Resource Configurations (VMs)
Resource Specifications
The HA deployment model of on-premises clusters applies to commercial scenarios and meets DR requirements. If you deploy on-premises clusters on VMs, use the following VM resource specifications.
|
Node Type |
Node Quantity |
vCPU |
Memory (GiB) |
System Disk (GiB) |
High-Performance Disk (GiB) |
Data Disk (GiB) |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Master nodes |
3 |
8 |
16 |
100 |
50 |
300 |
A virtual IP address is required for HA. |
|
Worker nodes |
As required |
2 |
4 |
40 |
- |
100 |
You can increase the number of nodes as required. |
|
Component |
vCPU |
Memory (GiB) |
|---|---|---|
|
Prometheus |
Requests: 1 Limits: 4 |
Requests: 2 Limits: 12 |
|
log-agent |
Requests: 0.5 Limits: 3 |
Requests: 1.5 Limits: 2.5 |
The non-HA deployment model of on-premises clusters applies to test scenarios and has low requirements on system resources. If you deploy on-premises clusters on VMs, use the following VM resource specifications.
|
Node Type |
Node Quantity |
vCPU |
Memory (GiB) |
System Disk (GiB) |
High-Performance Disk (GiB) |
Data Disk (GiB) |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Master nodes |
1 |
8 |
16 |
100 |
50 |
300 |
- |
|
Worker nodes |
As required |
2 |
4 |
40 |
- |
100 |
You can increase the number of nodes as required. |
|
Component |
vCPU |
Memory (GiB) |
|---|---|---|
|
Prometheus |
Request: 1 Limits: 4 |
Requests: 2 Limits: 12 |
|
log-agent |
Requests: 0.5 Limits: 3 |
Requests: 1.5 Limits: 2.5 |
External Dependencies
|
Dependency |
Description |
|---|---|
|
DNS servers |
DNS servers can resolve the domain names of cloud services such as OBS, SWR, IAM, and DNS. For details about the domain names of these cloud services, see Regions and Endpoints. If a node is accessed over a public network, the node can automatically identify the default DNS settings. You only need to configure public upstream DNS servers in advance. If a node is accessed over a private network, the node cannot identify the default DNS settings. You need to configure the DNS resolution for VPC endpoints in advance. For details, see Pre-Installation Check. If you do not set up a DNS server, set up it by referring to DNS. |
|
APT or Yum repositories |
An APT or Yum repository provides dependency packages for installing components such as NTP on nodes (servers) added to on-premises clusters.
NOTE:
APT repositories are suitable for nodes running Ubuntu, and Yum repositories for nodes running HCE or Red Hat. |
|
NTP servers |
(Optional) An NTP server is used for time synchronization between nodes in a cluster. An external NTP server is recommended. |
Disk Volumes
|
Node Type |
Disk Mount Point |
Available Size (GiB) |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Master nodes |
/var/lib/containerd |
50 |
Directory for storing containerd images |
|
/run/containerd |
30 |
Directory for storing containerd |
|
|
/var/paas/run |
50 |
Directory for storing etcd data (An SSD disk is recommended.) |
|
|
/var/paas/sys/log |
20 |
Directory for storing logs |
|
|
/mnt/paas |
40 |
Directory where volumes are mounted when containers are running. |
|
|
/tmp |
20 |
Directory for storing temporary files |
|
|
Worker nodes |
/var/lib/containerd |
100 |
Directory for storing containerd images |
|
/run/containerd |
50 |
Directory for storing containerd |
|
|
/mnt/paas |
50 |
Directory where volumes are mounted when containers are running. |
|
|
/tmp |
20 |
Directory for storing temporary files |
Load Balancing Planning
In the HA model, an on-premises cluster requires three master nodes for DR, and an IP address is required to allow access from worker nodes and other external services. There are virtual IP addresses and load balancers for cluster HA. Select either of them based on site requirements.
- Virtual IP address planning
An idle IP address must be planned as a virtual IP address that can be shared by the three master nodes. The virtual IP address is randomly bound to a master node. When the master node or a service on the master node becomes faulty, the virtual IP address is automatically bound to another master node to ensure cluster HA.
Table 7 IP address planning for VMs IP Type
IP Address
Description
Virtual IP addresses
10.10.11.10 (example)
An IP address used for HA. Plan the IP address based on site requirements.
- Load balancer planning
If you have a load balancer, on-premises clusters can connect to it for HA. Load balancer configurations are as follows:
- Listeners: 3 TCP listeners with three different ports (80, 443, and 5443)
- Backend server groups: 3 TCP backend server groups with three different ports (corresponding to ports 80, 443, and 5444 of the three master nodes)
Table 8 lists the requirements for the TCP backend server groups and listeners.
Table 8 VM listeners and backend server groups Listener (Protocol/Port)
Backend Server Group
Backend Server and Port
TCP/80
ingress-http
master-01-IP:80
master-02-IP:80
master-03-IP:80
TCP/443
ingress-https
master-01-IP:443
master-02-IP:443
master-03-IP:443
TCP/5443
kube-apiserver
master-01-IP:5444
master-02-IP:5444
master-03-IP:5444

- The configuration page varies by the load balancer provider. Configure backend servers and ports based on site requirements.
If Transfer Client IP Address is enabled for the load balancer provided by Huawei Cloud ELB, a server cannot serve as both a backend server and a client.
If the client and the backend server use the same server and Transfer Client IP Address is enabled, the backend server will think the packet from the client is sent by itself and will not return a response packet to the load balancer. As a result, the return traffic will be interrupted.
When using Huawei Cloud ELB, perform the following operations:
- To enable IP as a Backend, click the name of the load balancer to access its details page. On the Summary tab, click Enable for IP as a Backend.
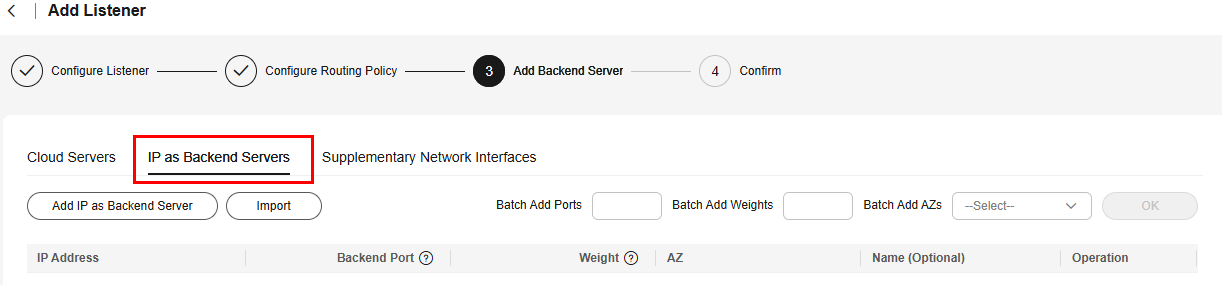
- To add backend servers in a VPC different from the VPC of the load balancer by using their IP addresses, click the name of the load balancer to access its details page. On the Listeners tab, click Add Listener. On the Add Backend Servers page, click the IP as Backend Server tab.
- Use the Huawei Cloud ELB configuration. For details, see Transfer Client IP Address.

- Before installing an on-premises cluster, configure the TCP listeners and TCP backend server groups on the load balancer and ensure that the load balancer is working normally.
- The load balancer can route traffic from processes (such as the kubelet process) on all nodes (including master nodes) to three master nodes. In addition, the load balancer can automatically detect and stop routing traffic to unavailable processes, improving service capabilities and availability. You can use load balancers or even hardware devices provided by other cloud vendors. You can also use Keepalived and HAProxy to implement high-availability deployment with multiple master nodes.
- Recommended configuration: Enable source IP transparency for the preceding listening ports and disable loop checking. If loop checking cannot be disabled separately, disable source IP transparency. To check whether loop checking exists, take the following steps:
- Create an HTTP service on a server that can be accessed over external networks, change default listening port 80 to 88, and add the index.html file for testing.
yum install -y httpd sed -i 's/Listen 80/Listen 88/g' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf echo "This is a test page" > /var/www/html/index.html systemctl start httpd
Enter ${IP-address-of-server-A}:88 in the address box of a browser. "This is a test page" is displayed.
- Configure a listening port (for example, 30088) for the load balancer to route traffic to port 88 of the server, and enable source IP transparency.
- Use the private IP address of the load balancer to access the HTTP service.
curl -v ${ELB_IP}:30088Check whether the HTTP status code is 200. If the status code is not 200, loop checking exists.
- Create an HTTP service on a server that can be accessed over external networks, change default listening port 80 to 88, and add the index.html file for testing.
User Planning
|
User |
User Group |
User ID |
User Group ID |
Password |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
root |
root |
0 |
0 |
- |
Default user for installing on-premises clusters. You can also specify another user that meets the following requirements:
NOTE:
After the installation is complete, you can change the password or restrict the root permissions. |
|
paas |
paas |
10000 |
10000 |
- |
User and user group used to run on-premises cluster services. They are created during the installation of on-premises clusters. The username and user group name are both paas, and the user ID and user group ID are both 10000. Before the installation, ensure that the username, user group name, user ID, and user group ID are not occupied. If any of them are occupied, delete the existing ones in advance. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





