Configuring Hive to Insert Data to a Directory That Does Not Exist
Scenario
hive.overwrite.directory.move.trash is a parameter related to data overwriting in Hive. It is used to determine whether to remove the data in the original directory to the HDFS Trash or directly delete the data when the INSERT OVERWRITE statement is used to overwrite the directory.
This section describes how to enable Hive to insert data to a non-existent directory. Take the insert overwrite directory "/path1/path2/path3" command as an example. The permission on the /path1/path2 directory is 700, the owner is the current user, and the path3 directory does not exist. After the preceding command is executed, the system automatically creates the path3 directory and writes data to the directory.

The preceding function is enabled when the Hive parameter hive.server2.enable.doAs is set to true. This document describes how to configure Hive to insert data to a non-existent directory when hive.server2.enable.doAs is set to false. The parameter is used to determine whether HiveServer2 executes Hive queries as the client user.
Procedure
- Log in to FusionInsight Manager, choose Cluster > Services > Hive, click Configurations, and click All Configurations.
- Choose HiveServer(Role) > Security and change the value of hive.server2.enable.doAs to false.
- Choose HiveServer(Role) > Customization, add a customized parameter to the hive-site.xml parameter file, set Name to hive.overwrite.directory.move.trash, and set Value to true.
- Click Save. Click Instances, select all Hive instances, click More then Restart Instance, enter the user password, and click OK to restart all Hive instances.
- Log in to the node where the client is installed as the client installation user.
For details about how to download and install the cluster client, see Installing an MRS Cluster Client.
- Configure environment variables and authenticate the user.
Go to the client installation directory.
cd Client installation directoryLoad the environment variables.
source bigdata_env
Authenticate the user. Skip this step for clusters with Kerberos authentication disabled.
kinit Hive service user - Create an HDFS directory, for example, /user/test.
hdfs dfs -mkdir /user/test - Log in to the Hive client.
beeline
- Create a Hive table, for example, test, and insert data into the table.
Create a table, for example, test.
create table test(id int,name string);Insert data into the table.insert into table test(id,name) values("11","A"); - Query the Hive table data and write the data to a directory in the HDFS, for example, /user/test/hive.
insert overwrite directory '/user/test/hive' select * from test;
The data is written successfully.
- Exit the Hive client.
!q
- Check whether there is a hive directory in the /user/test directory of HDFS and whether the written data is stored in this directory.
- Query the /user/test directory of HDFS.
hdfs dfs -ls /user/testThe directory is created successfully.
Figure 1 Querying directories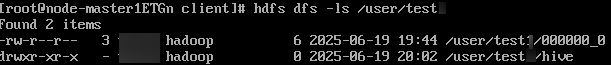
- View the file data in the /user/test/hive directory.
hdfs dfs -cat /user/test/hive/000000_0The file content is the same as the table data inserted in 9.
11A
- Query the /user/test directory of HDFS.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





