Application Lifecycle Management
The core of enterprise cloud adoption is to migrate various application systems that support enterprise production and operations to the cloud. The primary goal is to securely and reliably run application systems on the cloud while using cloud computing advantages to improve application system's resilience, agility, security, performance, etc. Additionally, the aim is to develop and update cloud-based applications, adopt new technologies for product, service, and model innovations, create advanced features, streamline operations, enrich user experience, and increase revenue.
However, migrating application systems to the cloud can be complex and systematic. It requires planning through every stage of the application's life based on Application Lifecycle Management (ALM). This ensures the benefits of cloud computing are maximized at each step.
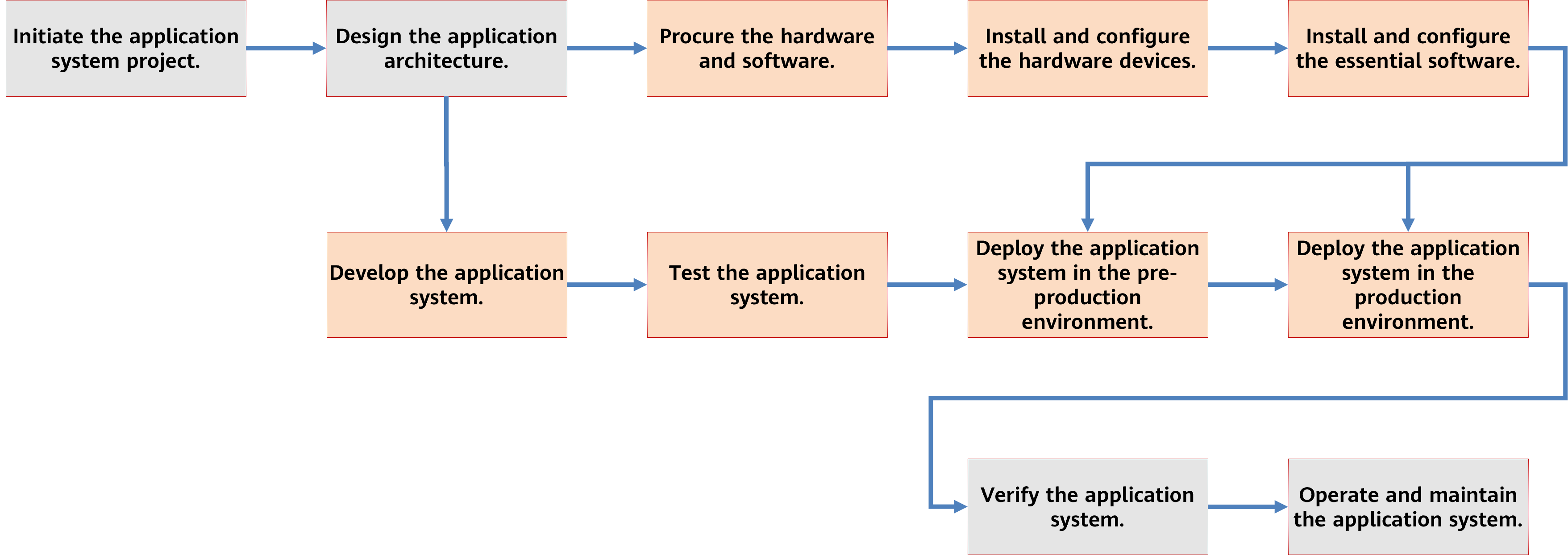
The following figure shows the application lifecycle management process based on traditional IT. Application systems are needed to be deployed on hardware resources. However, the procurement and delivery of hardware resources take a long time. Once an application system project starts, you must purchase both hardware devices and essential software. After the hardware devices are ready, you need to install them in your own or leased data center. Then, install and configure the operating system and virtualization software on the hardware devices to build the pre-production environment and production environment for the application systems. After the application system is developed and tested, it can be directly deployed and run in the pre-production and production environments. Enterprises often buy ready-made commercial software like ERP and CRM. With such software, enterprises do not need to develop custom code but might require integrating the software with peripheral systems. However, delays in buying and delivering hardware can slow down the deployment process.
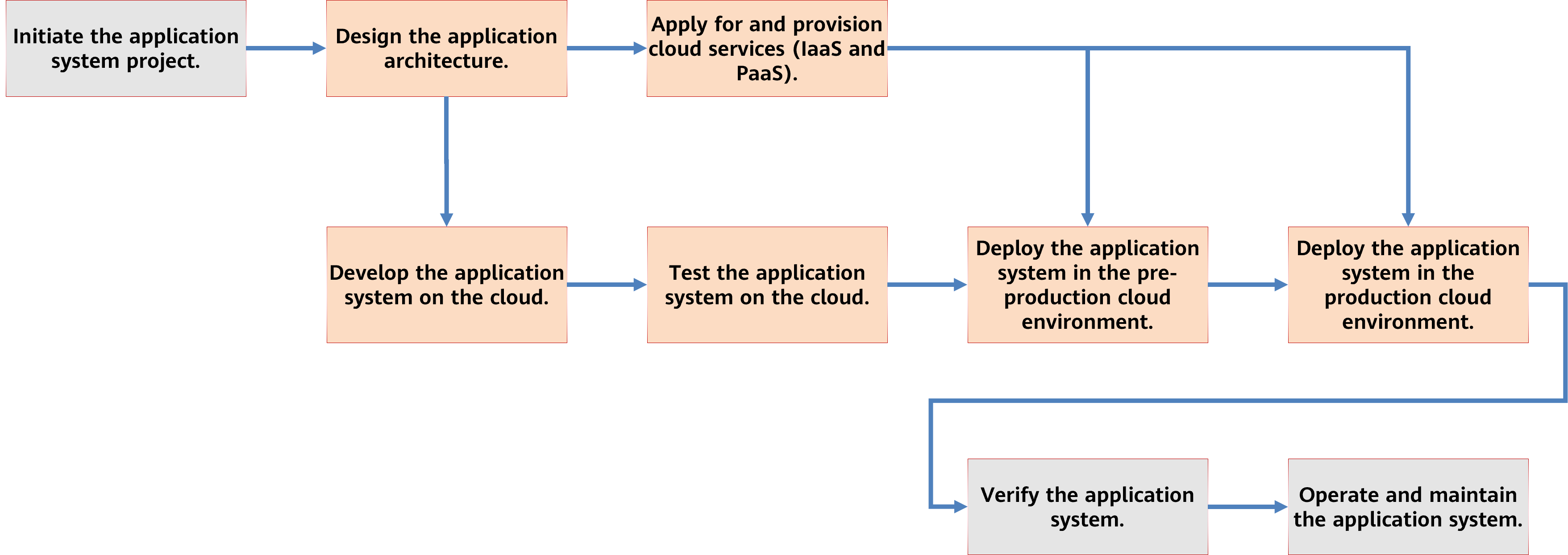
The basic process of constructing cloud computing-based application systems does not change too much. Yet, the processes (marked in light yellow in the above figure) in the application lifecycle need adjustments to fit cloud computing features and maximize its benefits.
The cloud platform has a unified resource pool that offers IaaS and PaaS services for application systems. This means you do not have to buy hardware devices or basic software like operating systems and virtualization software separately. Instead, you can simply buy and provision the IaaS and PaaS services from the cloud platform to set up test, pre-production, and production environments. This saves time on procurement and delivery. The steps, in the preceding figure, for software and hardware procurement, hardware installation and configuration, and essential software deployment and configuration, can be included in the cloud service application and provisioning process in the cloud computing environment.
