SEC10-03 Automatic Response to Security Incidents
The workflow of automatic response is the core component of security automation. It aims to reduce the response time of security incidents and improve the processing efficiency.
- Risk level
High
- Key strategies
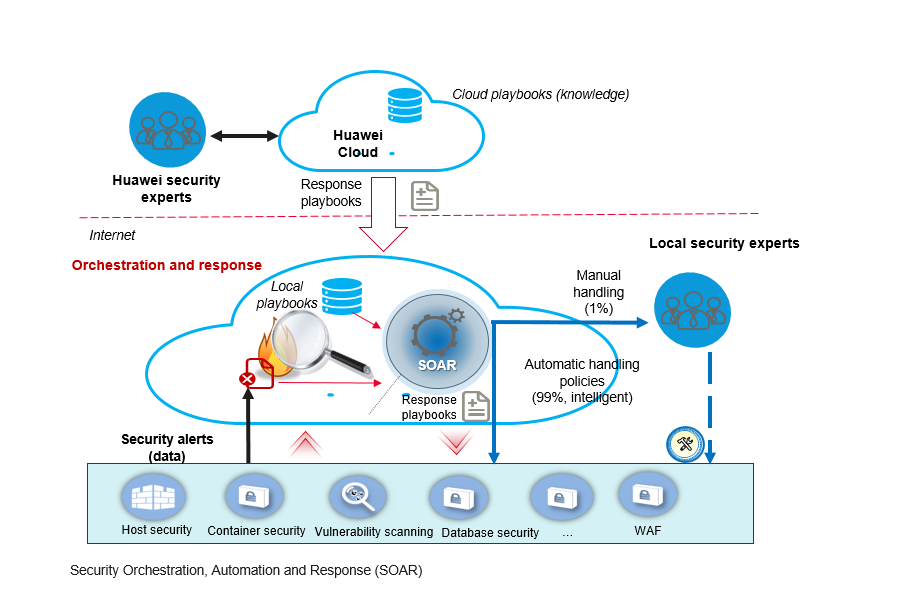
- Define response trigger conditions: Determine the conditions that trigger automatic response based on threat intelligence, abnormal behavior detection, and real-time monitoring results.
- Develop response policies: Develop specific response actions for each type of threat or incident, such as isolation, repair, notification, and investigation.
- Priority and level: Define the response priority based on the severity and urgency of incidents to ensure that important incidents are handled first.
- Continuous monitoring: Use tools such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and User and Entity Behavior Analysis (UEBA) to monitor networks, systems, applications, and user activities in real time.
- Intelligent alarm: When an event that meets the predefined trigger condition is detected, an alarm is automatically generated and classified based on the priority.
- Isolation and control: Infected devices or network segments are automatically isolated to prevent threat spreading.
- Automatic fixing: For known vulnerabilities or issues, automatically install patches, modify configurations, or clear malware.
- Evidence collection and recording: Automatically collect event-related logs, network packets, and other evidences and saves them for subsequent analysis.
- Notification and communication: Alarms are sent to security team members, and notifications are sent to the IT department, management, or other related parties.
- Automatic analysis: Machine learning and data analysis tools are used to automatically analyze the nature, source, and impact scope of incidents.
- Human-machine collaboration: Security analysts review the results of automated analysis and, if necessary, perform manual analysis to confirm the severity of the incident and the subsequent steps.
- Decision-making support: Based on the analysis result, determine whether further manual intervention is required or adjust the automatic response policy.
- Automatic recovery: Automatic system recovery, data recovery, or service restart is performed for resolved incidents.
- Report generation: Automatically generates incident handling reports, including incident details, response actions, handling results, and recommended measures.
- Compliance check: Ensure that the entire response process complies with laws, regulations, and industry standards.
- Incidents review: Periodically review the handled incidents, evaluate the effect of automatic response, and identify improvements.
- Rule and policy update: Update automatic response rules and policies based on the review result to enhance the system adaptability.
- Training and drill: Regularly train and drill the security team on the automatic response process to ensure that personnel are familiar with the process and efficiently execute it in actual operations.
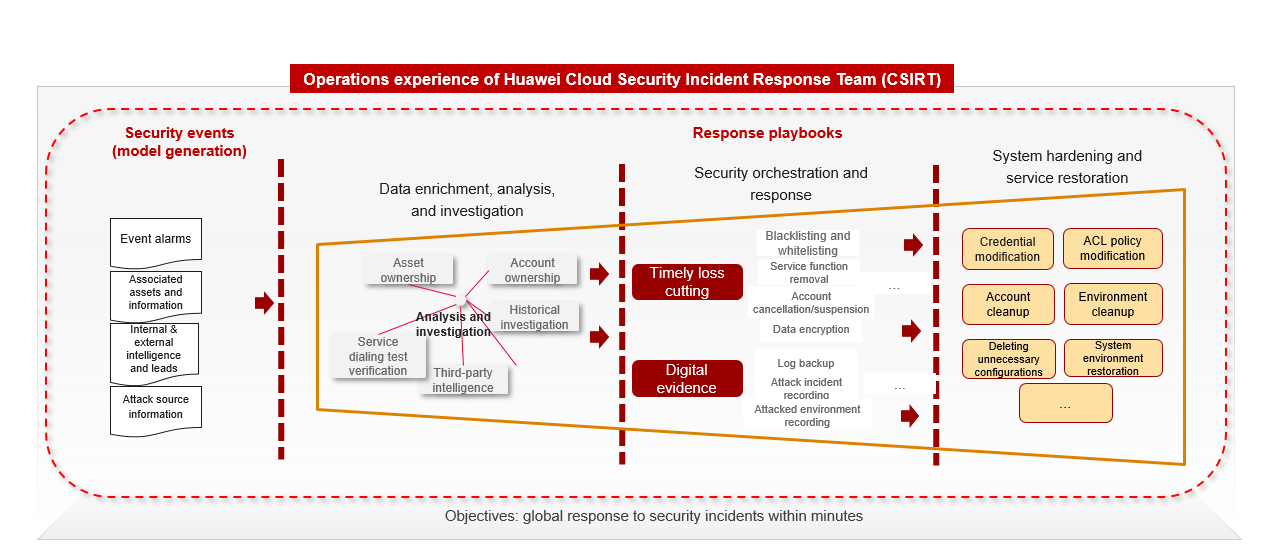
Implement the experience of top security experts in automatic threat handling based on a playbook. An incident response playbook is a set of defined response workflow. It leverages security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) technology to configure actions for different assets and protection components to achieve global response to single-point risks.
- Related cloud services and tools
SecMaster: SOAR
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





