Introduction
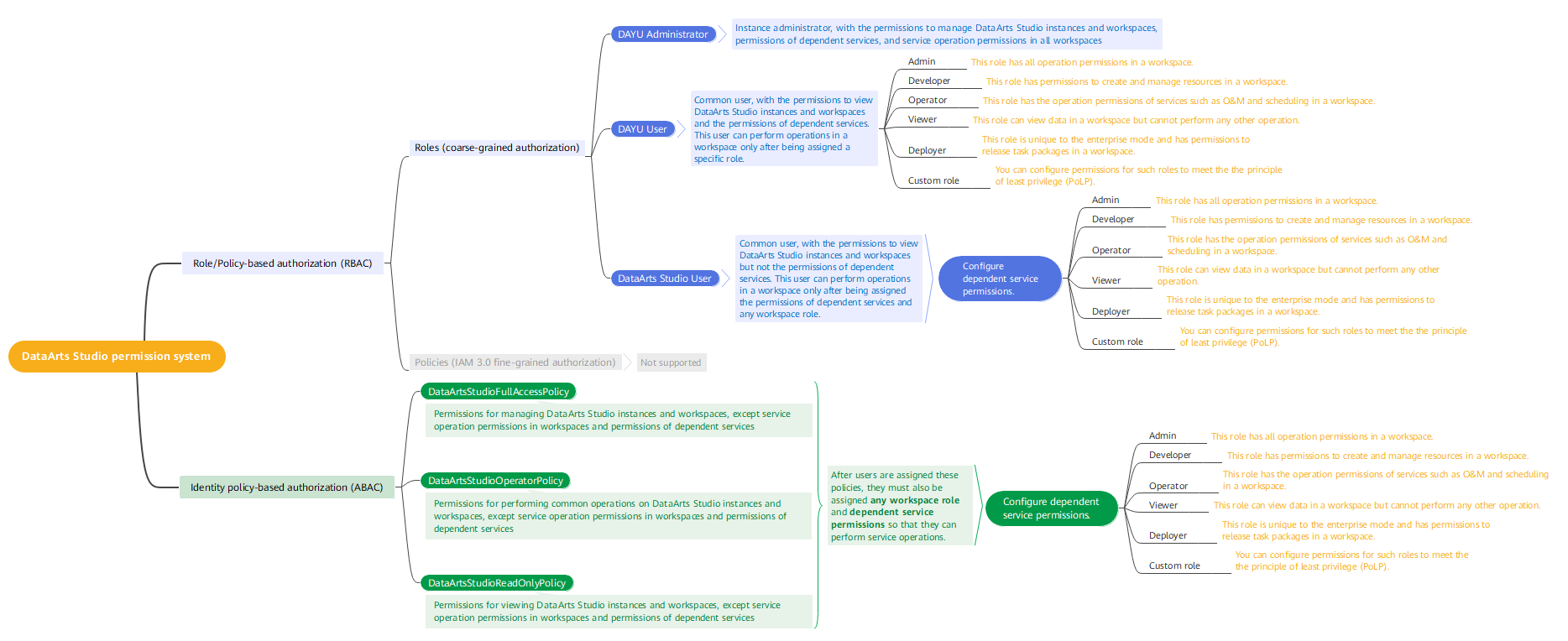
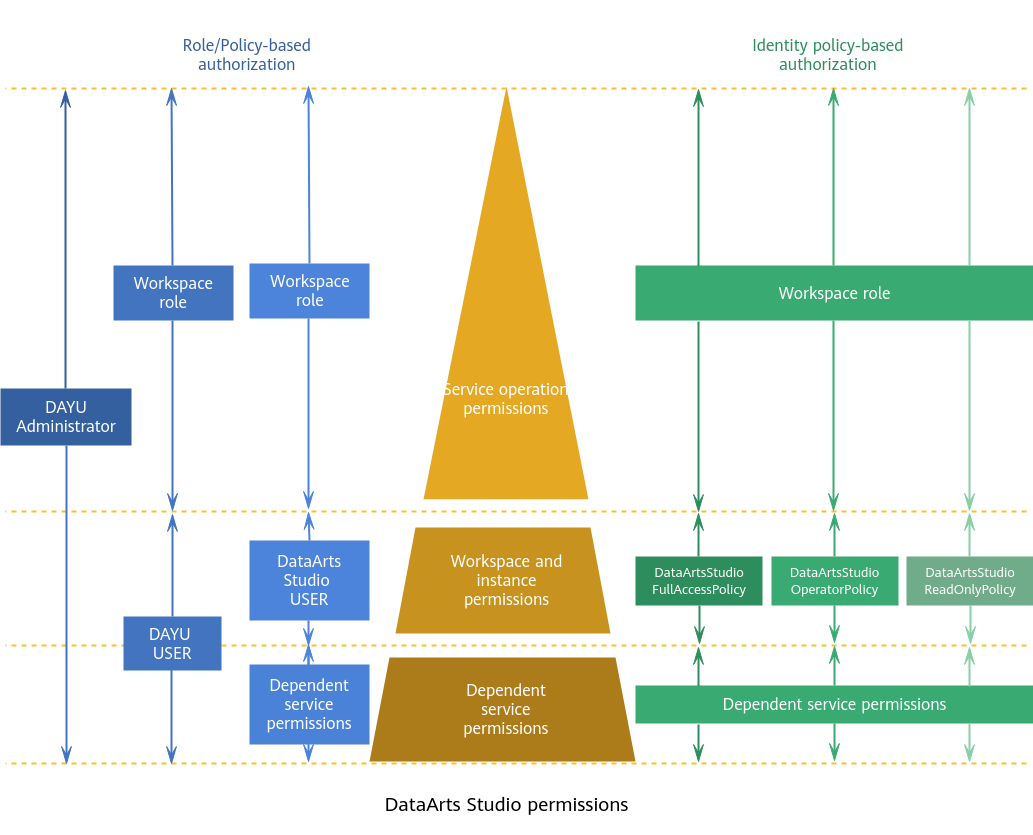
Permission System
You can use Identity and Access Management (IAM) for fine-grained permissions management of your DataArts Studio resources. If your HUAWEI IDaccount does not need individual IAM users, you can skip this section.
With IAM, you can control access to specific Huawei Cloudcloud resources from principals (IAM users, user groups, agencies, or trust agencies). IAM supports role/policy-based authorization and identity policy-based authorization.
The following table describes their differences.
|
Authorization Model |
Core Relationship |
Permissions |
Authorization Method |
Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Role/Policy |
User-permission-authorization scope |
NOTE:
DataArts Studio supports system-defined roles (DAYU Administrator, DAYU User, and DataArts Studio User) but does not support system-defined policies and custom policies. |
Assigning roles or policies to principals |
To authorize a user, you need to add it to a user group first and then specify the scope of authorization. It provides a limited number of condition keys and cannot meet the requirements of fine-grained permissions control. This method is suitable for small- and medium-sized enterprises. |
|
Identity policy |
User-policy |
|
|
You can authorize a user by attaching an identity policy to it. User-specific authorization and a variety of key conditions allow for more fine-grained permissions control. However, this model can be hard to set up. It requires a certain amount of expertise and is suitable for medium- and large-sized enterprises. |
Assume that you want to grant IAM users permission to create ECSs in CN North-Beijing4 and OBS buckets in CN South-Guangzhou. With role/policy-based authorization, the administrator needs to create two custom policies and assign both to the IAM users. With identity policy-based authorization, the administrator only needs to create one custom identity policy and configure the condition key g:RequestedRegion for the policy, and then attach the policy to the users or grant the users the access permissions to the specified regions. Identity policy-based authorization is more flexible than role/policy-based authorization.
- If both permissions contain the deny action, the deny policy prevails.
- The allow actions in the two permissions both take effect.
API Calling Permissions
If you use IAM users in your account to call an API, the IAM users must be granted the required permissions.
|
Authorization Method |
Required Permissions |
Authorization Content |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Role/Policy-based authorization |
To call an API, you must have the required role permissions. (DataArts Studio does not support system-defined policies or custom policies in role/policy-based authorization.) |
You can configure any of the following roles to grant permissions:
|
For example, an IAM user can call the API for querying the DataArts Studio instance list only if the user has been assigned one of the following roles: DAYU Administrator, DAYU User, and DataArts Studio User. |
|
Identity policy-based authorization |
To call an API, you must have the required system-defined policy permissions, or have the policy corresponding to the action. |
You can configure any of the following system-defined policies to grant permissions:
|
For example, an IAM user can call the API for querying the DataArts Studio instance list only if the user has been assigned the DataArtsStudioFullAccessPolicy system policy or a custom policy that contains the DataArtsStudio:instance:list action. |
|
The permissions for calling the following APIs can be assigned based on the corresponding actions. For details, see Table 2.
|
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot