MySQL
The MySQL connector allows you to connect applications with the MySQL database, and manage data transmission.
- MySQL is a popular, open-source relational database widely used as the backend of web applications. It supports multiple operating systems, such as Windows, Linux, Unix, and macOS X. MySQL features high performance, reliability, and flexibility, and is popular among enterprises and developers.
- The default MySQL port number is 3306. The administrator can change the port number as required. MySQL supports multiple storage engines, including InnoDB, MyISAM, and MEMORY. Each storage engine has its own pros and cons and can be configured flexibly.
Creating a MySQL Connection
- Log in to the new ROMA Connect console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Connector. On the page displayed, click New Connection.
- Select the MySQL connector.
- In the dialog box displayed, configure the connector and click Test connection. After the connection is successful, click OK.
Parameter
Description
Name
Enter the connector instance name.
Region
Select a region.
Project
Select a project.
Instance
Select an instance for subsequent connectivity verification.
Connection and Security
Select the connection mode for the database. Currently, the Default mode is supported.
IP Address
Enter the IP address of the database.
Port
Enter the port number to which the database is connected.
Database Name
Enter the name of the database to be connected.
Username
Enter the username used to connect to the database.
Password
Enter the password used to connect to the database.
Description
Enter the description of the connector to identify it.
Action
- Obtain Record: Retrieve data from a MySQL table by specifying the table name, WHERE condition, Order By field, Limit, and Offset.
- Incrementally Obtain Record: Periodically fetch new or updated records from a MySQL table since a specified start time. This action must be used together with a timer.
- Add Record: Insert a new row into a specified MySQL table.
- Update Record: Update one or more rows in a specified MySQL table by applying filter criteria and providing new values.
- Replicate Record: Replicate data to a specified MySQL data table. This action must be used together with a timer and CDC must be enabled
- Delete Record: Delete one or more rows from a specified MySQL table based on filter criteria.
- Custom SQL: Execute native SQL statements for operations on the MySQL database.
Configuring Parameters
- Obtaining records
Table 1 Configuration parameters Parameter
Description
Table Name
Select or enter the table name in the database to be queried.
Field Name
Select the field name of the data table to be queried. If this parameter is not specified, all fields will be returned.
WHERE Condition
Filter query results using conditions like column_name='value'. Supported operators: =, !=, >, <, >=, <=, like, in, not in, is null, and is not null.
Order By Field
Specify one or more columns to sort results, for example, id DESC.
Limits
Limit the number of returned rows, for example, 100.
Offset
Specify the starting row number for returned data, for example, 15.
Data Schema
Configure output fields. Fields are auto-generated when a table is selected but can be edited manually.
Table 2 Output parameters Parameter
Description
Payload
Response in JSON format, with keys as the database field names and values as their corresponding data. Entries on each line are comma-separated. For payload details, see Referencing Variables.
Selected Count
Number of rows in the query result. For details about the property, see Referencing Variables.
After the execution is successful, the payload value is as follows:
[ { "Product_Id": "f47ac10b-58cc-4372-a567-0e02b2c3d479", "Created_Time": "2024-11-29T15:06:09Z", "Product_Price": 1299, "Product_Name": "Product A", "Product_Desc": "Product A" }, { "Product_Id": "c3d7b1b7-4cd1-4d72-b1b8-7d38e1a1fe5a", "Created_Time": "2024-11-29T15:06:38Z", "Product_Price": 1099, "Product_Name": "Product C", "Product_Desc": "Product C" } ] - Obtaining incremental records
Table 3 Configuration parameters Parameter
Description
Table Name
Select or enter the name of the table to obtain incremental records.
Field Name
Select the field name of the data table to be queried.
WHERE Condition
Filter query results using conditions like column_name='value'. Supported operators: =, !=, >, <, >=, <=, like, in, not in, is null, and is not null.
Order By Field
Specify one or more columns to sort results, for example, id DESC.
Start Timezone for incremental database selection
Start time zone for obtaining incremental data.
Incremental Selection Timestamp Field Name
Timestamp field for obtaining incremental data. The selected field must be of the time or timestamp type.
Incremental Selection Timestamp Initial Value
Initial timestamp for obtaining incremental data.
Reset Initial Incremental Selection Time
Whether to enable the reset of the initial time for obtaining incremental data. If this function is disabled, the system obtains incremental data from the current time.
Incremental Selection Compensation Period (ms)
Specify the extended time range (ms) to avoid missing records that may arrive late.
Data Schema
Configure output fields. Fields are auto-generated when a table is selected but can be edited manually.
Table 4 Output parameters Parameter
Description
Payload
Response in JSON format, with keys as the database field names and values as their corresponding data. Entries on each line are comma-separated. For payload details, see Referencing Variables.
Example of obtaining incremental records:
Timer (triggered every day) → MySQL (obtaining incremental records) → Log collection

- Adding records
Table 5 Configuration parameters Parameter
Description
Table Name
Enter the name of the table where data will be inserted.
Data to Insert
Enter the value of the target field.
Data Schema
Configure output fields. Fields are auto-generated when a table is selected. This setting is not applicable for this action.
Table 6 Output parameters Parameter
Description
Updated Count
Row number of the inserted data. For details about the property, see Referencing Variables.
- Updating records
Table 7 Configuration parameters Parameter
Description
Table Name
Select or enter the name of the table where data is to be updated.
Data to Update
Enter the value of the target field.
WHERE Condition
Select the target row using conditions like column_name='value'. Supported operators: =, !=, >, <, >=, <=, like, in, not in, is null, and is not null.
Data Schema
Configure output fields. Fields are auto-generated when a table is selected. This setting is not applicable for this action.
Table 8 Output parameters Parameter
Description
Updated Count
Row number of the updated data. For details about the property, see Referencing Variables.
- Replicating records
Table 9 Configuration parameters Parameter
Description
Table Name
Select or enter the name of the table where data is to be synchronized.
Clear Table
Whether to clear the table each time data is replicated.
Table 10 Output parameters Parameter
Description
Payload
Response in JSON format, with keys as the database field names and values as their corresponding data. Entries on each line are comma-separated. For payload details, see Referencing Variables.
This action supports the following scenarios:
- Stream data from one database to another with identical table names
MySQL: Capture Database Changes → Replicate Record
Timer (any action) → MySQL (Incrementally Obtain Record) → MySQL (Replicate Record)
- Stream data between databases with different table names (data mapping processor for table name mapping)
MySQL (Capture Database Changes) → Data Mapper → MySQL (Replicate Record)
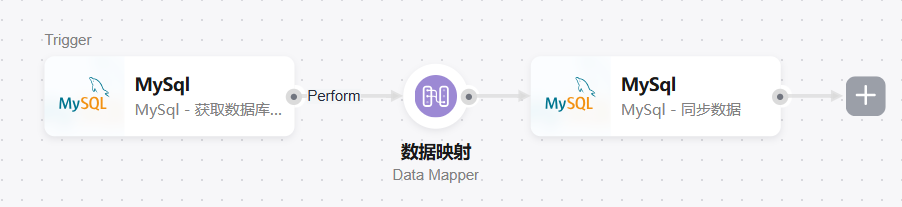
Timer (any action) → MySQL (Incrementally Obtain Record) → Data Mapper → MySQL (Replicate Record)
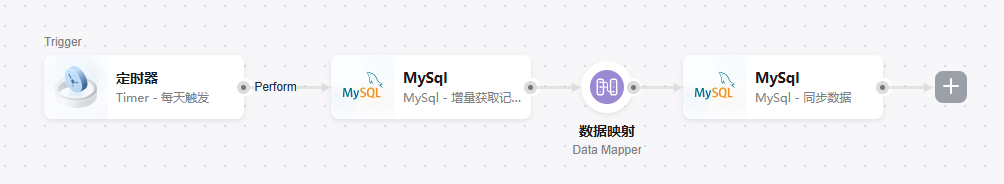
- Stream data from one database to another with identical table names
- Deleting records
Table 11 Configuration parameters Parameter
Description
Table Name
Select or enter the name of the table where data is to be deleted.
WHERE Condition
Select the target row using conditions like column_name='value'. Supported operators: =, !=, >, <, >=, <=, like, in, not in, is null, and is not null.
Data Schema
Configure output fields. Fields are auto-generated when a table is selected. This setting is not applicable for this action.
Table 12 Output parameters Parameter
Description
Updated Count
Row number of the deleted data. For details about the property, see Referencing Variables.
- Custom SQL
Table 13 Custom SQL Parameter
Description
Statement
Statements display all your inputs as plain text. Do not include sensitive information. Only one select, update, insert, or delete statement can be executed. The select statement can return up to 500 records.

If the table name contains a hyphen (-), use backquotes (`) to enclose the table name. For example, insert into `bfs-test`.source_01(id, name) values (01, 'testname01');. Otherwise, a syntax error is reported.
Table 14 Output parameters Parameter
Description
Payload
Response in JSON format, with keys as the database field names and values as their corresponding data. Entries on each line are comma-separated. For payload details, see Referencing Variables.
Updated count
Number of updated rows.
Selected count
Number of rows of data queried.
Start time
Start time of node execution.
End time
End time of node execution.
Execution time
Node execution duration, in milliseconds.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