Additionally, the cloud platform provides a cloud native DevOps development toolchain, like Huawei Cloud's CodeArts and open APIs. These tools and APIs enable you to develop and test application systems, and use pipelines to directly deploy application systems in the pre-production and production environments on the cloud. Such application systems are developed, tested, deployed, and run on the cloud, making them cloud-native applications. In this way, the value of cloud computing can be fully utilized. The following figure shows the lifecycle of cloud computing applications.
Cloud computing-based application lifecycle management must match the cloud operating model described in the preceding chapters. The roles of the CCoE (or central IT team) and application teams vary across different models, affecting their responsibilities and how they work together. As a result, the application lifecycle management process varies by cloud operating model.
Decentralized Operating Model
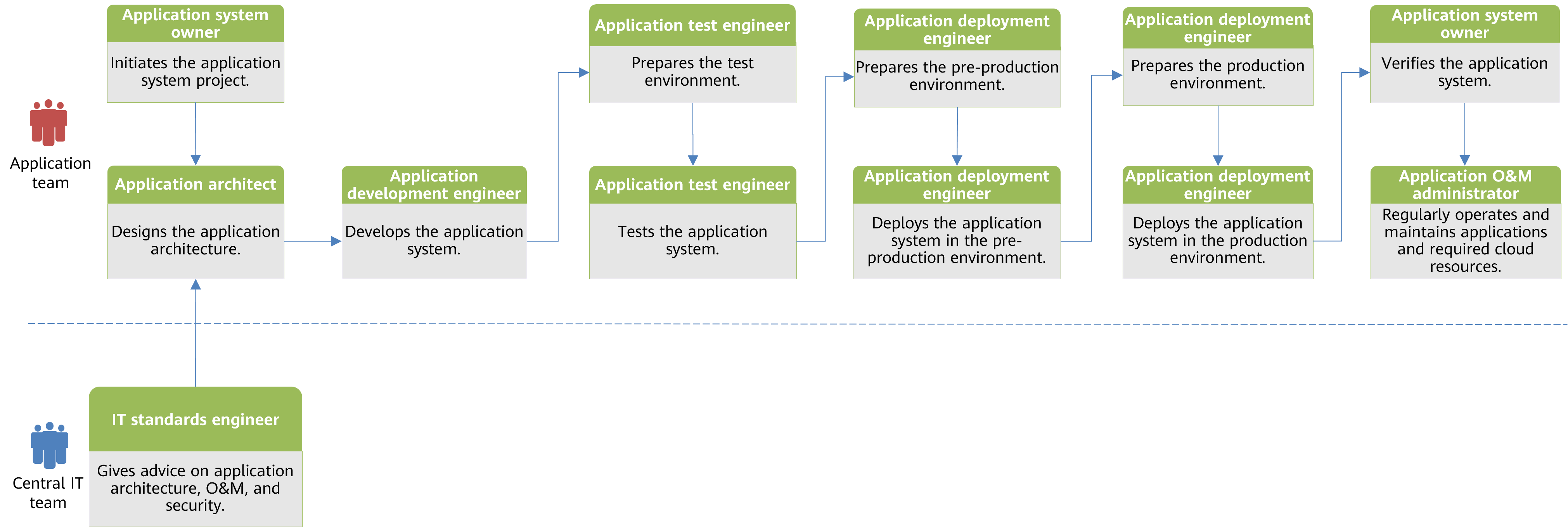
Centralized Operating Model
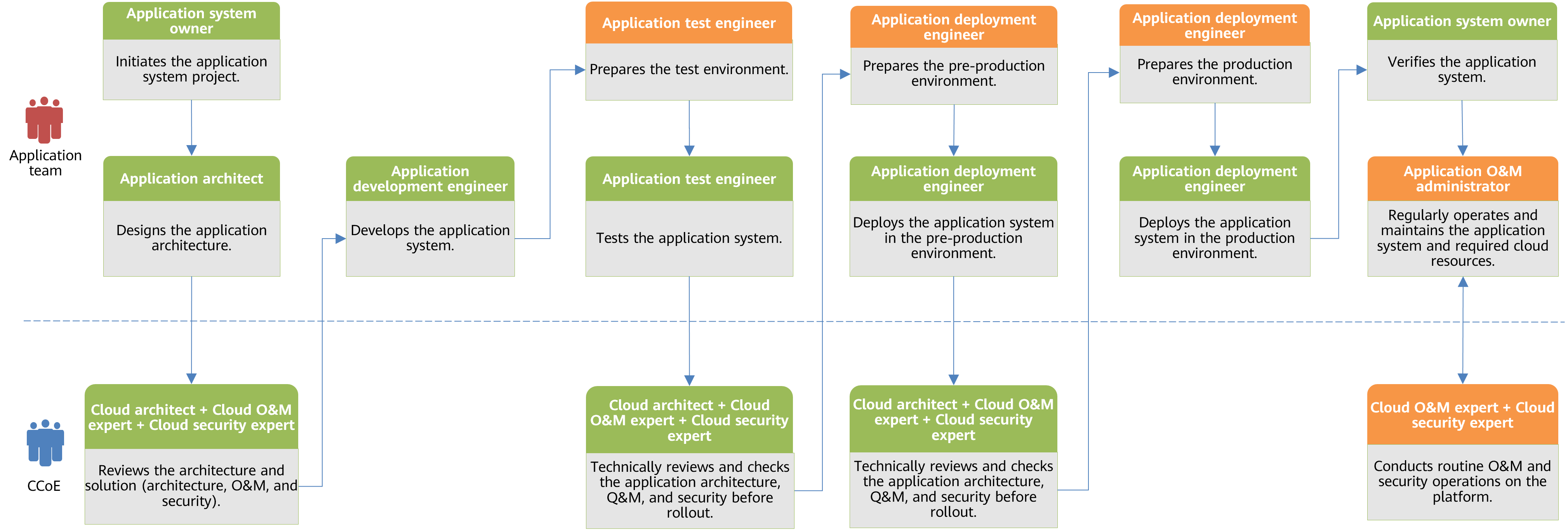
The following figure shows the application life cycle management process under the centralized operating model. The CCoE team deploys, operates, and maintains the cloud resources required by the application system. This allows the application team to concentrate solely on designing, developing, testing, deploying, and maintaining their applications without worrying about infrastructure or cloud resource deployment and management. Cloud architects, O&M experts, and security experts from the CCoE team participate in the application architecture design phase. They review the architecture, O&M, and security of the application team's design solution to ensure that the solution complies with the design principles and best practices of cloud technologies, maximizing the value of cloud computing. Cloud architects, O&M experts, and cloud security experts technically review and check the application system before deploying the application system in pre-production and production environments. This ensures the implemented solution matches the original design and prevents deviations between design and development phases. Through the reviews and checks, the CCoE team will be able to help the application team significantly improve the resilience, security, and performance of the application system on the cloud.
In the application O&M phase, the CCoE team handles daily O&M and security operations for cloud resources and the platform layer. The application team manages routine O&M and ensures security operations at the application layer, including measures like blocking SQL injections.
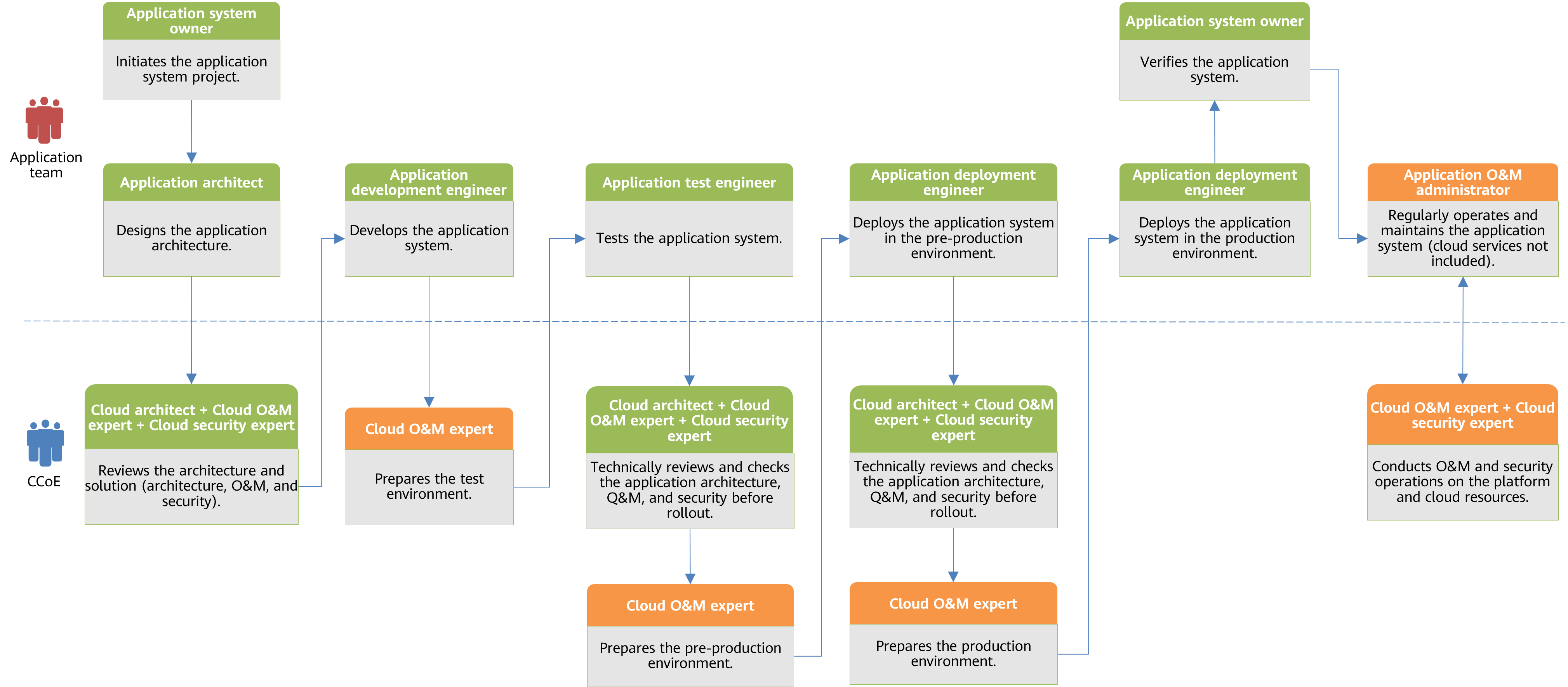
Enablement and Collaborative Operating Model
In this model, the application lifecycle management process remains similar to the centralized operating model. It includes all phases, though the owners and duties of some phases are changed. The phases marked in yellow in the following figure are changed.
In this model, the CCoE team enables the application team to take full responsibility for the deployment and O&M of cloud resources. This reduces the burden of the CCoE team, boosts the application team's independence, and enhances the application system's flexibility. To prevent inconsistent standards for independent cloud resource deployment and O&M by each application team, the CCoE team must formulate IT standards and ensure all teams follow them.
The CCoE team and application team must work closely to ensure secure and stable running of service systems on the cloud. In terms of O&M, the CCoE team performs routine O&M of the cloud platform or cloud IT infrastructure, and the application team manages routine O&M of applications and required cloud resources. If there is a service fault, the two teams work together to locate and rectify the fault. In terms of security operations, the CCoE team handles platform-level security and security operations. Application teams manage application system security and protect related cloud resources, including defenses against threats like SQL injections.
Like the centralized operating model, the cloud architects, O&M experts, and security experts from the CCoE team participate in the application architecture design phase. They review and check the application system before deploying the application system in pre-production and production environments.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





