Basic Syntax Examples of GeminiDB Influx Instances
This section describes the basic syntax of GeminiDB Influx instances.
- Database syntax
- Create a database.
create_database_stmt = "CREATE DATABASE" db_name
[ WITH
[ retention_policy_duration ]
[ retention_policy_replication ]
[ retention_policy_shard_group_duration ]
[ retention_policy_name ]
] .

The commands in square brackets ([]) are optional.
Example:
- Create a database named mydb.
CREATE DATABASE "mydb"
- Create a database named mydb using the specified retention policy myrp. Set the retention period to 1 day, the number of copies to 1, and the storage duration of shardGroup to 30 minutes.
CREATE DATABASE "mydb" WITH DURATION 1d REPLICATION 1 SHARD DURATION 30m NAME "myrp"
- Create a database named mydb using the default retention policy myrp.
CREATE DATABASE "mydb" WITH NAME "myrp"
- Create a database named mydb.
- Query databases.
- Switch to another database.
- Delete a database.
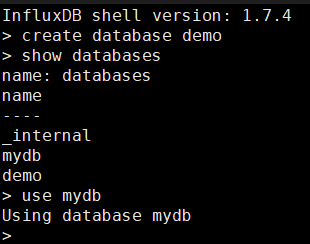
- Create a database.
- RETENTION POLICY
- Create a retention policy and ensure that the policy name does not contain periods (,), colons (:), semicolons (;), or dots (.).
create_retention_policy_stmt = "CREATE RETENTION POLICY" policy_name on_clause
retention_policy_duration
retention_policy_replication
[ retention_policy_shard_group_duration ]
[ "DEFAULT" ] .

The commands in square brackets ([]) are optional.
Example:
- Create a data retention policy.
CREATE RETENTION POLICY "10m_events" ON "somedb" DURATION 60m REPLICATION 2
- Create a data retention policy and set it as the default one.
CREATE RETENTION POLICY "10m_events" ON "somedb" DURATION 60m REPLICATION 2 DEFAULT
- Create a data retention policy and specify the storage duration of shardGroup.
CREATE RETENTION POLICY "10m_events" ON "somedb" DURATION 60m REPLICATION 2 SHARD DURATION 30m
- Create a data retention policy.
- View a retention policy.
show retention policies on <database name>
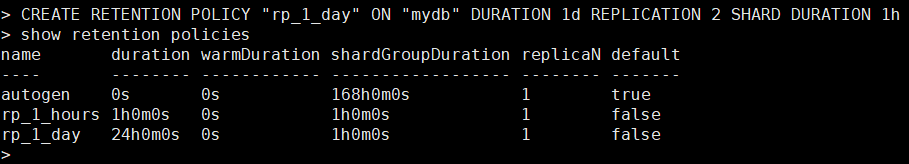

If you specify both parameters retention_policy_duration and retention_policy_shard_group_duration, ensure that the former parameter has a larger value than the latter.
- Delete a retention policy.
- Modify a retention policy.
Alter_retention_policy_stmt = "ALTER RETENTION POLICY" policy_name on_clause
retention_policy_option
[ retention_policy_option ]
[ retention_policy_option ]
[ retention_policy_option ] .

The commands in square brackets ([]) are optional.
Example:
- Create a retention policy and ensure that the policy name does not contain periods (,), colons (:), semicolons (;), or dots (.).
- Add data.
insert into <retention policy> measurement,tagKey=tagValue fieldKey=fieldValue timestamp

When data is inserted, the system creates a measurement as required.
- Query data.
- Modify data.
When you modify data using INSERT, if all tags and timestamps are the same, the existing data will be overwritten.
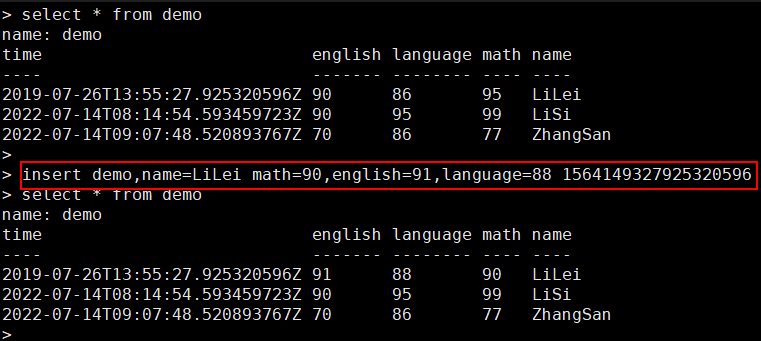
- Delete data.
You can create a retention policy to automatically delete data.
- HELP command
- Run HELP to view all supported commands.
Figure 1 Viewing all supported commands
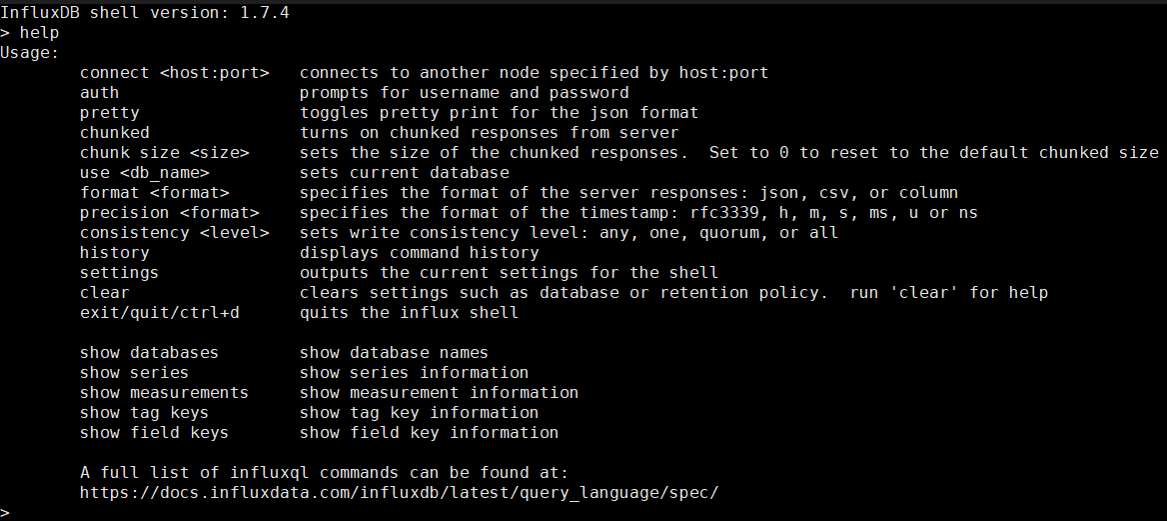
- Run HELP <COMMAND> to query the usage of a command.
Example: HELP DESC
- Run HELP to view all supported commands.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





