Access Control Policy Overview
CFW allows all traffic by default. If no access control policies are configured, all the communication between internal servers and the Internet will be allowed. Unauthorized access or the lateral threat movement will go unchecked. You can configure access control policies in Cloud Firewall to allow or block specific traffic and implement multi-dimensional protection.
Access Control Policy Types
Access control policies include protection rules, traffic filtering configuration, the blacklist, and the whitelist. Table 1 describes their differences. If traffic hits a policy, the action specified in the policy will be performed. For details about the priority of each configuration, see Priority of Access Control Policies.
|
- |
Protection Rule |
Blacklist |
Whitelist |
Traffic Filtering |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Protected object |
|
|
|
IP address |
|
Network type |
|
|
|
|
|
Action |
|
Traffic is blocked directly. |
Traffic is allowed by CFW and not checked by other functions. |
Traffic is blocked directly. |
|
Scenario and characteristics |
Identify specified traffic based on its characteristics. It is suitable for fine-grained control of specific traffic. For example, you can specify protocol types, port numbers, and applications in a rule. |
Quickly block identified security threats. It is suitable for handling known malicious traffic. |
Quickly allow trusted traffic. It is suitable for trusted IP addresses. |
Quickly block abnormal traffic based on the configured characteristics. It is suitable for quickly blocking a large number of IP addresses. |
|
Protection log |
||||
|
Configuration method |
Configuring Protection Rules to Block or Allow Internet Border Traffic |
Adding Blacklist or Whitelist Items to Block or Allow Traffic |
Adding Blacklist or Whitelist Items to Block or Allow Traffic |
|
|
CAUTION:
Traffic filtering is a new function. If you cannot access the page on the console, please submit a service ticket to upgrade the firewall engine. |
||||
Priority of Access Control Policies
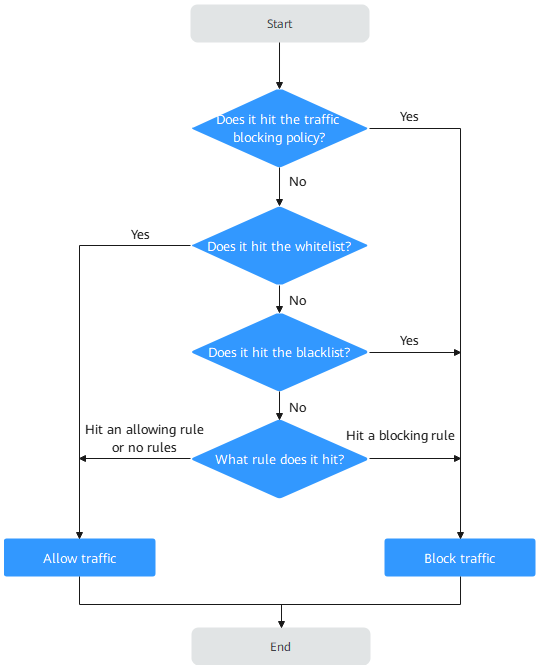
For details about the protection sequence of all CFW policies, see What Is the Protection Sequence of CFW?
Specification Limitations
To enable VPC border protection and NAT protection, use the CFW professional edition and enable VPC firewall protection.
Precautions for Configuring a Blocking Policy
The precautions for configuring a protection rule or a blacklist item for blocking IP addresses are as follows:
- You are advised to preferentially configure specific IP addresses (for example, 192.168.10.5) to reduce network segment configurations and avoid improper blocking.
- Exercise caution when configuring protection rules to block reverse proxy IP addresses, such as the CDN, Advanced Anti-DDoS, and WAF back-to-source IP addresses. You are advised to configure protection rules or whitelist to permit reverse proxy IP addresses.
- Blocking forward proxy IP addresses (such as company egress IP addresses) can have a large impact. Exercise caution when configuring protection rules to block forward proxy IP addresses.
- When configuring region protection, take possible EIP changes into consideration.
Elements in a Protection Rule
Protection rules can identify and match different traffic elements to allow or block related traffic.
Example configuration:
|
Parameter |
Input |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Source/Destination |
0.0.0.0/0 |
All IP addresses |
|
Domain name |
www.example.com |
Domain name www.example.com |
|
*.example.com |
All domain names ending with example.com, for example, test.example.com |
|
|
Service - Source port or destination port |
1-65535 |
All ports |
|
80-443 |
All ports in the range 80 to 443 |
|
|
Ports 80 and 443 |
References
- For details about how to add a blacklist or whitelist for traffic protection, see Adding Blacklist or Whitelist Items to Block or Allow Traffic. For details about how to add a protection rule for traffic protection, see:
- For details about how to protect the traffic from the Internet to cloud assets (EIPs), see Accessing from the Internet to Assets on the Cloud (Inbound).
- For details about how to protect the traffic from cloud assets (EIPs) to the Internet, see Accessing from the Cloud Assets to the Internet (Outbound).
- For details about how to protect the access traffic between VPCs, or between a VPC and an IDC, see Configuring Protection Rules to Block or Allow VPC Border Traffic.
- For details about how to protect the traffic of private network assets at the Internet border, see Configuring Protection Rules to Block or Allow NAT Gateway Border Traffic.
- For details about how to add protection policies in batches, see Importing and Exporting Protection Policies.
- Follow-up operations after adding a policy:
- Policy hits: For details about the protection overview, see Viewing Protection Information Using the Policy Assistant. For details about logs, see Access Control Logs.
- For details about the traffic trend and statistics, see Traffic Analysis. For details about traffic records, see Traffic Logs.
- If your traffic is incorrectly blocked by a protection policy, troubleshoot the problem by referring to What Can I Do If Services Cannot Be Accessed After a Policy Is Configured on CFW?
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





