Adding a Salt in the password Field When Creating a Node
When a node is created through the API, you need to add a salt to the password field to safeguard the password. The procedure is as follows:
The salt must be set based on the password complexity requirements:
- A string of 8–26 characters.
- Contains at least three of the following character types: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, and special characters !@$%^-_=+[{}]:,./?
- Cannot contain the username or the username spelled backwards.
- Cannot contain the username, the username spelled backwards, or more than two consecutive characters in the username (for Windows ECSs).
Python
To salt a password in the Python 3.7.7 environment, perform the following steps:
pip install passlib
python -c "import base64; from passlib.hash import sha512_crypt; salted_password = base64.b64encode(sha512_crypt.hash('*****', salt='salt', rounds=5000).encode()).decode(); print(salted_password)"
The python crypt package has compatibility issues in macOS. If the package cannot be executed, run it in Linux.
Java
To salt a password in the Java environment, perform the following steps:
- Obtain a random number as the salt.
private static String getCharAndNumr(int length) { String val = ""; Random random = new SecureRandom(); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { // Indicates whether to output letters or digits. String charOrNum = random.nextInt(2) % 2 == 0 ? "char" : "num"; // Character string if ("char".equalsIgnoreCase(charOrNum)) { // Indicates whether an upper-case or lower-case letter is obtained. int choice = random.nextInt(2) % 2 == 0 ? 65 : 97; val += (char) (choice + random.nextInt(26)); } else if ("num".equalsIgnoreCase(charOrNum)) {// Digit val += String.valueOf(random.nextInt(10)); } } return val; } - Generate a salt.
private static String generateSalt() { String salt; try { salt = "$6$" + getCharAndNumr(16); }catch (Exception e){ salt = defaultSalt; } return salt; } - Generate a ciphertext password based on the salt.
public static String getSaltPassword(String password) { if(StringUtils.isBlank(password)) { throw new BizException("password is empty"); } String salt = generateSalt(); Crypt crypt = new Crypt(); return crypt.crypt(password, salt); } - Encode the value of the password field using Base64.
(Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(AddSaltPasswordUtil.getSaltPassword(cceNodeCreateVo.getPassword()).getBytes()))
- A complete example is as follows:
import java.util.Base64; import java.util.Random; import java.security.SecureRandom; import org.apache.commons.codec.digest.Crypt; import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils; public class PassWord { static String defaultSalt = null; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { System.out.println(Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(PassWord.getSaltPassword("Custom password").getBytes())); } // Generate a ciphertext password based on the salt. public static String getSaltPassword(String password) throws Exception { if(StringUtils.isBlank(password)) { throw new Exception("password is empty"); } String salt = generateSalt(); return Crypt.crypt(password, salt); } //Generate a salt. private static String generateSalt() { String salt; try { salt = "$6$" + getCharAndNumr(16); }catch (Exception e){ salt = defaultSalt; } return salt; } // Obtain a random number as the salt. private static String getCharAndNumr(int length) { String val = ""; Random random = new SecureRandom(); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { // Indicates whether to output letters or digits. String charOrNum = random.nextInt(2) % 2 == 0 ? "char" : "num"; // Character string if ("char".equalsIgnoreCase(charOrNum)) { // Indicates whether an upper-case or lower-case letter is obtained. int choice = random.nextInt(2) % 2 == 0 ? 65 : 97; val += (char) (choice + random.nextInt(26)); } else if ("num".equalsIgnoreCase(charOrNum)) {// Digit val += String.valueOf(random.nextInt(10)); } } return val; } }
Go
The following is an example of adding a salt to a password in the Go environment:
package main
import (
"crypto/rand"
"encoding/base64"
"fmt"
"io"
"github.com/GehirnInc/crypt"
_ "github.com/GehirnInc/crypt/sha512_crypt"
)
var letters = []byte("0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ")
// Generate a random salt of a specified length and restrict its characters to the letters array.
func Salt(size int) ([]byte, error) {
salt := make([]byte, size)
_, err := io.ReadFull(rand.Reader, salt)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error generating salt: %s", err)
}
max := uint8(len(letters))
arc := uint8(0)
for i, x := range salt {
arc = x % max
salt[i] = letters[arc]
}
return salt, nil
}
// Use SHA-512 to encrypt the given password and return the Base64-encoded encryption result.
func PasswordEncrypt(password string) (string, error) {
saltBytes, err := Salt(16)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
salt := "$6$" + string(saltBytes) + "$"
sha512crypt := crypt.SHA512.New()
passwordEncrypted, err := sha512crypt.Generate([]byte(password), []byte(salt))
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("error encrypting the password: %s", err)
}
return base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString([]byte(passwordEncrypted)), nil
}
// Try to encrypt the given password. If the password has been encoded using Base64, the value is returned directly.
func TryPasswordEncrypt(password string) (string, error) {
if _, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(password); err != nil {
return PasswordEncrypt(password)
}
return password, nil
}
// Change the password and encrypt it.
func main() {
encrypt, err := TryPasswordEncrypt("Password ")
if err != nil {
return
}
fmt.Println(encrypt)
}
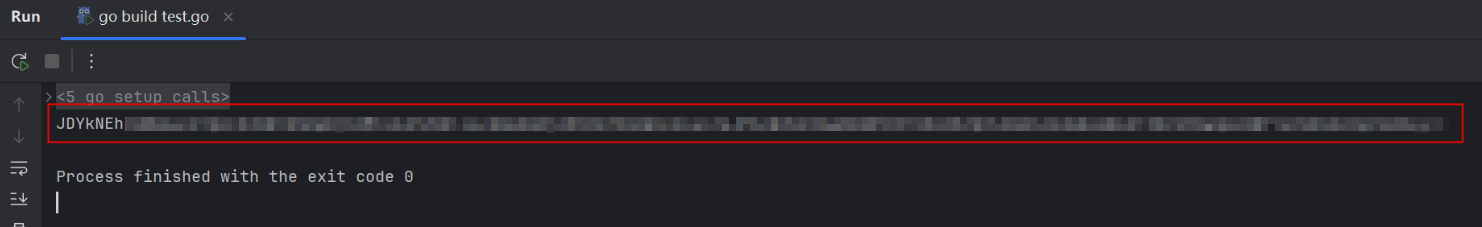
You can change the password in the preceding example. After the code is executed, the salted password is output.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





