How Do I Solve Out-of-Order Changelog Events in Flink SQL?
Symptom
The following is an example of the SQL statement:
-- CDC source tables: s1 & s2 CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE s1 ( id BIGINT, level BIGINT, PRIMARY KEY(id) NOT ENFORCED )WITH (...); CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE s2 ( id BIGINT, attr VARCHAR, PRIMARY KEY(id) NOT ENFORCED )WITH (...); -- sink table: t1 CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE t1 ( id BIGINT, level BIGINT, attr VARCHAR, PRIMARY KEY(id) NOT ENFORCED )WITH (...); -- join s1 and s2 and insert the result into t1 INSERT INTO t1 SELECT s1.*, s2.attr FROM s1 JOIN s2 ON s1.level = s2.id;
The primary key of the source table s1 is id. However, the Join operation needs to shuffle data by level. If the parallelism of the Join operator is not 1, the update events of s1 may be delivered to different subtasks of the Join, as shown in the following figure.
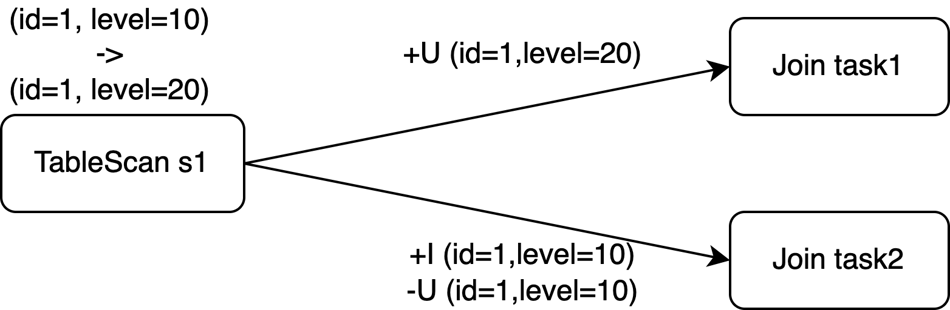
This can lead to an unpredictable order of Changelog events output by the Join, potentially resulting in incorrect output.
Cause Analysis
The issue occurs mainly because the Join operation breaks the order of unique keys, which are (s1.id), (s1.id,s1.level), and (s1.id,s2.id) in this example.
This issue may also occur in the following scenarios:
- The data written to the sink table lost its uniqueness although the primary key has been specified in the table. Generally, the following operations are involved:
- The source table lacks a primary key, but the sink table has a primary key.
- When data is inserted into the sink table, the primary key column is ignored, or non-primary key data of the source table is incorrectly used to fill the primary key of the sink table.
- Precision loss occurs after the primary key data of the source table is converted or grouped and aggregated. For example, the BIGINT type is degraded to the INT type.
- Operations are performed on the primary key column of the source table or the unique key after grouping and aggregation, such as data concatenation or a merge of multiple primary keys into a single field.
- Data is written in to the sink table without using the primary key. As a result, the original data sequence is disrupted.
Solution
Add the SinkUpsertMaterializer operator before Sink. It works by maintaining a RowData list in the state. When processing input rows, it checks whether there are identical rows in the state list based on the inferred upsert key or the entire row (if the upsert key is empty). In the case of an ADD operation, a row in the state is added or updated; in the case of a RETRACT operation, a row is deleted from the state. Finally, Changelog events are generated based on the primary key of the sink table. For details, see Common Issues About Flink.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





