Using Elasticsearch Pipelines for Incremental Data Migration
Elasticsearch ingest pipelines let you perform common transformations on your data before indexing. This capability makes it easier to identify incremental data updates, enabling reliable incremental data migration.
Scenario
- The indexes do not contain an incremental update time field that enables easy identification of incremental data updates.
- Due to complex service logic, incremental data updates cannot be identified reliably.
- Indexes use different incremental update time fields. A unified update method is needed.
- The incremental update time fields are not updated along with the data.
This solution uses Elasticsearch pipelines to automatically add an incremental update time field to indexes when data is written in, enabling more efficient and flexible incremental data migration.
Solution Architecture
Use Elasticsearch pipelines to automatically add an incremental update time field when data is written in. Based on this field, a data migration tool fetches and migrates incremental data.
- Configure a pipeline in the source Elasticsearch cluster to automatically add an incremental update time field.
- Associate an index with this pipeline, which automatically updates the incremental update time field when data is written into this index.
- Use a migration tool to migrate incremental data.
Highlights
- Simplified operations: There is no need to analyze incremental update time fields for indexes. An ingest pipeline automatically generates a unified field, reducing configuration complexity.
- Flexibility: This solution supports different indexes and service scenarios. There is no need to modify the index structure.
- Compatibility: This solution can be used with different data migration tools, such as Logstash, ESM, and Reindex.
Constraints
During incremental data migration, do not delete index data in the source cluster. Otherwise, incremental data may be lost, and after the migration, data in the destination cluster may be inconsistent with that in the source cluster.
Prerequisites
- The source and destination Elasticsearch clusters are available, and the cluster version is later than 6.x. Otherwise, they may not support Elasticsearch ingest pipelines.
- The network between the clusters is connected.
- If the source and destination clusters are in different VPCs, establish a VPC peering connection between them. For details, see VPC Peering Connection Overview.
- To migrate an in-house built Elasticsearch cluster to Huawei Cloud, you need to enable public network access for this cluster.
- To migrate a third-party Elasticsearch cluster to Huawei Cloud, you need to establish a VPN or Direct Connect connection between the third party's internal data center and Huawei Cloud.
- Ensure that _source has been enabled for indexes in the cluster.
By default, _source is enabled. You can run the GET {index}/_search command to check whether it is enabled. If the returned index information contains _source, it is enabled.
Procedure
- Log in to the Kibana console of the source Elasticsearch cluster.
The login method varies depending on the source cluster. If Kibana is not installed, you can run cURL commands to configure the cluster. This section uses a CSS Elasticsearch cluster as an example to describe the procedure.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > Elasticsearch.
- In the cluster list, find the target cluster, and click Kibana in the Operation column to log in to the Kibana console.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Dev Tools.
The left part of the console is the command input box, and the triangle icon in its upper-right corner is the execution button. The right part shows the execution result.
- Add an incremental update time field for an index in the source cluster.
PUT /{index_name}/_mapping { "properties": { "@migrate_update_time": { "type": "date" } } }Add an incremental update time field (for example, @migrate_update_time) and set the field type to date. {index_name} indicates the index name.
- Create a pipeline that automatically updates the incremental update time field.
PUT _ingest/pipeline/migrate_update_time { "description": "Adds update_time timestamp to documents", "processors": [ { "set": { "field": "_source.@migrate_update_time", "value": "{{_ingest.timestamp}}" } } ] }Pipeline processors will read the current machine time and write it to the incremental update time field (for example, @migrate_update_time) of the index.
- Associate the index and pipeline. The pipeline automatically updates the incremental update time field when data is written into this index.
PUT {index_name}/_settings { "index.default_pipeline": "migrate_update_time" }Configure the default pipeline of the index. When index data is added or updated, the pipeline will always update the incremental update time field @migrate_update_time.
- Query the incremental update time field @migrate_update_time to identify incremental data.
GET /{index_name}/_search { "query": { "range": { "@migrate_update_time": { "gte": "2025-01-01T00:00:00" } } } }Query documents whose incremental update time field (@migrate_update_time) is later than or equal to the specified time. The time format must match the field mapping type (date).
- Use a migration tool to perform incremental data migration.
For example, with ESM, run the following command:
./migrator-linux-amd6 -s http://source:9200 -d http://dest:9200 -x {index_name} -m admin:password -n admin:password -w 5 -b 10 -q "@migrate_update_time:[\"2025-04-08T00:00:00\" TO \"2030-01-01T 00:00:00\"]"For more about data migration commands and other migration tools, see About Elasticsearch Cluster Migration Solutions.
- Check data consistency.
After the data migration is complete, run the GET {index_name}/_count command in Kibana of both the source and destination clusters to check index consistency.
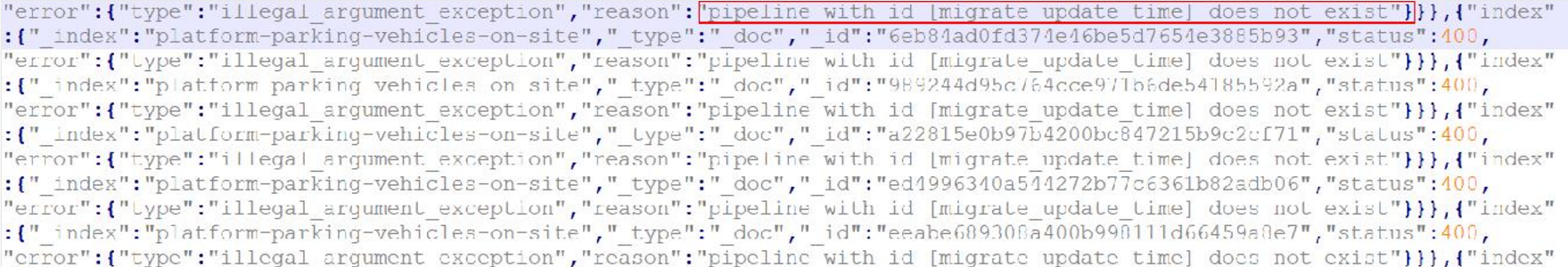
Common Issue: Pipeline (migrate_update_time) Does Not Exist
- Symptom: The error shown in Figure 1 is reported during migration.
- Cause: During index structure migration, pipelines created in the source Elasticsearch cluster are migrated along with indexes to the destination Elasticsearch cluster. However, if no such pipelines are created in the destination cluster, this error is reported.
- Solution: Cancel such pipelines in the destination Elasticsearch cluster.
Log in to the Kibana console of the destination Elasticsearch cluster, go to Dev Tools, and run the following command:
PUT {index_name}/_settings { "index.default_pipeline": null }
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot