Cloud Project Management
To ensure smooth and effective cloud migration, you need to run it as a standard project, and define clear objectives, scope, progress, costs, and quality for the project. Cloud migration is a long-term, complex, systematic project that impacting organizations, processes, and technology. Using effective project management and plans ensures better efficiency, quality, and success in achieving cloud migration objectives.
The cloud migration project management includes feasibility assessment, project preparation, project initiation, project process management, service rollout management, and service assurance. Based on Huawei Cloud project management and delivery experience, the following method is used to manage and control the entire cloud migration of an enterprise. The following describes each part of the cloud migration management process.
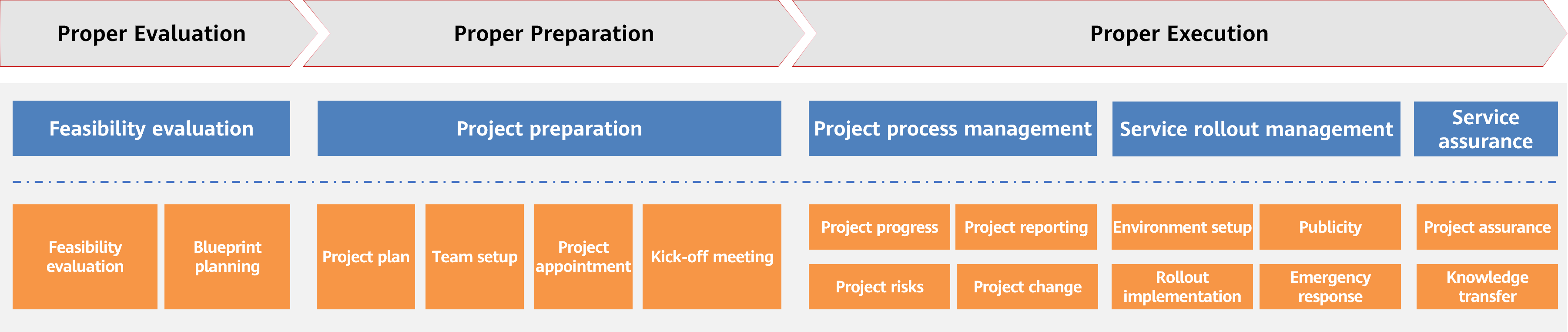
Feasibility Evaluation
Before starting cloud migration, company decision-makers may want to know how cloud migration can help their organization and whether it will benefit their short- or long-term plans. To obtain the information, the decision-makers usually ask the IT department to evaluate the value and benefits of cloud migration. Yet, the IT team typically relies on conventional IT practices and on-premises data center technologies, with limited knowledge or experience in cloud solutions. In this case, cloud migration experts are needed to assist the IT team in assessing the cloud value and benefits. This phase is called feasibility evaluation and blueprint planning phase. In this phase, cloud migration experts take the lead and the IT department assists them in evaluating the current services, organizations, operations, platforms, security, and O&M. Based on the evaluation conclusion and gap analysis, they estimate the value and benefits that will be brought by cloud migration, and design the post-migration overall blueprint. By doing all these evaluations, the company decision-makers will have a clear view of how cloud migration benefits their short- and long-term business goals, and to what extent the cloud platform will improve service continuity, agility, and innovation capabilities. This will help the decision-makers make scientific and reasonable decisions faster.
Project Preparation
Once the decision-makers approve the cloud migration, the project moves into its preparation stage. Project preparation defines the project objective, scope, plan, management mechanism, and acceptance criteria, and sets up a project team. In this phase, define the cloud migration's scope and goals with the customer. Set up a joint project team based on the impacted organizational areas. Also, coordinate with relevant organizations early about the project schedules, responsibilities, roles and involvement stages, and key tasks. Prepare the project plan before the kick-off meeting. Confirm the schedule, engaged personnel roles, and resources with relevant departments like the service department. The project management system ensures smooth operations. It covers regular meetings, risk control, changes, and reporting processes. The system helps projects run smoothly even in challenging situations. Clarify the project acceptance plan early by defining acceptance cases, metrics, and criteria based on project goals and service needs. This ensures the service system's functions and performance meet requirements after migration to the cloud. The service department and users should agree on the core processes and key metrics beforehand, with the service department providing the final acceptance metrics. Every project relies on people to push forward. Set up the CCoE team during the project preparation phase. Refer to CCoE for detailed steps on preparing and organizing this team.
After the project preparations are done, a formal project kick-off meeting must be held. The kick-off meeting officially starts the cloud migration project by setting clear objectives, plans, organizations, appointments, supervision, and evaluation criteria. It ensures team members follow their responsibilities and the project plan to meet its objectives. All CCoE members and the cloud service provider's project team need to attend the kick-off meeting.
An important and key part of the kick-off meeting is to assign roles and responsibilities and grant necessary permissions, and allocate KPIs to each member. It makes sure tasks for team members are proper, clear, and measurable, and maintains staff stability and increases their motivation to achieve objectives.
In addition to assign roles and responsibilities and grant necessary permissions, the project reporting and supervision mechanism must be clarified at the kick-off meeting. A project has multiple implementation phases. Can the result of each phase meet the expectation? Are there any bottlenecks and problems? Does the project team have the resources and capabilities to handle these problems? These are the problems that may be faced by the project team during the execution. Solving these problems quickly and effectively relies on the team's ability to understand the problems and manage resources. Yet, the team alone cannot resolve every problem. In this case, regular meetings and reporting to senior management are essential. In project delivery, agile project management is recommended. This includes daily stand-up meetings and weekly meetings to spot issues early, address them promptly, and reduce delays. Daily stand-up meetings and weekly meetings quickly raise project problems to decision-makers, who then allocate resources promptly to resolve these problems. This process forms the quality supervision mechanism described earlier. The system gathers top-level company expertise to guarantee successful projects, ensuring effective and quality outcomes.
In addition to the functions mentioned above, the kick-off meeting also sets up the daily operation management mechanism (daily and weekly reporting, issue escalation, etc.), risk change mechanism (personnel change, timeline change, environment change, etc.), and cross-team division and cooperation mechanism. You can manage these using standard project management practices.
Project Process Management
This phase includes project progress management, reporting management, risk management, and change management. We have mentioned the key steps of progress management and reporting management. For example, agile management (daily stand-up meetings and weekly meetings) can be used to help keep goals aligned and track the project schedule effectively. Regular updates to senior management enable swift monitoring on progress and risks, ensuring quick resolution of issues and obstacles. Cloud migration projects often face several challenges, including schedule risks, personnel change risks, technical feasibility risks, operation risks, and security risks. The following describes risk management (including change management) and agile management methods.
Cloud migration projects often face delays caused by unexpected issues like new service releases, critical database failures, or virus attacks. To avoid these, the project team must carefully assess potential risks at each phase, plan a proper schedule, and prepare backup plans for some extreme risks to finish the project on time.
Personnel changes often pose risks during a cloud migration. It is necessary to back up necessary roles before the project starts. Key roles held by one person require careful change management. If a company has only one database administrator (DBA), the project manager should create a backup plan before the project starts. In specific scenarios, personnel can be backed up across departments or personnel be reserved in advance. This issue affects both cloud migration projects and the long-term sustainability of core business operations.
The technical risks are manageable. The project team can test feasibility using POC verification. This checks if the functions support current services and if performance metrics like speed, latency, and throughput meet service running needs. In addition, for technical risks during migration, the project team should conduct migration and cutover drills to identify potential risks and issues. They can then create a runbook to address and prevent these risks effectively.
Cloud migration projects face different operating risks compared to traditional IT projects. Traditional IT projects rely on hardware platforms, needing one operator with several supervisors to achieve desired outcomes. Cloud migration operations rely on networks, where services and platforms are highly integrated and a single mistake can impact many components and services. To reduce human errors, automate cloud operations during service system transitions and rollouts. In short, use tools for automation when available, choose scripts only if no suitable tools are available, and avoid manual operations whenever possible.
Cloud migrations demand strict security measures. Teams must follow the "no vulnerable systems to the cloud" rule by thoroughly checking and scanning systems beforehand. This includes reviewing hardware, software, middleware, application status, logs, events, alarms, and using security tools to confirm the system runs smoothly and has no risks.
Cloud migration projects avoid the complexities and lengthy timelines tied to integrating multiple hardware vendors and software providers seen in traditional IT projects. Yet, cloud migrations feature broad involvement, high platform integration, making issue resolution challenging. This leads to potential centralized bottlenecks and risks in managing these projects. Even one missing feature can stall the whole project timeline. Traditional waterfall project management struggles with cloud migration projects, making agile project management more suitable.
The preceding chapters have briefly described the methods for handling project problems, such as daily stand-up meetings and weekly meetings, to quickly review, streamline, and remove project bottlenecks. Fundamentally, these methods are part of agile project management. Agile project management works backward through stages. It sets clear goals for each phase, reviews ongoing progress, identifies challenges, and finds quick solutions aligned with those goals. A cloud migration project manager should clearly know the goals for each phase and stay aligned with those goals. To achieve the goals, they should identify the bottlenecks and find solutions as early as possible.
Agile project management needs to be implemented based on agile management tools. Combining these tools with agile processes creates efficient, fast-closing loops for managing tasks effectively. Common agile management tools include Jira. The cloud native project management tool CodeArts Req provided by Huawei Cloud is also recommended. CodeArts Req integrates with other CodeArts tools and cloud native tool chain DevOps provided by Huawei Cloud, boosting end-to-end project management and application delivery efficiency.
Service Rollout Management
Service system rollout management aims to ensure that services can still run smoothly during service system rollouts and reduce or eliminate the impact and risks on services. Service system rollout management involves preparing environments, promoting awareness, handling risks, and executing smooth cutovers.
Before the service system cutover, the cloud environment preparation usually includes deploying the service environment, synchronizing data (like during migrations), configuring connections with related systems, and checking both internal and external connectivity. These preparations create the necessary foundation for the smooth running of the service system.
Publicizing the rollout is a key for companies moving to the cloud for the first time. Publicity activities ensure all team members and stakeholders know their roles and work together to support smooth service rollouts. For example, let them know the impact of service rollouts, roles and responsibilities, implementation contents, timelines, and problem feedback mechanism. Verify every step and metric to guarantee a successful system rollout. In addition, enterprise executives can convey a key message to their employees that cloud migration is essential for the company's future and everyone need to embrace this shift and get ready for the digital transformation.
Risk emergency preparation is a necessary step before each service rollout. Identify risks and problems that may be encountered and formulate solutions. Identifying risks goes beyond technical issues. It also includes systematic risks in terms of organization, process, security, and platform. For example, a system that has been running for years may face risks like irreparable hardware failures, harmful viruses in its environment, or missing critical roles during rollouts. These risks can severely disrupt the system running. To reduce their impacts, identify risks early, prepare backup plans, and conduct necessary drills.
The service rollout is the final and most crucial step. With proper preparation, thorough risk management, and completed verifications, this process typically runs smoothly. This phase involves verifying the system using the updated manual and assessing if the rollout meets success criteria. A key point is that this phase is personnel-intensive. All personnel need to assume their responsibilities in different phases based on the publicity requirements, execute related operations based on the standard requirements, verify related processes and results, and ensure accountability by signing off on acceptance criteria. Then all feedback data will be used to determine whether the service rollout is successful.
Service Assurance
After the service system is rolled out, it enters the assurance period for resolving issues and completing knowledge transfer. The assurance period is usually one week after each rollout. During this time, issues often arise the most frequently. The cloud migration project team must prioritize and manage this critical phase. A dedicated assurance team from the cloud service provider collaborates with the enterprise to maintain stable operations. In this phase, the problems raised by the service department are sorted by urgency and severity, then resolved according to their priority. Knowledge transfer involves training the service department's application O&M team on cloud technologies after the service system is rolled out. It equips them with the skills needed to manage daily O&M tasks and handle incidents effectively on the cloud platform.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





