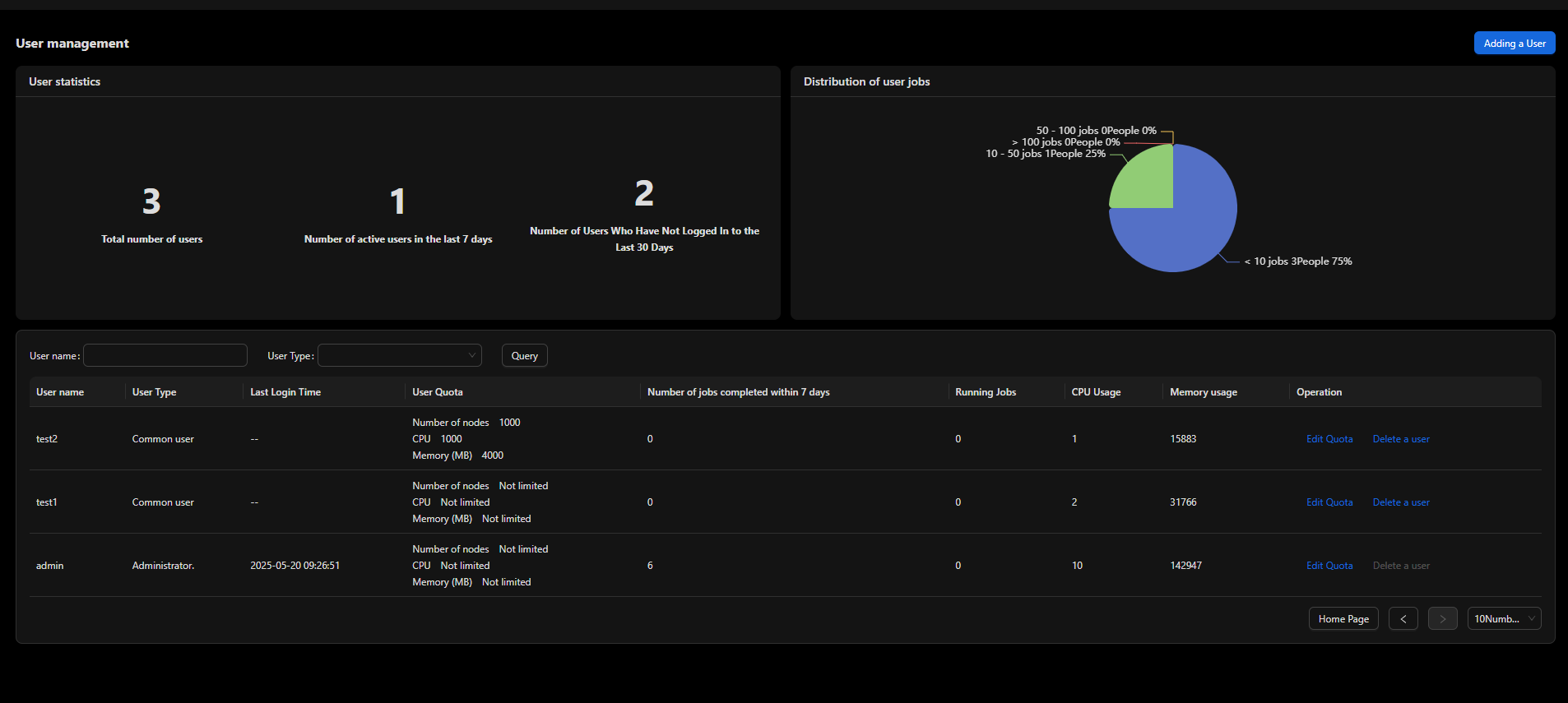
Quota Management
Quota management is used to limit the use of compute resources (such as CPUs, memory, nodes, and jobs) by users and partitions. Slurm does not directly manage storage or disk quotas. However, it can control compute resource quotas through Quality of Service (QoS), associations, and users/partitions.
Core Concepts of Quota Management
- Backend configuration
- Association
- Association is the core mechanism that defines the relationships between users and QoS in Slurm.
- Using association, you can set resource limits (such as the maximum number of jobs and maximum number of CPUs or nodes) for specific users.
- The table below describes the configuration parameters.
Parameter
Description
MaxJobs
Maximum number of jobs allowed to run
MaxCPUs
Maximum number of CPU cores
MaxNodes
Maximum number of nodes
MaxSubmit
Maximum number of jobs a user can submit
MaxWall
Maximum wall clock time a job can run (by partition or QoS)
- Quality of service (QoS)
- QoS is used to define resource limits and priorities for jobs. It can be associated with users, accounts, or jobs.
- You can set the following parameters using QoS.
Parameter
Description
Priority
Determines the scheduling order of jobs.
MaxWall
Sets the maximum wall clock time a job can run.
MaxJobs/MaxCPUs
Defines resource limits (the maximum number of jobs or the maximum number of vCPUs).
- Association
- Settings on the UI
You can set user quotas on the UI.

Quota Types and Configuration Methods
- Walltime limit
The walltime limit defines the maximum amount of time a job can run before it is automatically terminated. You can enforce the walltime limit at multiple levels to control how long a job can run:
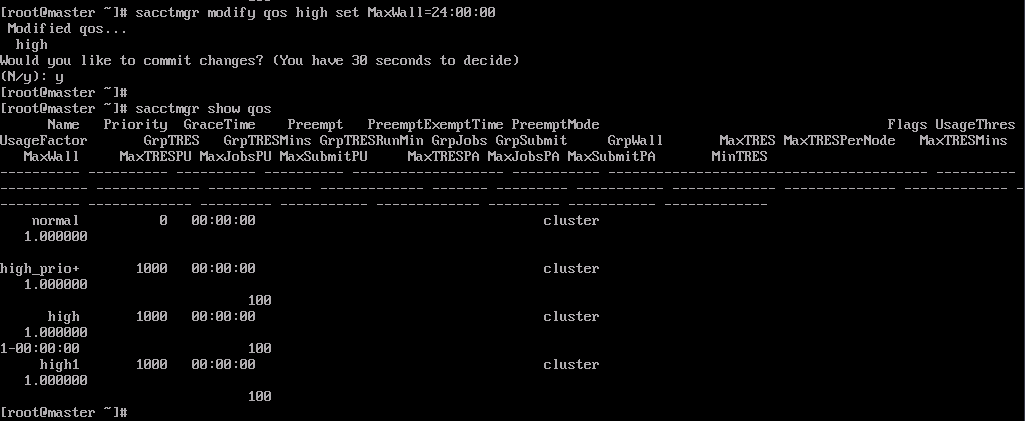
- QoS level: Set MaxWall for QoS by running the sacctmgr command.
# Example: Create a QoS with the walltime limit set to 24 hours.
sacctmgr modify qos normal set MaxWall=24:00:00
- User level:
sacctmgr modify user alice set MaxWall=2-00:00:00
- QoS level: Set MaxWall for QoS by running the sacctmgr command.
- Resource quotas (CPUs/Nodes/Jobs)
- QoS level:
acctmgr modify qos normal set MaxCPUs =100 MaxJobs=100
- User level:
Use sacctmgr to configure various resource limits, including MaxJobs, MaxCPUs, and MaxNodes.
# Set the maximum number of jobs to 10 and the maximum number of CPUs to 100 for user alice. sacctmgr modify user alice set MaxJobs=10 MaxCPUs=100
Settings on the UI
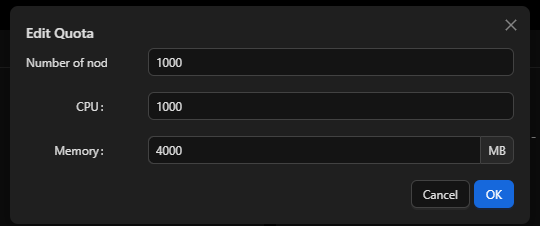
- QoS level:
Configuration Examples
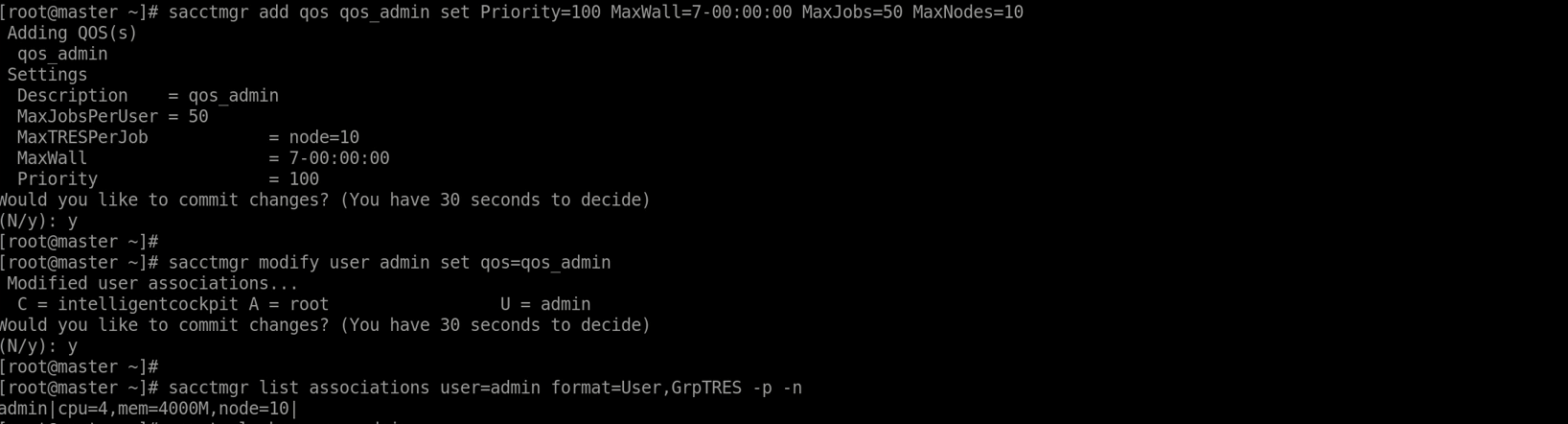
Example 1: Setting QoS and resource limits for a user
- Create a QoS.
sacctmgr add qos name=short_qos MaxWall=1:00:00 MaxJobs=5
- Associate the QoS with the user.
sacctmgr modify user alice set qos=short_qos
- Verify the settings.
sacctmgr show user alice format=User,Account,QOS,MaxJobs,MaxCPUs
Example 2: Denying requests that exceed the quota

Checking the Quota
Precautions
- Priority: In Slurm, user-level quotas generally take precedence over QoS-level quotas.
- Audit and monitoring: You can use sshare and sacct to monitor resource usages periodically.
Remarks
You can view the quota usage in the last 14 days.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot