Using Open-Source Logstash to Export Data in Batches from a CSS Elasticsearch Cluster
Use open-source Logstash to efficiently export data from a CSS Elasticsearch cluster for purposes like backup, migration, and analysis.
Scenarios
You may use this solution for the following purposes:
- Data backup: Regularly perform full backups on all indexes to ensure data security.
- Data migration: Migrate data to other storage systems (such as an object storage service or database).
- Data cleaning: Export data and preprocess it, including filtering by fields and converting formats.
- Data analysis: Export data to JSON files for offline analysis.
To export only a small amount of data (less than 10 MB), use Kibana. For details, see Can I Export Data from Kibana in CSS?.
Solution Architecture
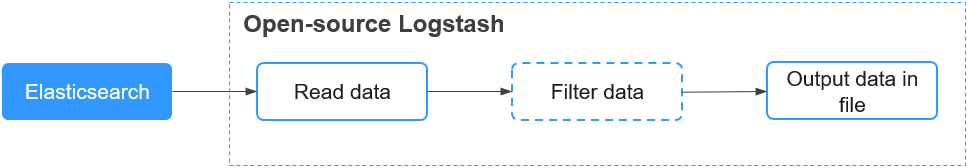
This solution consists of three key components:
- Input (reading data): The logstash-input-elasticsearch plugin connects to a CSS cluster to read data from specified indexes.
- Filter (filtering data): This one is optional. It is used for data cleaning (such as filtering data by field and converting formats).
- Output (outputting data in file): The logstash-output-file plugin writes data to a local JSON file.
Advantages
- Efficient batch processing: This solution supports both full data exporting and incremental data exporting based on filters.
- Flexible configuration: You can customize filters using Elasticsearch query DSL.
- Ecosystem compatibility: This solution fits perfectly into the Elasticsearch ecosystem. There are no additional development costs.
- Low cost: This solution uses an open-source tool.
Constraints
- The data exporting speed is affected by the load of the target CSS cluster and the performance (CPU and memory) of the ECS where the data is exported to.
- Make sure the CSS Elasticsearch cluster and Logstash versions are compatible. This example uses Logstash 7.10.2, in which case, Elasticsearch 7.10.2 is recommended.
Prerequisites
- You have obtained the address, username, and password for accessing the CSS Elasticsearch cluster.
- The ECS where you plan to export data to has been deployed and can communicate with the CSS Elasticsearch cluster (for example, they are in the same VPC and security group).
Step 1: Deploying Logstash on the Client
Deploy open-source Logstash on the ECS.
- Log in to the ECS.
ssh username@<ECS_IP>
- Download and install open-source Logstash.
cd ~ wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-7.10.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz tar -zxvf logstash-7.10.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
If the ECS cannot access the Internet, download the Logstash installation package and upload it to the ECS beforehand. Download Logstash at https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-7.10.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz.
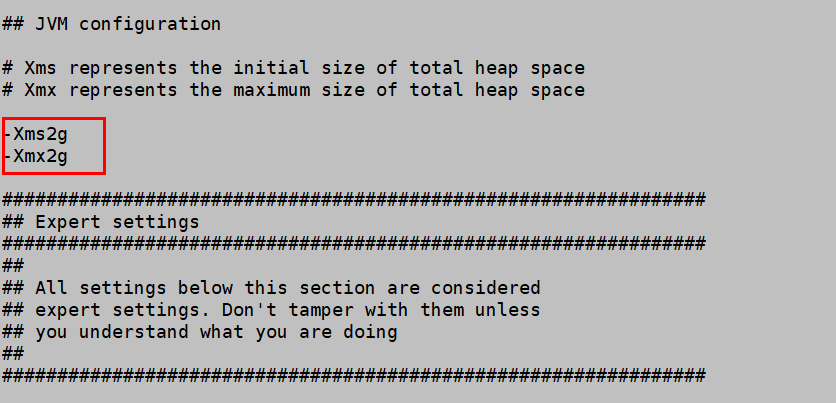
- Modify the Logstash memory configuration.
Change the JVM heap size for Logstash. The default value is 1 GB. We recommend that you set it to half of the ECS memory.
cd logstash-7.10.2 vi config/jvm.options
Figure 2 shows an example.
- Optimize Logstash's batch processing performance.
Modify the pipelines.yml file and change the value of pipeline.batch.size to 5000.
vi config/pipelines.yml
Figure 3 shows an example.
- Test connectivity.
Run a curl command to test the connectivity between the ECS and the CSS Elasticsearch cluster.
curl -ik http://<CSS_IP>:9200 #No user authentication curl -ik https://<CSS_IP>:9200 -u <Username>:<password> # HTTPS authentication
If the cluster information is returned, the two are connected.
Step 2: Exporting Elasticsearch Data
- Create a Logstash configuration file.
Create a configuration file, for example, es2file_all.conf, in the config directory under the Logstash installation path.
vi config/es2file_all.conf
- Modify the Logstash configuration file and save the change.
input { elasticsearch { hosts => ["http://<CSS_IP>:9200"] user => "<Username>" password => "<Password>" index => "kibana_sample_data_logs" query => '{"query":{"range":{"@timestamp":{"gte":"now-5m","lte":"now/m"}}}}' docinfo => true size => 5000 } } filter { mutate { remove_field => ["@version"] } } output { file { path => "./test_inc-%{+YYYY-MM-dd}.json" } }Table 1 Description of key configuration items Configuration Item
Mandatory (Yes/No)
Description
input
Yes
The input plugin reads data from the Elasticsearch cluster.
hosts
Yes
Address for accessing the Elasticsearch cluster.
user
No
Username for accessing the Elasticsearch cluster. This parameter is mandatory for a security-mode cluster. Without it, the Elasticsearch cluster cannot be accessed.
password
No
Password for accessing the Elasticsearch cluster. This parameter is mandatory for a security-mode cluster. Without it, the Elasticsearch cluster cannot be accessed.
index
Yes
Name of the index to be exported. Wildcards (such as *) can be used to match multiple indexes. If you specify multiple index names, use a comma (,) to separate them.
query
No
Use Elasticsearch query DSL to set filters.
To export all data, there is no need to set this parameter. To export only part of the data, use this parameter to set filters.
When setting this parameter, make sure the fields used in the filters already exist in the target indexes. Otherwise, data cannot be matched.
In the example above, data of the last 5 minutes is fetched. now-5m indicates the last 5 minutes prior to the current time, and now/m indicates the current minute rounded down.
docinfo
No
Whether to include document metadata (such as index names and IDs).
- true: to include document metadata. Such data can be useful for subsequent association analysis.
- false: not to include document metadata. If you only need the document content, set this parameter to false to reduce the output size.
slices
No
Number of concurrent slices.
The default value is 1. To accelerate data exporting, you can increase the value (for example, to 5 to 10), so long as your cluster has sufficient resources. Set this parameter based on the cluster load. Too many slices will increase the cluster load.
size
No
Number of documents read from Elasticsearch for each request. A larger value indicates higher efficiency, but at the cost of higher memory usage.
The maximum value is constrained by the Elasticsearch cluster. You are advised to set the value (for example, between 1000 and 10000) based on the ECS performance and Elasticsearch cluster load.
filter
No
The filter plugin used for data filtering.
In this example, the filter plugin only deletes fields automatically added by Logstash to avoid exporting too much redundant data.
output
Yes
The output plugin can be used to specify the output file path and file naming rule.
You are advised to specify an absolute path to ensure file accessibility.
- Execute the Logstash configuration file to start the export task.
cd logstash-7.10.2 bin/logstash -f config/es2file_all.conf
- Verify the export result.
Go to the output file path, and open the JSON file (for example, test_all-2025-06-05.json). Check that the exported data meets your expectation.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot