Performing In-Depth Diagnosis
Scenario
ECS supports in-depth diagnosis for OSs to help you quickly identify and resolve common problems.
This section describes the OS versions that support in-depth diagnosis and the in-depth diagnosis conclusion.
Constraints
- Cloud Operations Center (COC) needs to be enabled and authorized.
For IAM users, permissions for COC operations need to be granted. For details, see Configuring Custom Policies for ECS Self-Service O&M.
- UniAgent must be installed. UniAgent is a unified data collection agent that supports script delivery and execution.
If UniAgent is not installed on the ECS, commands cannot be submitted without login. For details, see Installing UniAgent on an ECS.
- Only ECSs running Linux support in-depth diagnosis.
- The following table lists the Linux distributions and versions that support in-depth diagnosis.
Distribution
Version
CPU Architecture
Huawei Cloud EulerOS
Huawei Cloud EulerOS 2.0
Huawei Cloud EulerOS 1.1
x86/Kunpeng
CentOS
CentOS 8.2 64bit
CentOS 8.0 64bit
CentOS 7.9 64bit
CentOS 7.8 64bit
CentOS 7.7 64bit
CentOS 7.6 64bit
CentOS 7.5 64bit
CentOS 7.4 64bit
CentOS 7.3 64bit
CentOS 7.2 64bit
x86
Ubuntu
Ubuntu 22.04 server 64bit
Ubuntu 20.04 server 64bit
x86
Debian
Debian 11.1.0 64bit
Debian 10.0.0 64bit
x86
Procedure
- Log in to the ECS console and access the ECS list page.
- In the ECS list, locate the target ECS and choose More > View O&M and Monitoring > Perform In-Depth Diagnosis in the Operation column.
- (Optional) On the Enable COC and Grant Permissions page, read and agree to the service statement, and click Enable and Authorize.
This page is displayed if COC is not enabled and authorized.
- On the slide-out Perform In-depth Diagnosis panel, select Comprehensive diagnosis for In-depth Diagnosis Scenario.

UniAgent is required for performing in-depth diagnosis. If a message is displayed indicating that UniAgent is not installed or failed to be installed, install it first by referring to Installing UniAgent on an ECS.
Figure 1 In-depth diagnosis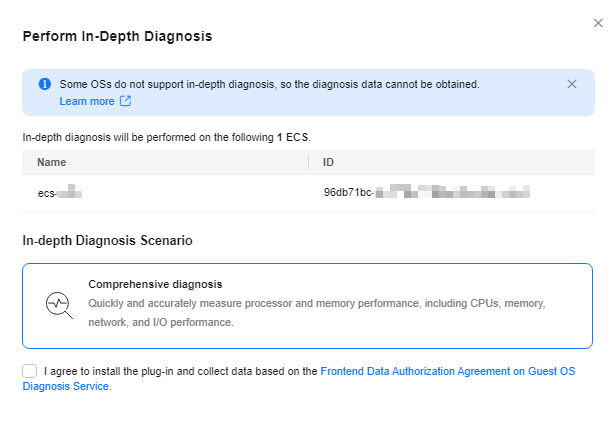
- Select the checkbox and click OK.
For details about the diagnosis results and details, see In-depth Diagnosis Conclusion.
- On the Diagnosis Report tab, view the diagnosis details.
Figure 2 Diagnosis report
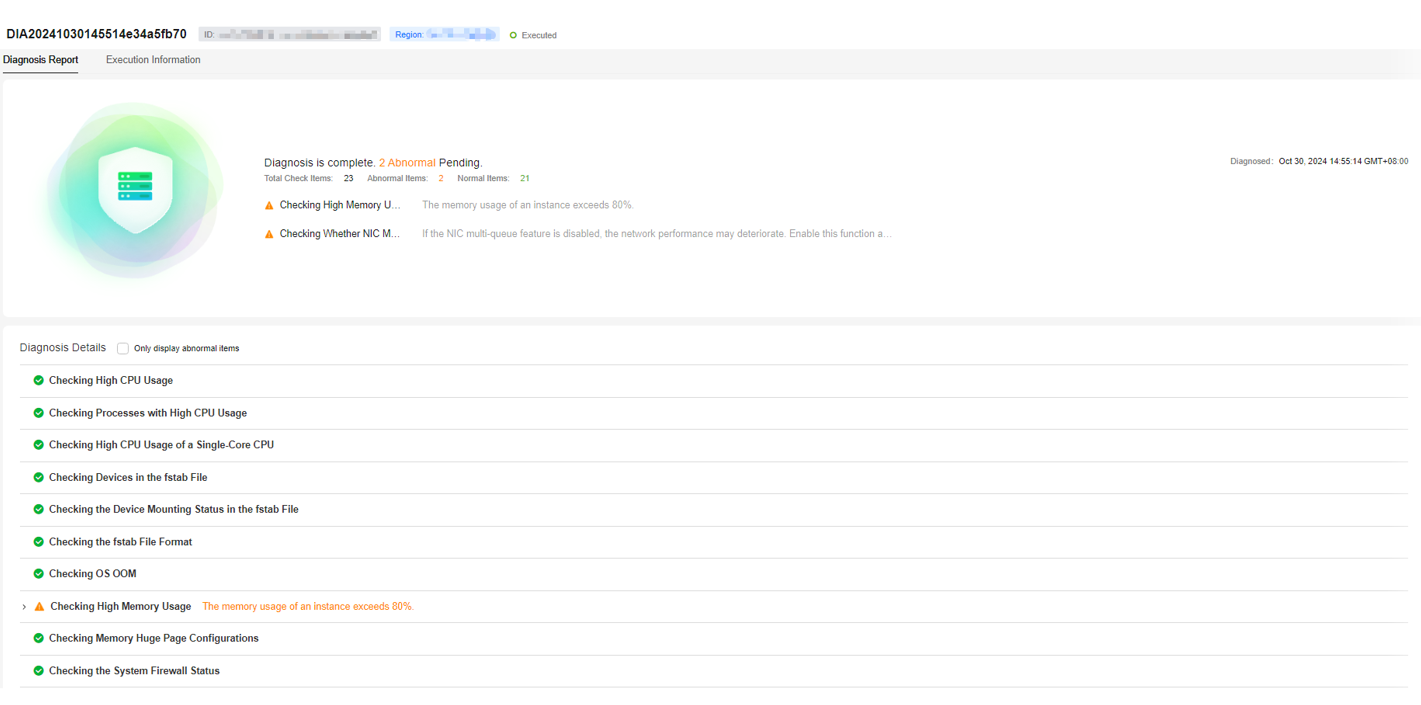
- In the Diagnosis Details area, click
 on the left of the abnormal items to view the exception details and rectify them based on the optimization suggestions.
Figure 3 Diagnosis abnormal items (example)
on the left of the abnormal items to view the exception details and rectify them based on the optimization suggestions.
Figure 3 Diagnosis abnormal items (example)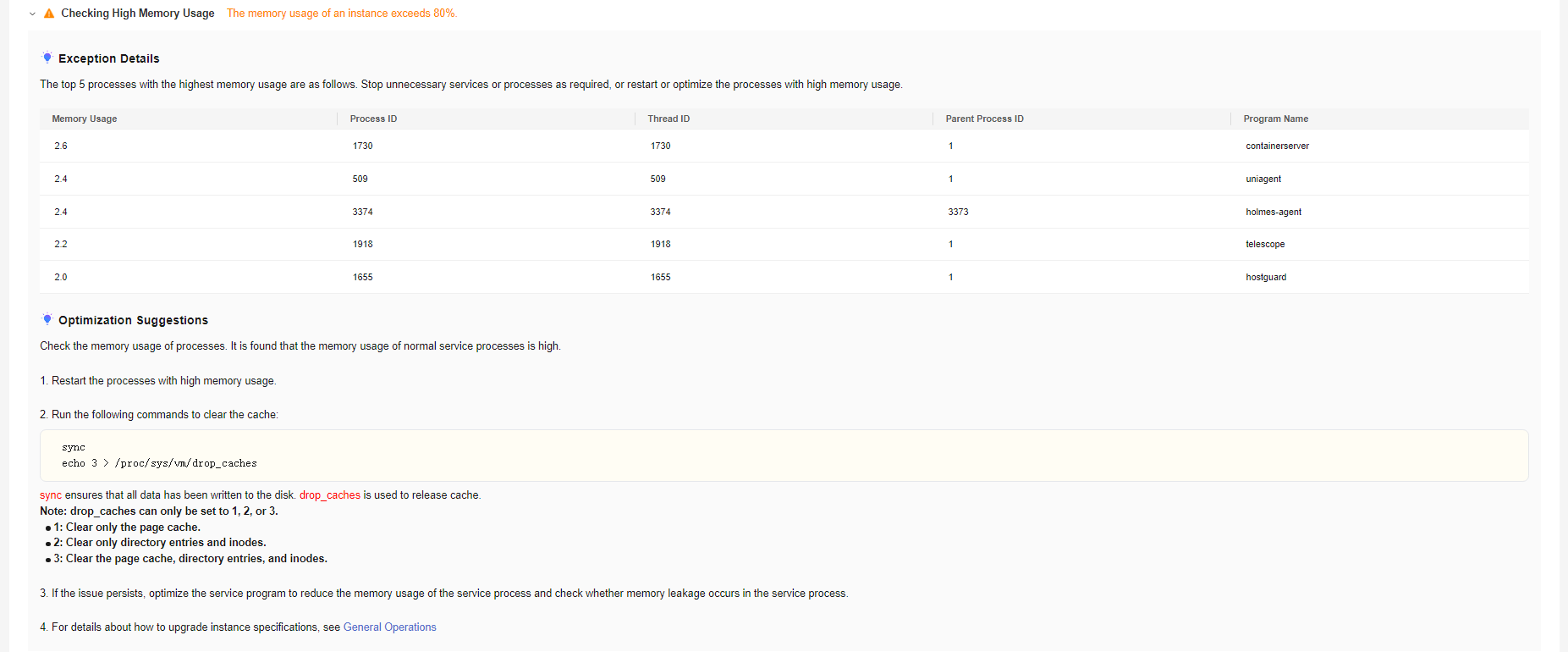
In-depth Diagnosis Conclusion
|
Diagnosis Item ID |
Diagnosis Item Name |
Conclusion |
|---|---|---|
|
guestos.cpu.high_total_usage |
Checking High CPU Usage |
The overall CPU usage exceeds 80% of the entire system. |
|
guestos.cpu.high_process_usage |
Checking Processes with High CPU Usage |
The CPU usage of a single process exceeds 50% of the entire system. |
|
guestos.cpu.high_core_usage |
Checking High CPU Usage of a Single-Core CPU |
The CPU usage of a single-core CPU exceeds 85%. |
|
guestos.storage.high_inode_usage |
Checking Disk Usage |
The file system usage or inode usage of some EVS disks in the instance exceeds 80%. As a result, new files cannot be created in corresponding partitions. |
|
guestos.filesystem.invalid_device |
Checking Devices in the fstab File |
A device configured in the fstab file under directory /etc/ on the current instance does not exist. As a result, the instance may fail to be started. |
|
guestos.filesystem.device_mount_failure |
Checking the Device Mounting Status in the fstab File |
The instance contains EVS disks that are not automatically mounted in fstab under /etc/. As a result, the instance may fail to be started. |
|
guestos.filesystem.invalid_format |
Checking the fstab File Format |
The configuration format of the fstab file is incorrect. As a result, the instance may fail to be started. |
|
guestos.network.firewall_status_check |
Checking the System Firewall Status |
The firewall (iptables setting) of the current instance is enabled. If the firewall is enabled on the server and rules for shielding external access are configured, remote access to the instance may fail. |
|
guestos.memory.oom_events |
Checking OS OOM |
The out-of-memory (OOM) issue occurred in the guest OS of the current instance. |
|
guestos.ssh.incorrect_file_permission |
Checking SSH Public or Private Key Access Permission |
Incorrect permissions on the public or private key file prevent SSH access to the instance. |
|
guestos.ssh.missing_critical_file |
Checking SSH Key Files |
If a key file or directory for the SSH service of the current instance is missing, the instance cannot be accessed through SSH. |
|
guestos.memory.high_total_usage |
Checking High Memory Usage |
The memory usage of an instance exceeds 80%. |
|
guestos.ssh.forbidden_root_login |
Checking SSH Login Using User root |
The SSH service of the current instance does not allow the root user to log in. As a result, the instance cannot be accessed using SSH as the root user. |
|
guestos.system.port_listenning |
Checking the Listening Status of Common Service Ports |
Port 22 is not being listened to. Log in to the instance, check whether the port service is normal, and rectify the fault as required. |
|
guestos.system.unreasonable_file_limits |
Checking Limits Settings |
Some configuration values in the system file /etc/security/limits.conf of the current instance are greater than the preset values. As a result, remote login to the instance may fail. |
|
guestos.memory.unreasonable_hugepage_config |
Checking Memory Huge Page Configurations |
The hugepage memory specified by the kernel parameter vm.nr_hugepages of the current instance is too large. As a result, remote login to the instance may fail. |
|
guestos.network.wrong_nat_config |
Checking the Kernel Parameters of the NAT Gateway Environment |
The kernel parameters related to NAT gateway access are incorrectly configured for the current instance. As a result, users cannot connect to the instance through SSH, and HTTP-based access to the instance is abnormal. Check and change the values of net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle and net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps in /etc/sysctl.conf. |
