Usage Principle
Huawei Cloud nodes can be staked separately. To stake a node, you need to purchase a Huawei Cloud staking node, activate a validator, and interconnect the node with the validator. Huawei Cloud keeps the Ethereum nodes running stably by managing the Execution Layer (EL) and Consensus Layer (CL) clients. Note that Huawei Cloud will not keep your keys.
The following figure shows the staking process.
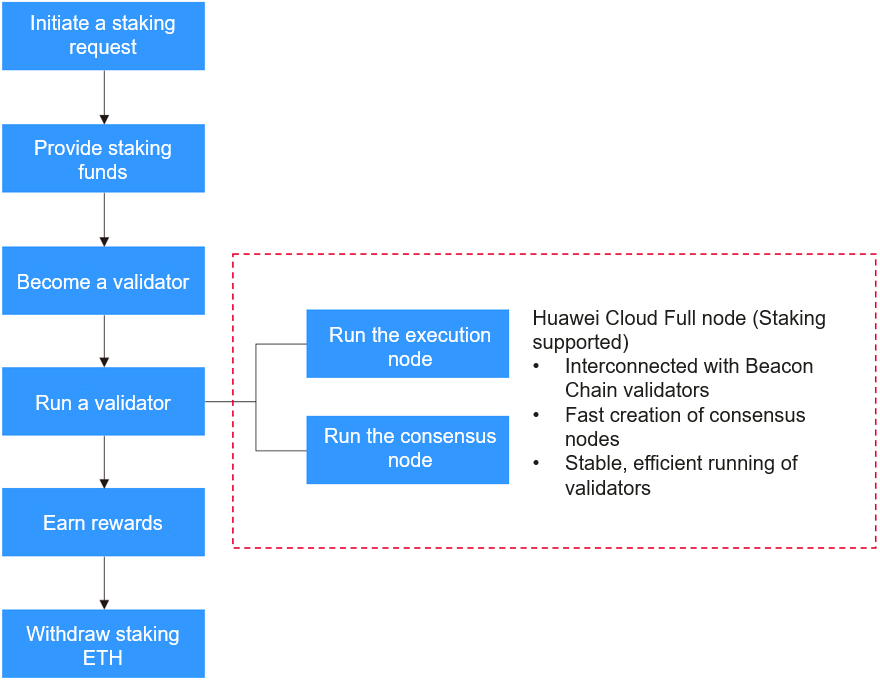
The operations in the red box are performed by NES. Other operations are performed by you.
The following explains the details.
- Initiate a staking request.
You initiate a staking request and learn about the advisories provided by Ethereum.
- Provide staking funds.
You deposit a certain amount of ETH to the staking contract. These ETH will support the validator running.
- Become a validator.
By depositing funds, you will be able to participate in reaching consensus. To become a validator, an individual must stake a specific amount of ETH, for instance, solo staking requires 32 ETH to be staked, and has some technical skills such as knowing how to set up and start a validator client.
- Run a validator.
You need to verify transaction validity and batch blocks as a validator. To ensure that your validator runs and operates properly, usually, you will need to start an execution node and a consensus node. Huawei Cloud NES provides open gRPC for Beacon Chain validator interconnection. With just a few clicks, EL/CL nodes with the 8 vCPUs | 32 GB flavor can be created effortlessly, eliminating the need for O&M. Additionally, Huawei Cloud-developed algorithms ensure efficient operations of validators.
- Earn rewards.
Validators will receive block rewards and earn transaction fees. These awards will be allocated based on the staking funds and contribution from the participants.
- Withdraw staking ETH.
This is optional. The Shanghai/Capella upgrade enabled staking withdrawals on Ethereum.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





