Forward Access Sessions
Forward Access Sessions (FAS) is a technology that enables a cloud service to forward requests to downstream cloud services. When a cloud service needs to interact with downstream cloud services to complete a user request, the service initiates a FAS request as the caller. It will pass your identity, permissions, and session attributes. In FAS, a cloud service initiates a request to a downstream cloud service as a caller over the protocol used by the downstream cloud service. When a FAS request is made:
- The cloud service that receives an access request from an IAM principal checks the IAM principal's permissions.
- The cloud service receives a subsequent FAS request also checks the permissions of the same IAM principal.
For example, when SSE-KMS is used to encrypt objects, OBS uses FAS to call KMS to decrypt the objects. When downloading an SSE-KMS encrypted object, the user directly calls OBS to obtain the object, instead of calling KMS to obtain the key to decrypt the object. After receiving a request for obtaining an object, OBS initiates a FAS request to KMS to decrypt the object data. KMS checks whether the user has the required permission on the KMS key. In other words, the user must have both the permissions to access OBS objects and the permissions to obtain KMS keys.
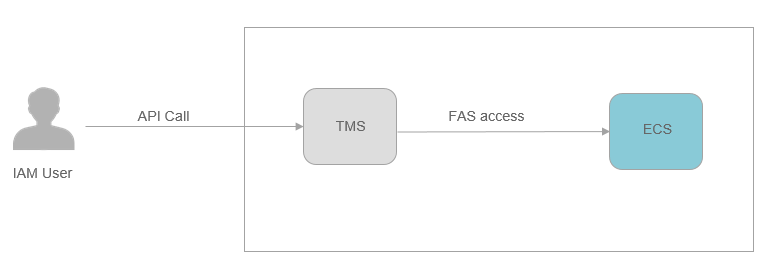

A service that receives a FAS request can send other FAS request. The requester must have the permissions for all the services called in the FAS request chain.
FAS Requests and IAM Condition Keys
When a FAS request is initiated, the g:CalledVia, g:CalledViaFirst, and g:CalledViaLast condition keys are filled with the information about the cloud service principal initiating the FAS request. The g:ViaService condition key is set to true whenever a FAS request is initiated. In the following figure, the request directly sent to OBS does not have any g:CalledVia or g:ViaService condition key. These condition keys will be populated when OBS initiates downstream FAS requests on behalf of the user. For more information about these condition keys, see Global Condition Key.
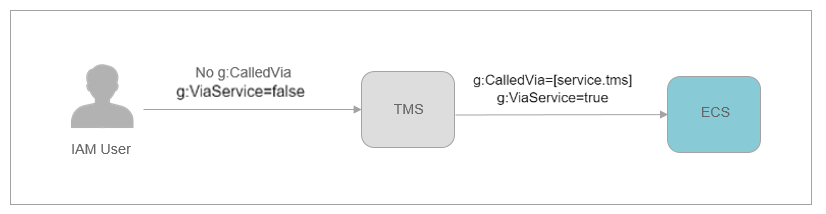
When you need to restrict source IP addresses or source VPCs, you must use the condition keys related to FAS requests to allow exceptions. Using the g:ViaService condition key can provide exceptions for all FAS requests. If you need to allow access to a specific cloud service, use the g:CalledVia condition key.
When you send a request through a VPC endpoint or over the public network, the condition key values g:SourceVpce, g:SourceVpc, g:VpcSourceIp, and g:SourceIp of the initial request are not passed to FAS requests. When you write g:SourceVpce, g:SourceVpc, g:VpcSourceIp, and g:SourceIp in a policy, you must use g:ViaService and g:CalledVia to allow FAS requests.
Example: Allowing ECS Access Across Services with FAS
The following example allows users to programmatically access ECS with specified IP addresses and allows other IP addresses to access ECS with FAS from another service.
{
"Version": "5.0",
"Statement": [{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["ecs:*:*"],
"Resource": ["*"],
"Condition": {
"IpAddress": {
"g:SourceIp": ["103.218.xxx.xxx/32"]
}
}
}, {
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["ecs:*:*"],
"Resource": ["*"],
"Condition": {
"Bool": {
"g:ViaService": "true"
}
}
}]
}
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