|
guestos.network.wrong_tcp_sack |
Checking tcp_sack Configuration |
tcp_sack is not enabled for the current instance, which may affect the network performance of the Linux instance. |
|
guestos.system.wrong_selinux_status |
Checking SELinux Status |
The SELinux service is enabled for the instance. As a result, an error is reported when you remotely connect to the instance using SSH. Disable the SELinux service temporarily or permanently based on service requirements. |
|
guestos.system.missing_critical_user |
Checking Settings of Key System Users |
The system account of the current instance does not exist. As a result, you may fail to log in to the instance. |
|
guestos.network.disabled_multi_queue |
Checking Whether NIC Multi-Queue Is Enabled |
If the NIC multi-queue feature is disabled, the network performance may deteriorate. Enable this function as required. |
|
guestos.system.critical_file_exists |
Checking the Existence of Key System Files |
Some key system files in the system directory of the instance are missing. As a result, the instance may fail to be logged in to. |
|
guestos.system.critical_service_exists |
Checking the Startup Status of Key System Processes |
Key system processes (such as the SSH process) of the instance are not running. As a result, the instance may fail to be accessed. |
|
guestos.system.critical_file_format_invalid |
Checking the Format of Key System Files |
The format of the file corresponding to the system account of the current instance is incorrect (not in UNIX format). As a result, the instance may fail to be logged in. |
|
guestos.network.nic_dropped |
Checking NIC Packet Loss |
There is packet loss on the NIC of the current instance. As a result, the latency of some service requests is high or some service requests fail. |
|
guestos.cpu.res_interrupts |
Checking High IPI Rescheduling Interruption Rate |
There are a large number of IPI rescheduling interrupts on the current instance, which may incur extra overhead and service performance deterioration. Checking the number of IPI rescheduling interrupts based on service requirements is recommended. |
|
guestos.cpu.tlb_interrupts |
Checking Excessive TLB Interrupts |
There are a large number of TLB interrupts on the current instance, which may incur extra overhead and service performance deterioration. Checking the number of TLB rescheduling interrupts based on service requirements is recommended. |
|
guestos.cpu.syscall_high_usage |
Checking High CPU Usage for the System Kernel Space |
The sys kernel space of the current instance occupies a large number of CPU resources. This is usually due to an excessive number of calls from an application, which may affect the CPU usage of the application. |
|
guestos.cpu.irq_not_balanced |
Imbalanced Inter-CPU Interrupt Usage |
The interrupt usage between CPU cores of the current instance is unbalanced. The interrupt usage is concentrated on one or more cores. As a result, the SI of a single core is high, and services may be affected by the single-core CPU bottleneck. Check it. |
|
guestos.storage.high_latency |
Checking High Storage Latency |
If the storage latency of the current instance disk is too high, service freezing and high response latency may occur. Check the disk specifications based on the service storage I/O requirements. |
|
guestos.network.too_much_close_wait_connections |
Excessive Connections in CLOSE_WAIT State |
There are too many connections in the CLOSE_WAIT state on the current instance, which may cause new request failures. You need to troubleshoot this issue. |
|
guestos.network.nf_conntrack_table_full |
Checking Conntrack Table Overflow |
Conntrack tables of the current instance overflow. As a result, new connections may be discarded, causing service request failures. |
|
guestos.network.too_much_new_connections |
Checking Excessive New Connections |
There are a large number of new connections on the current instance, which may increase the latency of new requests or cause new request failures. |
|
guestos.network.possible_ddos_attack |
Checking Suspected DDoS Attack |
The current instance may have DDoS attack risks. Check it. |
|
guestos.storage.io_bottleneck |
Checking That Storage I/O Reaches The Upper Limit Of Disk QoS |
The disk storage IOPS or bandwidth of the current instance exceeds the upper limit of the disk QoS, which may cause service freezing or failure. |
|
guestos.network.socket_listenning_queue_overflow |
Checking Socket Listening Queue Overflow |
The socket listening queue of the current instance overflows and packet loss occurs. As a result, new connections may fail to be established. |
|
guestos.network.udp_buffer_overflow |
Checking Packet Loss Caused by UDP Buffer Overflow |
Packet loss occurs due to buffer overflow caused by UDP burst traffic in the current instance. |
|
guestos.network.too_much_time_wait_connections |
Checking Excessive Connections in the TIME_WAIT State |
Too many connections in the TIME_WAIT state may cause new request failures and service unavailability. |
|
guestos.network.too_much_fin_wait2_connections |
Checking Excessive Connections in FIN_WAIT2 State |
Too many connections in the FIN_WAIT2 state may occupy a large number of local ports. |
|
guestos.network.too_much_established_connections |
Checking Excessive Connections in ESTABLISHED State |
Too many connections in the ESTABLISHED state of the current instance occupy a large number of local ports and memory. Check whether the connections are normal based on services. |
|
guestos.system.file_descriptor_not_enough |
Checking Too Few File Handles |
Too few file handles are configured for the current instance. When the number of file handles used by services reaches the upper limit, the system becomes unavailable. |
|
guestos.network.local_port_range_too_small |
Checking Too Small Local Port Range |
The local port range configured for the current instance is too small. When a large number of concurrent requests are sent to other services, the error message "Cannot assign requested address" may be displayed. As a result, new connections fail to be created. |
|
guestos.network.qdisc_queue_overflow |
Checking Packet Loss Due To QDisc Sending Queue Overflow |
QDisc queue packet loss data. |
|
guestos.memory.swap_check |
Checking Service swap |
If swap occurs in the current instance service, the service performance deteriorates, and services with high performance requirements are greatly affected. |
|
guestos.memory.transparent_hugepage_check |
Checking Transparent Huge Page Configuration |
Transparent huge page is enabled for the current instance. Determine whether to enable transparent huge page based on service performance. |
|
guestos.memory.buffer_cache_too_high |
Checking High Memory Buffer/Cache Usage |
The memory buffer/cache usage of the current instance is high. As a result, the free memory may be insufficient. When malloc is performed at the application layer, cache reclamation is frequently triggered, causing service performance deterioration. |
|
guestos.memory.process_used_too_high |
Checking High Memory Usage of Service Processes |
The memory usage of the current instance service process is high. The available memory may be insufficient. As a result, the service performance deteriorates. |
|
guestos.network.traffic_exceed |
Checking Network Traffic Over-Upper-Limit |
The network traffic of the current instance exceeds the upper limit of the current network QoS, which may affect service performance. |
|
guestos.network.socket_tcp_buffer_overflow |
Checking TCP Buffer Overflow |
The number of pages used by the socket of the current instance is close to the upper limit of the TCP buffer. As a result, packet loss may occur due to TCP buffer overflow. |
|
guestos.network.socket_udp_buffer_overflow |
Checking UDP Buffer Overflow |
The number of pages used by the socket of the current instance is close to the upper limit of the UDP buffer. As a result, packet loss may occur due to UDP buffer overflow. |
|
guestos.gpu.gpu_status |
GPU Status |
After the "nvidia-smi" command is executed, the GPU status returned becomes abnormal. |
|
guestos.gpu.gpu_card_lost |
GPU Card Drop |
GPUs are disconnected. |
|
guestos.gpu.core_temp_too_high |
GPU Core Overtemperature |
GPU core temperature is too high. |
|
guestos.gpu.mem_temp_too_high |
GPU Memory Overtemperature |
GPU memory temperature is too high. |
|
guestos.gpu.fan_error |
Abnormal GPU Fan |
The GPU fan is abnormal. There is an error. |
|
guestos.gpu.power_error |
Abnormal GPU Power Consumption |
The GPU power consumption is abnormal. There is an error. |
|
guestos.gpu.memory_usage_too_high |
High GPU Memory Usage |
Excessive use of GPU memory may cause program crashes. |
|
guestos.gpu.gpu_usage_too_high |
High GPU Computing Power Usage |
GPU computing power usage is too high, which may result in insufficient computing power. |
|
guestos.gpu.pcie_link_error |
GPU Bandwidth Exception |
The GPU bandwidth is abnormal. There may be a hardware error. |
|
guestos.gpu.pstate_low |
Poor GPU Performance |
GPU performance falls short, failing to unlock its full potential for optimal use. |
|
guestos.gpu.ecc_mode |
Disabled ECC Mode |
ECC mode is disabled, and ECC errors cannot be identified. |
|
guestos.gpu.volatile_ecc_error |
Too Many Volatile ECC Errors for GPU |
The number of volatile ECC errors for the target GPU exceeds threshold 4. |
|
guestos.gpu.aggregate_ecc_error |
Too Many Aggregate ECC Errors for GPU |
The number of aggregate ECC errors for the target GPU exceeds threshold 4. |
|
guestos.gpu.retired_pages_count_error |
DRAM ECC Page Retirement Error |
The number of retired pages for DRAM ECC exceeds the threshold 60. |
|
guestos.gpu.retired_pages_pending_error |
Pending Page Retirement for DRAM ECC |
Pending page retirement for GPU DRAM ECC. |
|
guestos.gpu.xid_error |
GPU XID Error |
The GPU has a XID error. |
|
guestos.gpu.kernel_version_error |
Inconsistent GPU Kernel Versions |
The version of the installed kernel of the GPU driver is inconsistent with the current kernel version. |
|
guestos.gpu.nouveau_error |
nouveau Driver Not-disabled |
The nouveau driver is not disabled. |
|
guestos.gpu.cuda_tips |
Non-installation of CUDA |
The CUDA is not installed. |
|
guestos.gpu.fabricmanager_error |
Non-installation of fabricmanager |
The fabricmanager is not installed. |
|
guestos.gpu.sram_ecc_too_many_error |
Too many SRAM ECC Errors |
There are SRAM ECC errors. |
|
guestos.gpu.remapped_dram_ecc_error |
Row Remapping Fails Due to Excessive DRAM ECC |
DRAM ECC errors lead to remapping failures. |
|
guestos.gpu.dram_ecc_pending_error |
Pending Row Remapping Error for DRAM ECC |
There is a pending row remapping error for DRAM ECC. |
|
guestos.gpu.volatile_dram_correctable_too_many_error |
Too Many Correctable ECC Errors for DRAM |
The number of correctable ECC errors for DRAM is greater than 1,000. |
|
guestos.gpu.volatile_dram_uncorrectable_too_many_error |
Too Many Uncorrectable ECC Errors for DRAM |
The number of uncorrectable ECC errors for DRAM is greater than 60. |
|
guestos.system.missing_initramfs |
initramfs File Check |
The instance does not have the initramfs file required for system startup. As a result, the instance could not start and the system cannot be accessed. |
|
guestos.system.missing_initramfs_module |
initramfs File Key Driver Configuration Check |
The instance does not have the virtio_scsi configuration, which is required for starting the QingTian instance. With some flavors, this can result in startup errors. |
|
guestos.system.missing_grubcfg |
GRUB Configuration File Check |
The GRUB configuration file required for system startup is missing. |
|
guestos.system.missing_vmlinuz |
vmlinuz File Check |
The vmlinuz configuration file, which is needed for system startup, could not be found. |
|
guestos.system.conflict_ntp_service |
Time Synchronization Service Check |
The instance runs both the chronyd and ntpd services. The two services conflict in some scenarios, and the clock stability of the instance node cannot be ensured. |
|
guestos.system.ntp_service_status_abnormal |
Status Check for the Time Synchronization Service |
The time synchronization service of the instance is not running properly. It is not in the running state. |
|
guestos.system.ntp_service_enablestatus_abnormal |
Automatic Startup Configuration Check for the Time Synchronization Service |
The automatic startup status of the time synchronization service of the instance is abnormal and is not enabled. |
|
guestos.filesystem.duplicate_fs |
Check for Duplicate File Systems in the fstab File |
The fstab file of the instance contains duplicate file system mounting configurations. |
|
guestos.filesystem.fstab_uuid_status |
fstab File UUID Check |
UUID is not used in the fstab file of the instance. |
|
guestos.filesystem.fstab_duplicate_mount |
Check for Duplicate Mount Points in the fstab File |
There are duplicate mount points in the fstab file of the instance. |
|
guestos.filesystem.mount_path_mismatch |
fstab Consistency Check |
Mounting mapping between file systems and directories in the fstab file is inconsistent with the actual mounting. |
|
guestos.filesystem.fstype_mismatch |
Check for the Consistency Between the fstype of the fstab File and the fstype of the Real-world File System |
The fstype in the fstab file is inconsistent with the actual file system fstype. |
|
guestos.filesystem.blkid_duplicate_uuid |
The Same UUID for Multiple File Systems of an Instance |
There are multiple file systems that have the same UUID in the instance. |
|
guestos.filesystem.ext4_not_clean |
Abnormal ext4 File System |
There is an abnormal ext4 file system in the instance. |
|
guestos.network.static_ip_not_work |
Invalid Static IP Address of Instance NIC |
The static IP address configuration of the instance NIC does not take effect. |
|
guestos.network.dhclient_not_work |
Abnormal Resident Process of the DHCP Client |
The resident process of the DHCP client is abnormal. |
|
guestos.network.network_service_abnormal |
Instance Network Service Exception |
The network service of the instance is abnormal. |
|
guestos.system.serial_port_log_not_configured |
Serial Port Log Output Check |
Check the serial port log output. |
|
guestos.system.page_allocation_failure |
Memory Page Allocation Failure |
Failed to allocate the memory page for printing instance logs. |
|
guestos.system.fork_failed |
Log Printing Process Creation Failure |
Threads cannot be created for an instance. |
|
guestos.system.too_many_open_files |
Failed to Open a New File During Instance Log Printing |
The instance cannot open new file handles. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





