Configuring Heartbeat and Data Consistency Check for a Synchronization Task
Scenario
The heartbeat and data consistency check function is used to collect full-link information about CDL synchronization tasks, including the time required for sending data from the database management system RDBMS to Kafka, the time required for writing data from Kafka to Hudi, and the number of data records, and writes the data to a specific topic (cdl_snapshot_topic). You can consume the data in the topic and write the data to a specific Hudi table for data consistency check. The heartbeat data can be used not only to determine whether data before the heartbeat time has been synchronized to the data lake, but also to determine the data latency based on the transaction time, Kafka write time, data import start time, and data import end time.
In addition, for PgSQL tasks, configuring a heartbeat table can periodically push forward the LSN information recorded by the slot in the PgSQL database. This prevents database log stacking caused by the configuration of some tables with little changes in a task.
Configuring the Heartbeat Table for Capturing Data from Oracle GoldenGate (OGG) to a Hudi Job
- Run the following commands in the Oracle database where data needs to be synchronized to create a heartbeat table. The heartbeat table belongs to the CDC_CDL schema, the table name is CDC_HEARTBEAT, and the primary key is CDL_JOB_ID.
CREATE TABLE "CDC_CDL"."CDC_HEARTBEAT" (
"CDL_JOB_ID" VARCHAR(22) PRIMARY KEY,
"CDL_LAST_HEARTBEAT" TIMESTAMP,
SUPPLEMENTAL LOG DATA (ALL) COLUMNS
);
- Add the CDC_HEARTBEAT table to the Oracle or OGG job to ensure that heartbeat data can be properly sent to Kafka.
- Configure the thirdparty-kafka (ogg) link on the CDL web UI and add the Oracle link information.
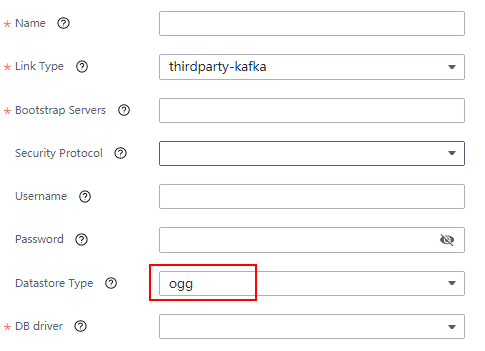
- After the configuration is complete, create a job for capturing data from OGG to Hudi on the CDL web UI and start the job to receive heartbeat data.
Configuring the Heartbeat Table for Capturing Data from PostgreSQL to a Hudi Job
- Run the following commands in the PostgreSQL database to be synchronized to create a heartbeat table. The heartbeat table belongs to the cdc_cdl schema, the table name is cdc_heartbeat, and the primary key is cdl_job_id.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cdc_cdl.cdc_heartbeat;
CREATE TABLE cdc_cdl.cdc_heartbeat (
cdl_job_id int8 NOT NULL,
cdl_last_heartbeat timestamp(6)
);
ALTER TABLE cdc_cdl.cdc_heartbeat ADD CONSTRAINT cdc_heartbeat_pkey PRIMARY KEY (cdl_job_id);
- After the heartbeat table is created, create a job for capturing data from PostgreSQL to Hudi on the CDL web UI and start the job to receive heartbeat data.
Configuring the Heartbeat Table from openGauss to a Hudi Job
- Run the following commands in the openGauss database to be synchronized to create a heartbeat table. The heartbeat table belongs to the cdc_cdl schema, the table name is cdc_heartbeat, and the primary key is cdl_job_id.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cdc_cdl.cdc_heartbeat;
CREATE TABLE cdc_cdl.cdc_heartbeat (
cdl_job_id int8 NOT NULL,
cdl_last_heartbeat timestamp(6)
);
ALTER TABLE cdc_cdl.cdc_heartbeat ADD CONSTRAINT cdc_heartbeat_pkey PRIMARY KEY (cdl_job_id);
- Add the heartbeat table to the DRS job to ensure that the heartbeat table data is properly sent to the DRS Kafka.
- On the CDL web UI, add the openGauss link information when configuring the thirdparty-kafka link of openGauss. If one primary openGauss node and multiple standby openGauss nodes are deployed, enter all IP addresses in Host.
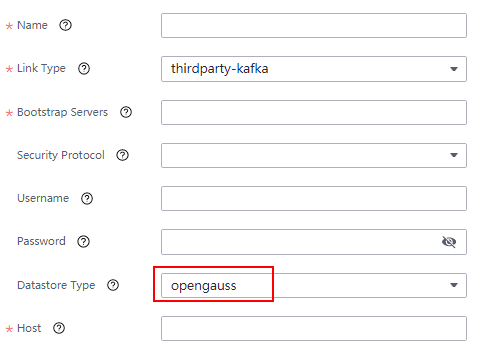
- After the configuration is complete, create a job for capturing data from thirdparty-kafka to Hudi on the CDL web UI and start the job to receive heartbeat data.
Fields in a Data Consistency Check Message
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
cdl_job_name |
The name of the synchronization task to which the data in this batch belongs. |
|
target_table_schema |
The name of the schema to which the data in this batch is written. |
|
target_table_name |
The name of the Hudi table to which the data in this batch is written. |
|
target_table_path |
The path of the Hudi table to which the data in this batch is saved. |
|
total_num |
The total number of data records in this batch. |
|
cdl_original_heartbeat |
The maximum duration of heartbeat data in this batch. If this batch does not contain heartbeat data, the value is empty. |
|
cdl_last_heartbeat |
The minimum duration of heartbeat data in this batch. If this batch does not contain heartbeat data, the value of event_time_min is used. |
|
insert_num |
The total number of data insert events in this batch. |
|
update_num |
The total number of data update events in this batch. |
|
delete_num |
The total number of data delete events in this batch. |
|
event_time_min |
The minimum transaction submission time of the data source in this batch. |
|
event_time_max |
The maximum transaction submission time of the data source in this batch. |
|
event_time_avg |
The average transaction submission time of the data source in this batch. |
|
kafka_timestamp_min |
The minimum time for sending data in this batch to Kafka. |
|
kafka_timestamp_max |
The maximum time for sending data in this batch to Kafka. |
|
begin_time |
The time when the data in this batch starts to be written to Hudi. |
|
end_time |
The time when the data in this batch stops to be written to Hudi. |
|
cdc_partitioned_time |
The time partition field in the heartbeat table. |
|
cdc_last_update_date |
The time when the check record is written. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot






