Monitoring a Real-Time Job
You can view information such as the running status, start time, and end time of the real-time processing job on the Real-Time Job Monitoring page, and start and stop the real-time processing job.
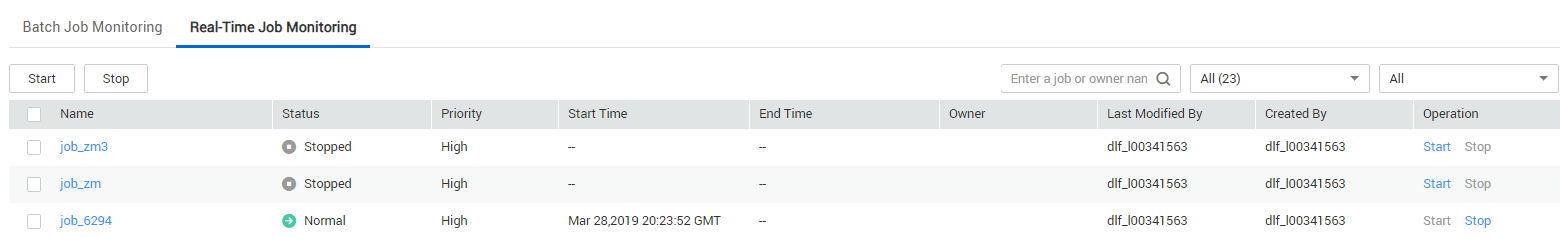
- Batch processing jobs: Select jobs and click Start/Stop.
- Viewing node information of the job: Click a job name. On the page that is displayed, view the node connection relationship and monitoring information.
- Viewing status of the latest instances: Click the drop-down arrow next to the name of a job to view the latest instance status.
Real-Time Jobs: Configuring Event-based Scheduling on a Node
If event-driven scheduling is configured for a node in a real-time job, right-click the node and choose Configure Scheduling from the shortcut menu to view and modify the scheduling information about the node.
- Log in to the DLF console.
- In the navigation tree of the DLF console, choose .
- On the Real-Time Job Monitoring tab page, click a job name.
- Click the node where event-driven scheduling is configured and choose Configure Scheduling. Set the parameters described in Table 1.
When you click View Startup Log, you can view the job startup log information.Figure 2 Configuring scheduling
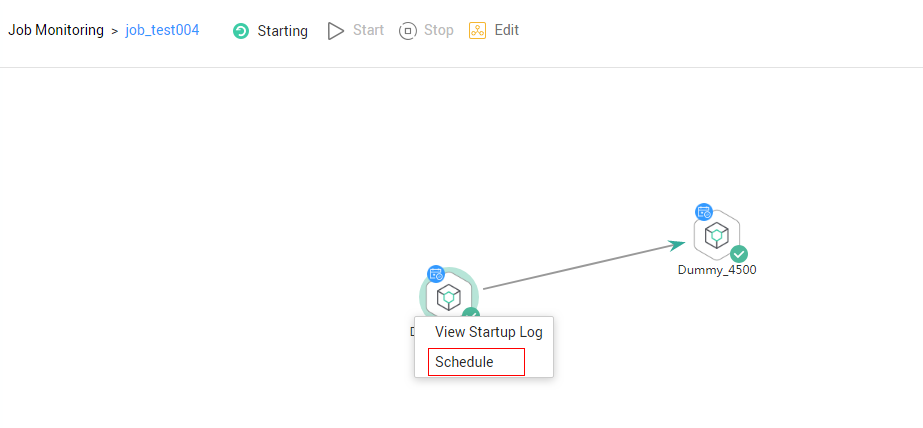
- When Triggering Event Type of Event-Driven Scheduling is set to DIS, configure a DIS scheduling policy as follows:
Figure 3 Configuring a DIS scheduling policy
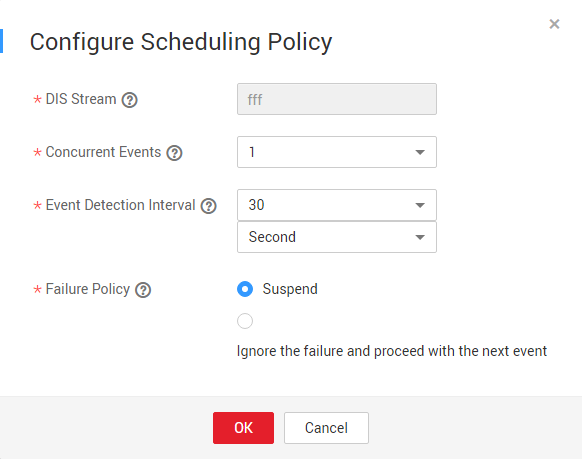
Table 1 Policy parameters Parameter
Description
DIS Stream
Name of the DIS stream. When a new message is sent to the specified DIS stream, Data Development transfers the new message to the job to trigger the job running.
Concurrent Events
Number of jobs that can be concurrently processed. The maximum number of concurrent events is 10.
Event Detection Interval
Interval at which the system detects the DIS stream or OBS path for new messages. The unit of the interval can be set to second or minute.
Failure Policy
Select a policy to be performed after scheduling fails.
- Stop scheduling
- Ignore failure and proceed
- When Triggering Event Type of Event-Driven Scheduling is set to DIS, configure a DIS scheduling policy as follows:
Rerunning a Job After the Job Is Paused
If event-based scheduling is configured for a node in a real-time job, you can disable the node and then restore it. When the node is restored, you can select where you can resume running.
- Log in to the DLF console.
- In the navigation tree of the DLF console, choose .
- On the Real-Time Job Monitoring tab page, click a job name.
- On the job monitoring page, right-click a node with event-driven scheduling configured and choose Disable from the shortcut menu.
- Right-click the node and choose Resume from the shortcut menu. The Resume Node Running dialog box is displayed, as shown in Table 2.
Figure 4 Resuming node running
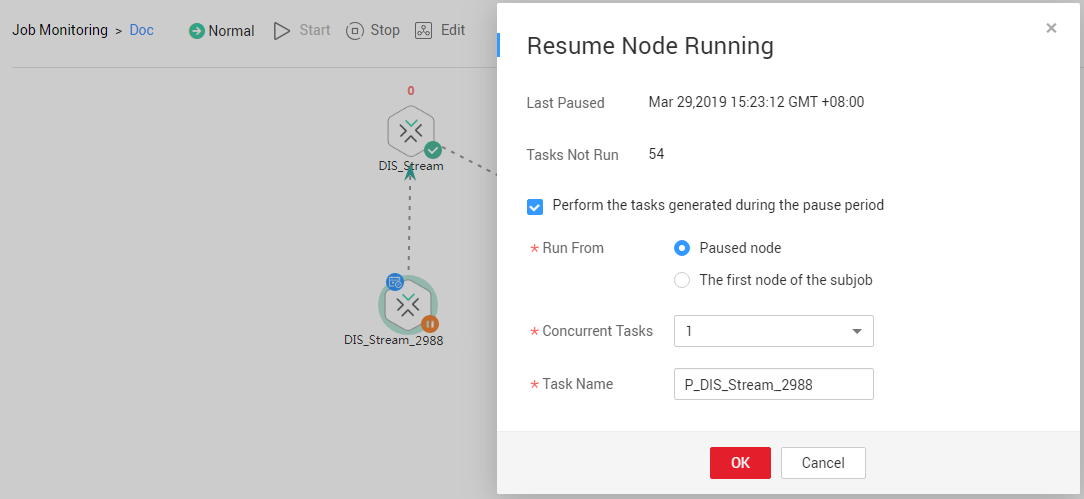
Table 2 Resumption parameters Parameter
Description
Last Paused
Start time when a node is suspended.
Tasks Not Run
Number of tasks that are not running during node suspension.
Parameters for performing the tasks generated during the pause period
Run From
Position from which running restarts.
- Paused node
- The first node of the subjob
Concurrent Tasks
Number of tasks to be processed.
Task Name
Task to be resumed.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





