Connecting an On-Premises Data Center to a VPC Through a VPN
Scenarios
By default, ECSs in a VPC cannot communicate with devices in your on-premises data center or private network. To enable communication between them, you can configure VPN. After that, you need to configure security group rules and check subnet connectivity to ensure that the VPN is available. VPNs can be classified into the following two types:
- A site-to-site VPN functions as a communication tunnel between a VPC and a single on-premises data center.
- By contrast, a hub-and-spoke VPN is between a VPC and multiple on-premises data centers.
- The local and remote subnets cannot conflict.
- The IKE policies, IPsec policies, and PSKs configured on the cloud and in the on-premises data center must be the same.
- The parameters configured for the local and remote subnets and gateways must be symmetric.
- Security group rules permit access to and from the ECSs in the VPC.
- The status of a VPN changes to Normal only after ECSs and on-premises servers access each other.
Prerequisites
You have created the VPC and subnets that the on-premises data center wants to access.
Procedure
- On the management console, select the appropriate IKE and IPsec policies to create a VPN.
- Check the IP address pools for the local and remote subnets.
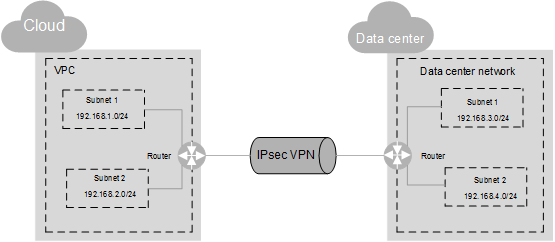
In Figure 1, the VPC has subnets 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24. Your on-premises data center has subnets 192.168.3.0/24 and 192.168.4.0/24. You can set up a VPN to connect these subnets.
The IP address pools for the local subnets cannot overlap with those for the remote subnets. Like in this example, the IP address pool for the remote subnets cannot contain the two subnets of the VPC.
- Configure security group rules for the ECSs to allow packets from and to the on-premises data center over the VPN.
- Ping the ECSs from the on-premises data center to verify that the security group allows packets from and to the on-premises data center over the VPN.
- Check the on-premises network configuration.
A route must be configured for the on-premises network to enable traffic to be forwarded to network devices on the network over the VPN. If the data transmitted through the VPN cannot be forwarded to the network devices, check whether the remote LAN has rules configured to refuse the traffic.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot