Functions
KMS is a secure, reliable, and easy-to-use cloud service that helps users create, manage, and protect keys in a centralized manner.
It uses Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) to protect keys. All keys are protected by root keys in HSMs to avoid key leakage. The HSMs meet the FIPS 140-2 Level 3 security requirements.
It also controls access to keys and records all operations on keys with traceable logs. In addition, it provides use records of all keys, meeting your audit and regulatory compliance requirements.
Functions
- On the KMS console, you can:
- Create, query, enable, and disable CMKs, as well as schedule and cancel CMK deletion.
- Modify the alias and descriptions of CMKs.
- Use the online tool to encrypt and decrypt small-size data.
- Add, search for, edit, and delete tags.
- Create, cancel, and query grants.
- You can use the APIs to:
- Create, encrypt, or decrypt DEKs.
- Retire grants.
- Sign or verify the signature of messages or message digests.
- Generate and verify message authentication codes.
For details, see the Data Encryption Workshop API Reference.
- Generate hardware true random numbers.
You can generate 512-bit random numbers based on hardware using the KMS API. The 512-bit true random numbers can be used as basis for key materials and encryption parameters. For details, see the Data Encryption Workshop API Reference.
Key Algorithms Supported by KMS
Symmetric keys created on the KMS console use AES and SM4 algorithms. Asymmetric keys created by KMS support the RSA, SM2, and ECC algorithms.
|
Key Type |
Algorithm Type |
Key Specifications |
Description |
Application Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Symmetric key |
AES |
AES_256 |
AES symmetric key |
|
|
Digest key |
SHA |
|
Digest key |
|
|
Asymmetric key |
RSA |
|
RSA asymmetric password |
|
|
Asymmetric key |
ECC |
|
Elliptic curve recommended by NIST |
Digital signature and signature verification |
|
Asymmetric key |
ML-DSA
NOTE:
To enable the ML-DSA algorithm, submit a service ticket. |
|
Machine learning (ML) algorithm |
Quantum-resistant digital signature and signature verification |
The following table lists the key wrapping encryption and decryption algorithms supported by imported keys.
|
Algorithm |
Description |
Configuration |
|---|---|---|
|
RSAES_OAEP_SHA_256 |
RSA algorithm that uses OAEP and has the SHA-256 hash function |
Select an algorithm based on your HSM functions. If your HSM supports the RSAES_OAEP_SHA_256 algorithm, use RSAES_OAEP_SHA_256 to encrypt key materials. |
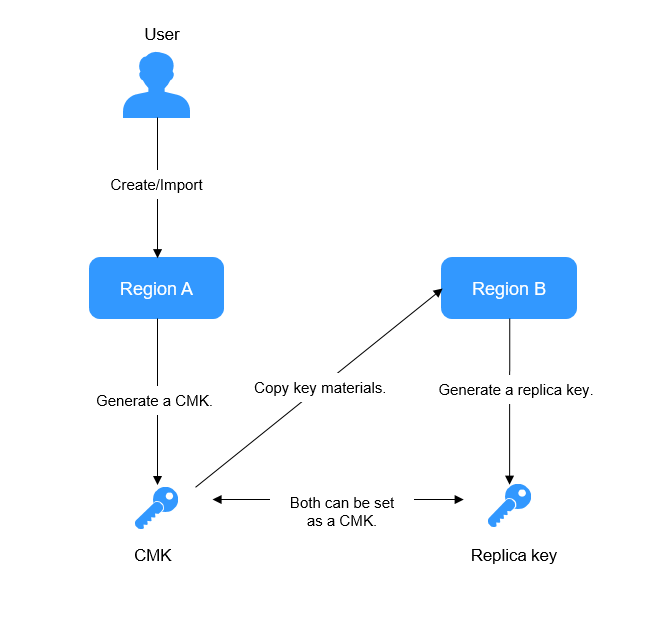
Multi-Region Keys
KMS allows you to use keys across regions. Each pair of CMK and replica key share the same key materials, so that data encrypted in a region can be decrypted in another.
You can manage keys of multiple regions, edit replica key alias, enable, disable, tag, and authorize replica keys. You can also encrypt and decrypt replica keys online. The rotation of replica keys cannot be configured independently, which is synchronized with CMK rotation.
The following figure shows the principle of multi-region keys.
|
Scenario |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Disaster recovery (DR) |
If resources in the region where a key is created are frozen due to arrears or data cannot be decrypted due to exceptions, replica keys in another region can be used to ensure service continuity. |
|
Cross-region signature verification |
If services are deployed in different regions, you can use multi-region keys to verify and decrypt signatures, improving service interconnection efficiency. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





