MRS Storage-Compute Decoupling Overview
MRS allows you to store data in OBS and use MRS clusters for data computing only. This decoupled storage-compute mode enables you to flexibly scale resources on demand and provides a low-cost solution for massive data analysis.
MRS Storage-Compute Decoupling Solution
The storage-compute decoupling solution allows to read MRS cluster data from the local storage (such as disks or HDFS) and store the data to the local storage after real-time computing, stream batch processing, and interactive analysis are complete.
However, this solution faces challenges as a result of rapid business growth and data expansion. The challenges include such as high cost of local disk resources, inflexible and unbalanced distribution of the cluster computing and storage resources, and low disk utilization because the Hadoop distributed system stores data in three copies by default. MRS provides a storage-compute decoupling solution based on OBS. In scenarios where a large amount of big data needs to be stored and computing resources need to be elastically expanded, you can store data in OBS and use MRS clusters only for data computing. In this way, resources can be flexibly expanded on demand, achieving a cost-effective massive data analysis solution.
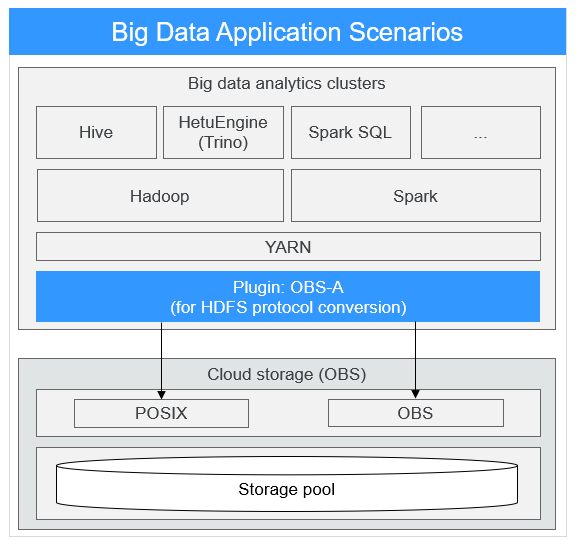
Based on the large capacity and high bandwidth of OBS, the MRS storage-compute decoupling solution is compatible with multiple computing engines such as Hive and Spark in the Hadoop ecosystem. Compared with traditional on-premises IDC deployment of big data services, the MRS storage-compute decoupling solution features high convergence efficiency, high resource utilization, and low costs.
For details about the HDFS principles, see HDFS Basic Principles. For details about the OBS principles, see Object Storage Service (OBS).
Notes and Constraints
- In storage-compute decoupling scenarios, make sure to use an OBS parallel file system. For details, see Parallel File System. Using a regular object bucket can significantly impact the performance of the cluster.
- To delete a component or cluster connected to OBS (including storage-compute decoupling and cold-hot data separation scenarios), you must also delete the service data on OBS.
- After storage-compute decoupling is configured for the MRS cluster, components can access the OBS file system and the HDFS in the cluster. For details, see Interconnecting an MRS Cluster with OBS Using an IAM Agency or Interconnecting an MRS Cluster with OBS Through Guardian.
- Only MRS 3.3.0-LTS and later versions support interconnection with OBS based on Guardian. For clusters of other versions, use IAM agencies to interconnect with OBS. For details, see Interconnecting an MRS Cluster with OBS Using an IAM Agency.
- On the Guardian-based storage and compute decoupling management plane, job submission depends on the JobGateway instead of the Executor.
Video Tutorial
Configuring Storage and Compute Decoupling Using Guardian

- If you need to configure permission policies for OBS paths of components using Ranger, that is, enable the OBS AccessLabel function for Guardian, see Enabling Ranger OBS Path Authentication for Guardian. For details about OBS permission configuration, see Granting OBS Permissions.
- If you only need to configure Guardian to connect to OBS, but do not need to use Ranger to configure permission policies for OBS paths, see Disabling Ranger OBS Path Authentication for Guardian.
- Create an MRS cluster.
The MRS cluster must contain basic components such as Guardian, Ranger, and Hadoop.
Only MRS 3.3.0-LTS or later supports interconnection with OBS using Guardian.
- Create an OBS agency.
Create an agency with OBS access permissions, which allows Guardian to connect to OBS.
- Enable the interconnection between Guardian and OBS and configure parameters.
Modify Guardian service parameters and configure IAM agency authentication information to provide temporary authentication credentials and fine-grained permission control for other components to access OBS.
- Configure the policy for clearing component data in the recycle bin directory.
In the storage-compute decoupling scenario, the prevention against accidental deletion is enabled by default for components connected to OBS. When you delete data, the deleted object is moved to the corresponding recycle bin directory. You need to configure a lifecycle rule for the corresponding directory in the OBS file system to prevent the storage space from being used up.
- Interconnect components with OBS.
- Components in the MRS cluster can directly access the corresponding path after being granted required permissions for accessing OBS buckets. You can use the component client to directly access resources in the OBS file system in absolute path mode.
Configuring Storage-Compute Decoupling Using IAM Agencies
- Create an ECS agency with OBS access permissions.
You need to create an ECS agency with OBS access permissions. The ECS agency is used to automatically obtain temporary AK/SK to access OBS.
- Create an MRS cluster with decoupled storage and compute.
- Creating a cluster with decoupled storage and compute
Create an MRS cluster and bind an ECS agency to it. Add components as required. Components that can be connected to OBS through an IAM agency include Hadoop, Hive, Spark, Presto, Flink, Flume, Hudi and Sqoop.
- Configuring storage-compute decoupling for an existing cluster
Bind an ECS agency to an existing cluster to implement decoupled storage and compute.
- Creating a cluster with decoupled storage and compute
-
You need to create an OBS parallel file system for storing cluster data.
- Configure the policy for clearing component data in the recycle bin directory.
In the storage-compute decoupling scenario, the prevention against accidental deletion is enabled by default for components connected to OBS. When you delete data, the deleted object is moved to the corresponding recycle bin directory. You need to configure a lifecycle rule for the corresponding directory in the OBS file system to prevent the storage space from being used up.
- Interconnect components with OBS.
- Components in the MRS cluster can directly access the corresponding path after being granted required permissions for accessing OBS buckets. You can directly access resources in the OBS file system via the component client using an absolute path.
Granting OBS Permissions
Enabling storage-compute decoupling and Ranger authentication for an MRS cluster that connects to OBS using Guardian allows Ranger administrators to grant cluster users permissions to read and write OBS directories and files.
In addition, with the Guardian-based storage-compute decoupling architecture and the Hive cascading authorization function, you just need to be granted permissions on the service table through Ranger. Then the system will grant you the permissions on the data storage source, for example, the storage directory on OBS, in a fine-grained manner. You do not need to query the storage path of the table and perform secondary authorization.
- Before configuring permission policies for OBS paths on Ranger, ensure that the AccessLabel function has been enabled for OBS. For how to enable it, contact OBS O&M personnel.
- On Ranger, only users in Ranger custom user groups can be granted OBS permissions. Enter 1 to 52 characters for each user group name. Only letters, numbers, underscores (_), and number signs (#) are allowed. Or, the policy fails to add.
- For clusters with Kerberos authentication enabled, permissions need to be granted based on Ranger. For clusters with Kerberos authentication disabled, OBS permissions are granted by default, and no additional configuration is required.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





