backup/snapshot_1/_restore {"indices":"*,-.monitoring*,-.security*,-.kibana*","ignore_unavailable":"true"} - Restore a specified index from a snapshot and renames the index. For example, in snapshot_1, restore index_1 to restored_index_1 and index_2 to restored_index_2.
POST /_snapshot/my_backup/snapshot_1/_restore { # Restore only indexes index_1 and index_2 and ignore other indexes in the snapshot. "indices": "index_1,index_2" # Search for the index that is being restored. The index name must match the provided template. "rename_pattern": "index_(.+)", # Rename the found index. "rename_replacement": "restored_index_$1" }
- Restore all the indexes from a snapshot. For example, to restore all the indexes from snapshot_1, run the following command:
- View the snapshot restoration result.
- Run the following command to view the restoration results of all snapshots:
GET /_recovery/
- Run the following command to check the snapshot restoration result of a specified index:
GET {index_name}/_recovery
- Run the following command to view the restoration results of all snapshots:
- Check information about all snapshots.
- (Optional) After the migration, promptly delete the OBS bucket used for storing snapshots if these snapshots are no longer needed. This is to prevent ongoing storage costs.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.