Cryptographic Attestation
QingTian Enclave Attestation
QingTian Enclave supports boot measurement and remote attestation. QingTian Enclave measurements are a group of hash values obtained by using the standard trusted measurement operations (ExtendPCR). The hash values are stored in the platform configuration registers (PCRs) of QTSM. QTSM supports a maximum of 32 PCR measurement attributes. PCR16 to PCR31 can be customized by Enclave applications. PCR0 to PCR15 are reserved by the QingTian system. The currently supported measurement attributes include PCR0 (QingTian Enclave image file), PCR3 (IAM Agency URN), PCR4 (ECS instance ID), and PCR8 (signing certificate of the QingTian Enclave image file).
Enclave applications can obtain an attestation document of the current Enclave environment through QTSM. An attestation document includes the PCR measurement attribute list, QingTian PKI certificate chain, cryptographic algorithm declaration, and user-defined parameters. QingTian Enclave attestation documents support various user-defined parameters, including pubkey (user-defined public key signed by QTSM), nonce (one-off data to prevent replay attacks), and user_data (any user-defined data). It can support multiple user-defined security protocols (such as secure key negotiation and end-to-end encryption) between Enclave applications and external entities to provide complex application security solutions.
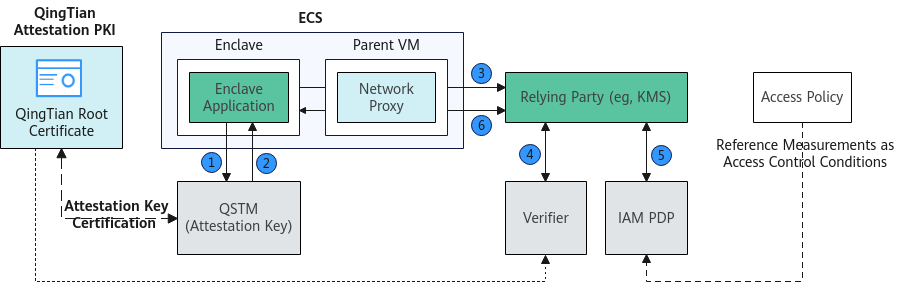
Huawei Cloud KMS and IAM support the QingTian Enclave attestation protocol. Tenants' IAM administrators can set condition-based authorization policies to achieve specific security control objectives. For example, only specified Enclave applications can call specified KMS APIs (such as generating random numbers, encryption, and decryption). The figure below shows how an Enclave application uses an attestation document that contains a custom public key to access the KMS Decrypt API to decrypt ciphertext data.
- The Enclave application randomly generates an RSA key pair (private key and public key) and uses the public key as a parameter to call the QTSM API to generate an attestation document.
- QTSM calculates the attestation document (containing the public key) and returns it to the Enclave application.
- The Enclave application carries the attestation document and ciphertext data blob and calls the KMS Decrypt API.
- KMS uses Verifier SDK to verify the attestation document.
- KMS provides the verification result to IAM Policy Decision Point (PDP) for access control decision-making.
- KMS decrypts the blob after the access control policy check is passed, re-encrypts the decryption result using the public key carried in the attestation document, and returns the result. After receiving the response, the Enclave application uses the private key generated in 1 to obtain the plaintext.
QingTian TPM Attestation
When creating an ECS, you can configure the UEFI secure boot mode and enable QingTian TPM. QingTian TPM is a virtual device provided by the QingTian system for ECSs and complies with the TPM 2.0 technical specifications. QingTian TPM provides measurement boot and remote attestation. You can obtain the signed PCR values from QingTian TPM and use them to prove the integrity of ECSs to remote entities. QingTian TPM can also generate keys for encryption or signing. The keys generated by QingTian TPM can be used to provide device attestation to relying parties.
ECS Identity Attestation
- Using an instance identity document
Each ECS you start has an instance identity document that provides metadata about the instance, including the instance specifications, instance ID, image ID, account ID, private IP address, and creation time. You can use the instance identity document to verify instance attributes. Applications running on ECSs can obtain the instance identity document and digital signature of the instance identity document through Instance Meta Data Service (IMDS). When an application needs to send the instance metadata document to a remote entity (relying party) for verification, the instance metadata document and its digital signature must be provided. When obtaining the digital signature of the instance metadata document from IMDS, you can provide a custom audience parameter (for example, a one-time challenge value) to prevent replay attacks.
The instance metadata document and digital signature can be regarded as the default birth certificate provided by the ECS service for each ECS instance. When an application in an instance needs to interact with a remote entity, the birth certificate can be used for initial identity authentication of the instance. With the "birth certificate", based on the security principle of transitive trust, the application can use the initial identity to obtain application-related access credentials. This method can effectively solve identity security issues (such as hardcoding static credentials in application configuration files).
- Using an IAM agency for an instance
You can configure an IAM agency when creating an ECS. An IAM agency for an instance is a virtual identity created by an IAM administrator. It represents the IAM identity for ECSs to access cloud service resources. An IAM agency does not have static credentials. This effectively reduces the risk of static credential (or long-term credential) leakage. An application running on an ECS can obtain a temporary security token of the IAM agency for the instance via IMDS. The security token is issued by the Security Token Service (STS) and represents an identity session of the IAM agency for the instance. After the IAM agency for the instance is authorized by IAM, the application can use the temporary security token of the IAM agency for the instance to access authorized cloud service resources (for example, OBS objects).
The IAM agency for the instance can be regarded as a custom machine identity provided by the tenant's IAM administrator for the ECS. When an application running on the ECS needs to access authorized Huawei Cloud service resources or APIs, the application can directly use the temporary security token of the machine identity without hardcoding static credentials (such as AK/SK) in the application code or configuration file, thereby preventing static credential leakage.
ECS IMDSv2 is recommended for accessing IMDS. Compared with IMDSv1, IMDSv2 uses the PUT method and dynamic token to initialize IMDS sessions. This effectively reduces SSRF vulnerability risks of tenant web applications and potential security risks caused by incorrect configurations of WAF, reverse proxy, layer 3 firewall, or NAT. IMDSv2 can significantly enhance the in-depth security defense capability of tenant ECSs.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





