Overview
Health check is used to check whether your application instances are working properly. It is a mechanism used to ensure normal service running. CAE provides three health check mechanisms: liveliness probe, readiness probe, and startup probe.
- Liveliness probe is used to check whether applications are alive. If an instance is abnormal, Kubernetes deletes the instance and performs the detection again until the instances are normal.
When only the liveliness probe is used, if the network fluctuates or the program starts slowly, the instance will keep restarting and remains in the Not ready state. The following solutions are available:
- Use startup probe together. For details, see Cooperation Between Startup and Liveliness Probes.
- Increase Failure Threshold to increase the fault tolerance rate and increase Latency to ensure that the program accepts the liveliness probe detection after startup.

- If status code 200 is returned, the check is successful.
- If a status code other than 200 is returned and the number of consecutive failures reaches Failure Threshold, the check fails.
- Readiness probe is used to check whether an application has been started and is ready to receive requests. If the instance is healthy, traffic will be switched.
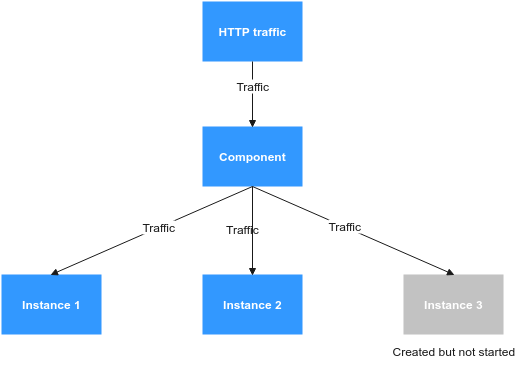
For example, if the number of component instances is increased from 2 to 3, the comparison before and after the readiness probe is configured is as follows:
- When the readiness probe is not configured, the instance has been created, but are not ready to receive traffic due to program reasons. In this case, some traffic still enters instance 3, as shown in Figure 1.
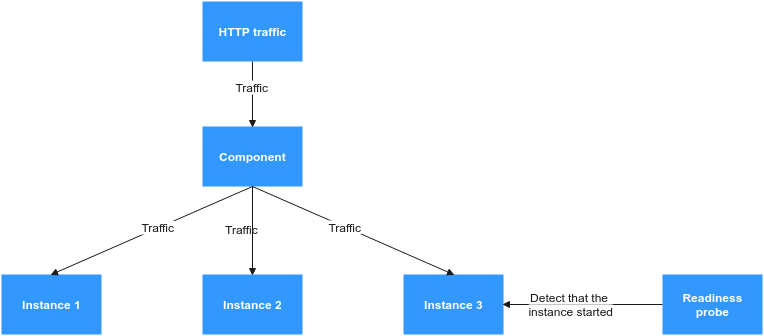
- After the readiness probe is configured, it detects that instance 3 is not started or ready. So instance 3 does not receive traffic, ensuring that all traffic flows to healthy instances 1 and 2.
Figure 2 Before health check

- When detecting that instance 3 is healthy, the readiness probe allows the traffic to pass through and stops the detection.
Figure 3 After health check
- When the startup probe is running, readiness and liveliness probes are disabled. If the startup probe health check fails, the instance will be restarted.
You are advised to use the startup probe together with the liveliness probe.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot