Sending and Receiving Transactional Messages
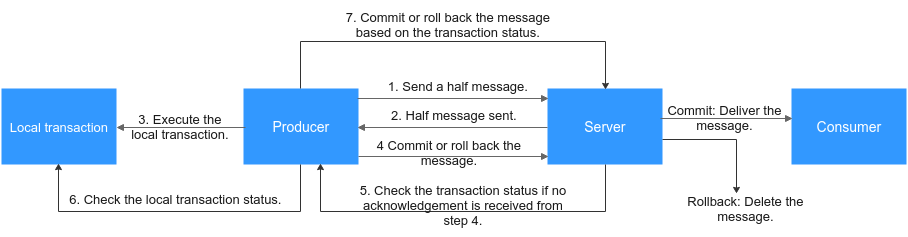
DMS for RocketMQ ensures transaction consistency between the service logic and message transmission, and implements transaction support in two phases. Figure 1 illustrates the interaction of transactional messages.
The producer sends a half message and then executes the local transaction. If the execution is successful, the transaction is committed. If the execution fails, the transaction is rolled back. If the server does not receive any commit or rollback request after a period of time, it initiates a check. After receiving the check request, the producer resends a transaction commit or rollback request. The message is delivered to the consumer only after being committed. The consumer is unaware of the rollback.
Before sending and receiving transactional messages, collect RocketMQ connection information by referring to Collecting Connection Information.
Notes and Constraints
- The gRPC protocol is only supported by RocketMQ v5.x but not v4.8.0.
- To receive and send transactional messages, ensure the topic message type is Transactional before connecting a client to a RocketMQ instance of v5.x.
Preparing the Environment
- Run the following command to check whether Go has been installed:
go version
If the following information is displayed, Go has been installed:
go version go1.16.5 linux/amd64
If Go is not installed, download and install it.
- Add the following code to go.mod to add the dependency:
module rocketmq-example-go go 1.13 require ( github.com/apache/rocketmq-clients/golang/v5 )
Sending Transactional Messages
The following code is an example. Replace the information in bold with the actual values.
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"strconv"
"time"
"github.com/apache/rocketmq-clients/golang"
"github.com/apache/rocketmq-clients/golang/credentials"
)
const (
Topic = "topic01"
Endpoint = "192.168.xx.xx:8080"
AccessKey = os.Getenv("ACL_User_Name")
SecretKey = os.Getenv("ACL_Secret_Key")
)
// ACL_User_Name is the username and ACL_Secret_Key is the key. For details about how to create a user, see Creating a User. Hard-coded or plaintext username and key are risky. You are advised to store them in ciphertext in a configuration file or an environment variable.
func main() {
os.Setenv("mq.consoleAppender.enabled", "true")
golang.ResetLogger()
producer, err := golang.NewProducer(&golang.Config{
Endpoint: Endpoint,
Credentials: &credentials.SessionCredentials{
AccessKey: AccessKey,
AccessSecret: SecretKey,
},
},
golang.WithTransactionChecker(&golang.TransactionChecker{
Check: func(msg *golang.MessageView) golang.TransactionResolution {
log.Printf("check transaction message: %v", msg)
// Check local transaction and return its status.
return golang.COMMIT
},
}),
golang.WithTopics(Topic),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
err = producer.Start()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer producer.GracefulStop()
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
msg := &golang.Message{
Topic: Topic,
Body: []byte("this is a message : " + strconv.Itoa(i)),
}
// Set the message key and tag.
msg.SetKeys("a", "b")
msg.SetTag("ab")
// Start a transaction branch.
transaction := producer.BeginTransaction()
resp, err := producer.SendWithTransaction(context.TODO(), msg, transaction)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
for i := 0; i < len(resp); i++ {
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", resp[i])
}
/**
* Execute a local transaction and check the result.
* 1. Commit a transactional message if local transaction is committed.
* 2. Rollback transaction if local transactional message fails to be committed.
* 3. Wait for transaction re-check if unknown exception occurs.
*
*/
err = transaction.Commit()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
time.Sleep(time.Second * 1)
}
}
The parameters in the example code are described as follows. For details about how to obtain the parameter values, see Collecting Connection Information.
- Topic: Enter a topic name.
- Endpoint: Enter the gRPC address or gRPC public address.
- AccessKey: Enter the username if ACL was enabled during instance creation.
- SecretKey: Enter the user key if ACL was enabled during instance creation.
- SetKeys: Enter the message key.
- SetTag: Enter the message tag.
For transactional messages, the producer needs to construct a transaction checker to check the intermediate status of abnormal transactions. Three transaction statuses can be returned:
- TransactionResolution.COMMIT: Transaction committed. The consumer can retrieve the message.
- TransactionResolution.ROLLBACK: Transaction rolled back. The message will be discarded and cannot be retrieved.
- TransactionResolution.UNKNOWN: The status cannot be determined and the server is expected to check the message status from the producer again.
Subscribing to Transactional Messages
The code for subscribing to transactional messages is the same as that for subscribing to normal messages.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot