Creating a Secret
When you create a secret on CSMS for secret hosting, the secret value will be stored in the original secret version, which is marked as SYSCURRENT.
- Username and password: A username is the identity of a user, and a password is the key secret value for user identity authentication.
- Digital certificate: The public key and identity, which are the secret values of a certificate, are used to verify the identity of a user or device.
- Key pair: The private key, which is the secret value, is used for signature and decryption.
- Token: A token is a temporary secret value used for identity authentication.
- Biometric recognition information: Biometric feature data, such as fingerprint, facial recognition, and iris recognition, is the secret value.
- One-time password (OTP): An OTP generated via SMS, email, or a certain application is the secret value.
Constraints
- At most 500 secrets can be created on CSMS.
- A secret can be no larger than 64 KB.
- By default, the default key csms/default created by CSMS is used as the encryption key of the current secret. You can also create a user-defined symmetric key and use a user-defined encryption key on the KMS console.
- RDS secrets support MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLServer, MariaDB, and TaurusDB engines.
- TaurusDB is supported for TaurusDB secrets.
Creating a Secret
CSMS allows you to create a shared secret or a rotated secret as required.
- Log in to the DEW console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region or project.
in the upper left corner and select a region or project. - In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
- Click Create Secret. Configure parameters in the Create Secret dialog box, as shown in Figure 1. For details about the parameters, see Table 1.
Table 1 Secret parameters Parameter
Description
Type
Secret type. The default value is Shared secret. You can select Shared secret or Rotated secret. For details, see Overview.
Secret Name
Secret name
NOTE:Only letters, digits, periods (.), hyphens (-), and underscores (_) are allowed.
Enterprise Project
This parameter is provided for enterprise users. If you are an enterprise user and have created an enterprise project, select the required enterprise project from the drop-down list. The default project is default.
NOTE:If you have not enabled enterprise management, this parameter will not be displayed.
Secret Value
Secret key/value pair or the plaintext secret to be encrypted
Secret value, the detailed content of a secret, is used to verify user identity or authorization during authentication. It can be of various forms, depending on the used authentication mechanism. Typical secret values include:- Username and password: A username is the identity of a user, and a password is the key secret value for user identity authentication.
- Digital certificate: The public key and identity, which are the secret values of a certificate, are used to verify the identity of a user or device.
- Key pair: The private key, which is the secret value, is used for signature and decryption.
- Token: A token is a temporary secret value used for identity authentication.
- Biometric recognition information: Biometric feature data, such as fingerprint, facial recognition, and iris recognition, is the secret value.
- One-time password (OTP): An OTP generated via SMS, email, or a certain application is the secret value.
KMS Encryption Key
The following modes are supported:- Select from list: Select this if you want to use the key used or shared by the current account. Select the default key csms/default or a custom key created on KMS.
- Enter: Enter the ID of the authorized key. Enter an encryption key if an authorized key is used. Only symmetric algorithm key IDs are supported. Do not enter an asymmetric key ID.
NOTE:- CSMS encrypts secret values using the encryption key provided by KMS. When you use the KMS encryption function, KMS creates a default key csms/default for you to use.
- For details about how to create a custom key on KMS, see Creating a Key.
- After a grant is created, you can switch to the manual input mode, and enter the key ID to use the granted key for encryption. For details, see Creating a Grant for a Custom Key.
Advanced settings
- Associated events
Select an associated event for the secret. You can check information such as secret rotation and version expiration.
- Description
Description of a secret
- Tag
You can add tags to a secret as you need.
NOTE:You can add at most 20 tags to a secret.
- Click Next. You cannot select a rotation period for common secrets. Go to the next step.
- Click Next and confirm the creation information.
- Click OK. In the secret list, you can view the created secrets. The default status of a secret is Enabled.
- Log in to the DEW console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region or project.
in the upper left corner and select a region or project. - In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
- Click Create Secret and set Type to Rotated secret.
Figure 2 Creating a rotated secret
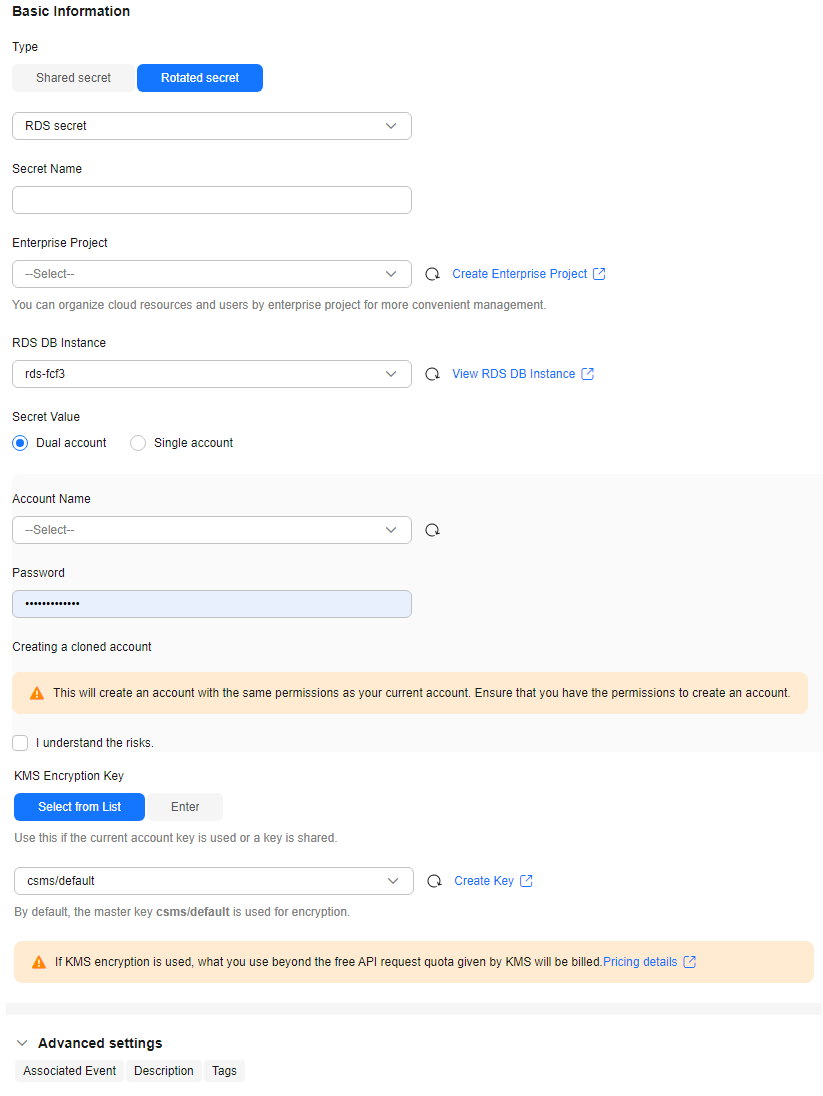
- On the displayed Create Secret page, set the parameters. For details about the parameters, see Table 2.
Table 2 Parameters for rotated secrets Parameter
Description
Type
Type of the secret to be rotated. The following secrets are supported:
- RDS secret
- TaurusDB secret
- APIG secret
- GaussDB secret
Secret Name
Secret name
Enterprise Project
This parameter is provided for enterprise users. If you are an enterprise user and have created an enterprise project, select the required enterprise project from the drop-down list. The default project is default.
NOTE:If you have not enabled enterprise management, this parameter will not be displayed.
Database
This parameter is mandatory if Type is set to RDS rotated secret.
RDS secrets support MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLServer, MariaDB, and TaurusDB databases.
RDS DB Instance
Select the RDS instance corresponding to the target database type.
TaurusDB Instance
If Type is set to , select a TaurusDB instance as needed.
Click View TaurusDB Instances. You can buy a TaurusDB instance on the displayed console.
GaussDB Instance
If Type is set to , select a GaussDB instance as needed.
Click View GaussDB instances. You can buy a GaussDB instance on the displayed console.
APIG Instance
If Type is set to , select an APIG instance as needed.
After selecting the target instance, you need to set App and APIG Secret Type.
App
This parameter is mandatory if Type is set to . You can click View App to go to the APIG console and view the created APIG secret.
APIG Secret Type
If Type is set to , select an APIG secret type as needed. The following secret types are supported:
- Secret: After an app is selected, an app key is automatically generated.
- AppCode: If this option is selected, you need to select an existing AppCode from the drop-down list. You can also click View AppCode to add an AppCode on the displayed console.
Secret Value
Account name and password to be encrypted.- If Single account is selected, you need to enter an available database account.
- If Dual account is selected, after you enter an available database account, a cloned account with the same permissions will be created. Select I understand the risks.
For details, see Rotation Policy.
KMS Encryption Key
The following modes are supported:- Select from list: Select this if you want to use the key used or shared by the current account. Select the default key csms/default or a custom key created on KMS.
- Enter: Enter the ID of the authorized key. Enter an encryption key if an authorized key is used. Only symmetric algorithm key IDs are supported. Do not enter an asymmetric key ID.
NOTE:- CSMS encrypts secret values using the encryption key provided by KMS. When you use the KMS encryption function, KMS creates a default key csms/default for you to use.
- For details about how to create a custom key on KMS, see Creating a Key.
- After a grant is created, you can switch to the manual input mode, and enter the key ID to use the granted key for encryption. For details, see Creating a Grant for a Custom Key.
Advanced settings
- Associated events
Select an associated event for the secret. You can check information such as secret rotation and version expiration.
- Description
Description of a secret
- Tag
You can add tags to a secret as you need.
NOTE:You can add at most 20 tags to a secret.
- Click Next. Enable Automatic Rotation, set the rotation period and function, select I understand the risks, and click Next.
You can select an existing period or set a custom one.Figure 3 Enabling automatic rotation

After automatic rotation is enabled, if no agency is created for the current user, a dialog box is displayed, showing the permission name and items. Click OK to complete the authorization.
Table 3 Rotation setting parameters Parameter
Description
Example
Automatic Rotation
Choose whether to enable automatic secret rotation.
Enabled
Set Rotation Period
Select an existing period or set a custom one.
6 hours
Rotation function
Create or use an existing rotation function in FunctionGraph to rotate secret values.
CloudSecretManager-kl15
- Click Next. Confirm the secret information and click OK.
Viewing Secret Details
This section describes how to check secret names, statuses, and creation time on the CSMS console. The secret status can be Enabled or Pending deletion.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
- Check the secret list. For more information, see Table 4.
Figure 4 Secret list
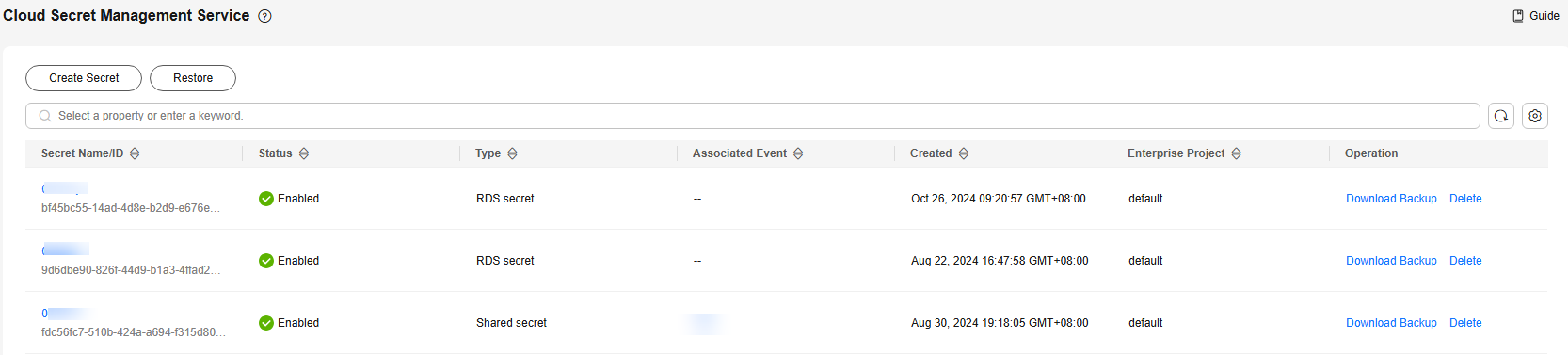
Table 4 Secret list parameters Parameter
Description
Secret Name/ID
Secret name and ID
Status
Status of a secret. The value can be Enabled or Pending deletion.
Type
Secret type, including shared secret, RDS DB secret, and TaurusDB secret.
Associated events
Bound event notification when the secret was created.
Creation Time
Time when the secret is created
Enterprise Project
Enterprise project that the secret is to be bound to
- Click a secret to view its details, as shown in Figure 5.
- You can click Edit to modify the encryption key and description of a secret.
- You can click Refresh to refresh secret information.
Downloading a Secret Backup
To download a secret to a local PC for backup, perform the following steps:
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
- Locate the target secret in the list and click Download Backup in the Operation column.
The secret file will be downloaded to the local host and is named Secret name.secretbackup.
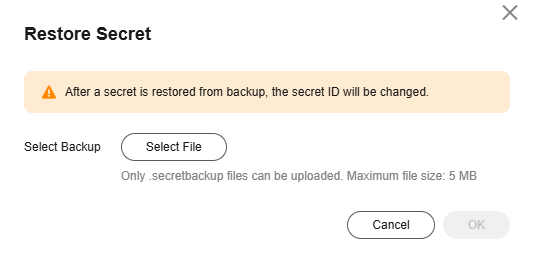
Restoring a Secret from a Backup
DEW allows you to restore a secret from backup. After a secret is restored from backup, the secret ID will be changed.
Only secret backup files smaller than 5 MB can be uploaded.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
- Click Restore Secret, select a backup file, and click OK.
Figure 6 Restoring a secret backup
Deleting a Secret
Before deleting a secret, ensure that it is not in use and will not be used.
- A secret will not be deleted until its scheduled deletion period expires. You can set the period to a value within the range 7 to 30 days. Before the specified deletion date, you can cancel the deletion if you want to use the secret. If the scheduled deletion period of a secret expires, the secret will be deleted and cannot be restored.
- For details about the billing information about a secret to be deleted, see Are Credentials Scheduled to Be Deleted Billed?
- If you delete a secret immediately, you can restore it using the secret backup that you have downloaded in advance. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
- Locate the target secret and click Delete.
- On the displayed page, select a deletion mode. If you want to delete the secret in a specific time, set Schedule deletion.
Figure 7 Setting schedule deletion
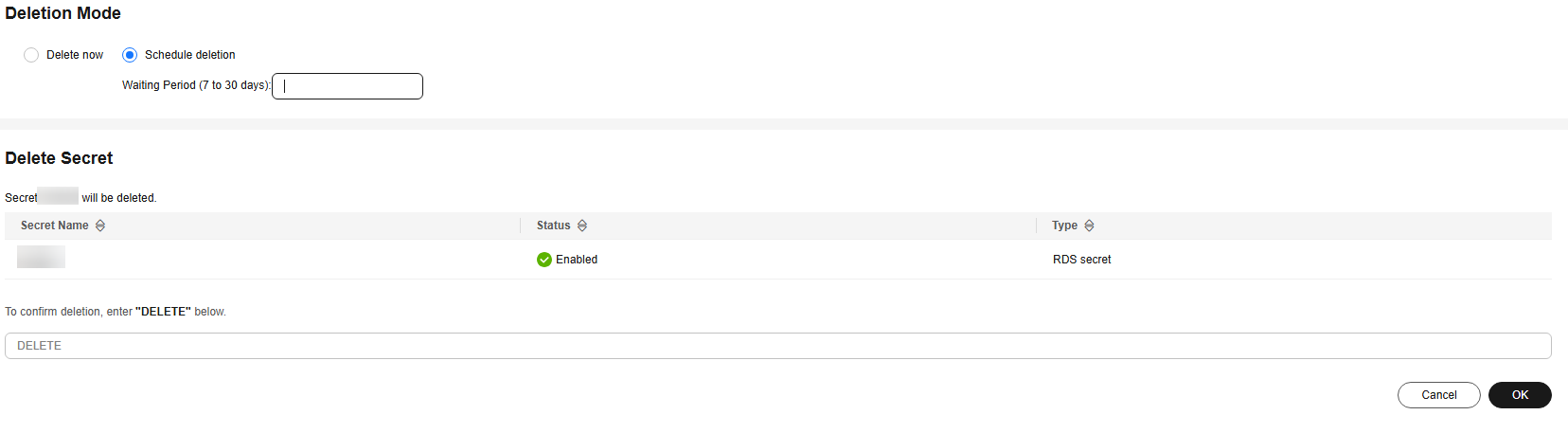
- Enter DELETE in the confirmation dialog box if deletion verification is disabled and click OK.
If you have enabled deletion verification, select a verification mode, click Get Code, enter the code, and click OK.
To disable operation protection, go to the Security Settings page, click Disable next to Operation Protection in the Critical Operations tab, or click Disable Operation Protection on the deletion page.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot







