Submodules
Background
A submodule is a Git tool used to manage shared repositories. It allows you to embed a shared repository as a subdirectory in a repository. You can isolate and reuse repositories, and pull latest changes from or push commits to shared repositories.
You may want to use project B (a third party repository, or a repository developed by yourself for multiple parent projects) in project A, and use them as two separate projects. Submodules allow you to clone a Git repository as a subdirectory into another Git repository while keeping commits separate.
The submodules are recorded in a file named .gitmodules, which records the information about the submodules.
[submodule "module_name"] # Submodule name path = file_path # File path of the submodule in the current repository (parent repository). url = repo_url # Remote repository IP address of the submodule (sub-repository).
In this case, the source code in the file_path directory is obtained from repo_url.
Using the Console
- Creating a submodule
- Entry 1:
You can create a submodule on the Files tab page.
Click
 and select Create Submodule, as shown in the following figure.
and select Create Submodule, as shown in the following figure.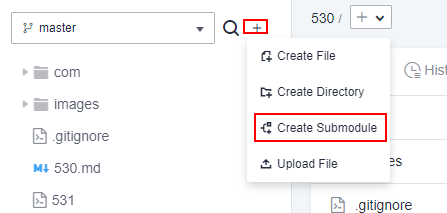
- Entry 2
You can create a submodule in the repository settings.
Choose .
- Remarks:
You can use either of the preceding methods to Create submodule.
Configure the following parameters and click OK.
Table 1 Parameters of creating a sub-repository Parameter
Description
Submodule
Select a repository as the submodule.
Submodule Branch
Select the target branch of the submodule to be synchronized to the parent repository.
Submodule Path
The storage path of the submodule in the parent repository. Use slashes (/) to separate levels, as shown in the following figure.
Commit Message
Remarks for creating a submodule. You can find the operation in the file history.
After the creation is complete, you can find the submodule (sub-repository) in the corresponding directory of the repository file list. The icon on the left of the corresponding file is
 .
.
- Entry 1:
- Viewing, synchronizing, and deleting a submodule
Choose Settings > Repository Management > Submodules. On the displayed page, repository administrators can view, synchronize, and delete submodules.
- Synchronizing deploy keys
If a submodule is added on the Git client, the repository administrator needs to synchronize the deploy key of the parent repository to the submodule on the Settings > Repository Management > Submodules page. In this way, the submodule can also be pulled during the build of the parent repository.
Using the Git Client
Creating a submodule
git submodule add <repo> [<dir>] [-b <branch>] [<path>]
Example:
git submodule add git@***.***.com:****/WEB-INF.git
Pulling a repository that contains a submodule
git clone <repo> [<dir>] --recursive
Example:
git clone git@***.***.com:****/WEB-INF.git --recursive
Updating a submodule based on the latest remote commit
git submodule update --remote
Pushing changes to a submodule
git push --recurse-submodules=check
Deleting a submodule
- Delete the entry of a submodule from the .gitsubmodule file.
- Delete the entry of a submodule from the .git/config file.
- Run the following command to delete the folder of the submodule.
git rm --cached {submodule_path} # Replace {submodule_path} with your submodule path.
Omit the slash (/) at the end of the path.
For example, if the submodule is stored in src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/, run git rm --cached src/main/webapp/WEB-INF.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





