Configuring an LDAP Domain
Overview
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is a standard protocol for interacting with directory servers. An LDAP server can centrally manage the ownerships of users and groups. After you bind your file system to an LDAP server, when a user accesses a file in the file system, SFS Turbo will access your LDAP server for user authentication and obtain the user and group ownerships. In this way, standards Linux file UGO permissions are checked. To use this function, you need to first set up an LDAP server (SFS Turbo only supports LDAP v3 currently). Common directory servers that provide LDAP services include OpenLDAP (Linux) and Active Directory (Windows). The implementation varies depending on the directory server. When binding to an LDAP server, you need to specify the corresponding schema. If the configured schema is incorrect, SFS Turbo cannot obtain the correct user and group information, and users will fail to access files in the file system. Schemas that SFS Turbo supports include:
- RFC2307 (Usually selected for OpenLDAP)
- MS-AD-BIS (Usually selected for Active Directory. It supports RFC2307bis and nested groups.)
SFS Turbo also supports active/standby deployment of LDAP servers. If one LDAP server fails and cannot be accessed, SFS Turbo access authentication automatically switches to the standby LDAP server. If all configured LDAP servers are unreachable, all users will lose their access permissions.
After a file system is added to an LDAP domain, SFS Turbo will no longer grant any permissions to users who are not in the LDAP domain.
Constraints
- You can only configure the LDAP domain for NFS SFS Turbo file systems.
- After an SFS Turbo file system is added to an LDAP domain, a single user can be added to a maximum of 512 user groups.
- After an SFS Turbo file system is added to an LDAP domain, any access from users who are not in the LDAP domain will be denied.
- After an SFS Turbo file system is added to an LDAP domain, SFS Turbo fully depends on the LDAP server to determine the users' group memberships. Local group information is no longer valid.
- Before an SFS Turbo file system is added to an LDAP domain, ensure that all users who need to access the file system are in the LDAP domain and added to the desired user groups.
Joining a Domain
- Log in to the SFS Turbo console.
- In the SFS Turbo file system list, find the NFS file system you want to add to an LDAP domain and click its name to go to its details page.
- Click the LDAP Domain tab.
- Click Join Domain.
Figure 1 LDAP domain configuration page
- Enter the information required for joining an LDAP domain and click OK.
Figure 2 Entering configuration information
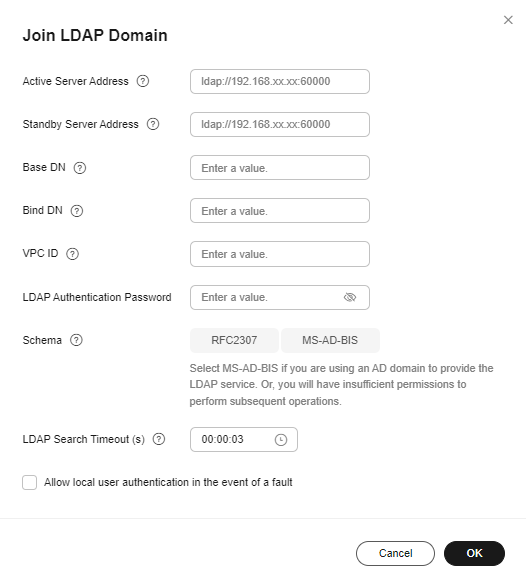
Table 1 Parameters required for joining an LDAP domain Parameter
Description
Active Server Address
Mandatory
The URL of the LDAP server. The server address is in either of the following format: ldap://{ip_address}:{port_number} or ldaps://{ip_address}:{port_number}, for example, enter ldap://192.168.{xx}.{xx}:60000.
Standby Server Address
Optional
The URL of the standby LDAP server. The server address is in either of the following format: ldap://{ip_address}:{port_number} or ldaps://{ip_address}:{port_number}, for example, enter ldap://192.168.{xx}.{xx}:60000.
Base DN
Mandatory
The start distinguished name (DN). Search operations start below the entry specified by this base DN.
Bind DN
Optional
The DN to bind to the LDAP server. This bind operation is used to authenticate the client (SFS Turbo file system) to the LDAP server and specify the authorization information that will be used for subsequent operations. Later, when users behind the client access the LDAP server, they need to specify this bind DN.
VPC ID
Optional
The ID of the VPC that the LDAP server can connect to in SFS Turbo multi-VPC scenarios.
LDAP Authentication Password
Optional
The LDAP authentication password.
Schema
Optional
The LDAP template information. Supported options are RFC2307 and MS-AD-BIS.
Select MS-AD-BIS if you are using an AD domain to provide the LDAP service. Or, you will have insufficient permissions to perform subsequent operations.
LDAP Search Timeout (s)
Optional
The timeout interval when the SFS Turbo file system is querying the LDAP server. You can select no more than 30 seconds.
Allow local user authentication in the event of a fault
Select this parameter.
- Wait for a while and check that the active server address, standby server address, task type, task status, base DN, bind DN, VPC ID, schema, LDAP search timeout, and allow local authentication upon fault information are displayed on the LDAP domain configuration page.
Leaving a Domain
- Log in to the SFS Turbo console.
- In the SFS Turbo file system list, find the NFS file system you want to remove from an LDAP domain and click its name to go to its details page.
- Click the LDAP Domain tab.
- Locate the domain that the file system has joined and click Leave Domain in the Operation column.
- Confirm the information and click OK.
- Check that the LDAP domain disappears from the LDAP Domain page.
Figure 3 Domain left successfully
You can perform the remove operation if an SFS Turbo file system fails to join a domain.
Related Operations
For an NFS file system, you can also click Edit in the Operation column to modify the information of the joined domain.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





