Enablement and Collaborative Operating Model
The enablement and collaborative operating model combines the strengths of both decentralized and centralized operating models, striking a balance between centralized management and service system agility. In the enablement and collaborative operating model, the CCoE team is responsible for centrally building and maintaining Landing Zone, including key components like the backbone network, IAM, and compliance audit systems on the cloud. The CCoE team defines unified IT standards, processes, and architectures while implementing centralized IT governance across the enterprise-wide cloud environment. The CCoE team also enables the application teams to take full ownership of the deployment and O&M of the cloud resources required by service systems. This division of responsibilities eases the workload of the CCoE team, enhances the autonomy of the application teams, and further boosts system agility. To avoid inconsistencies stemming from independent deployments and cloud resource O&M, the CCoE team establishes IT governance policies, mandating compliance across business units. It also creates a unified service catalog to ensure the application teams use only cloud services authorized by the CCoE team for development and deployment.
Close collaboration between the CCoE team and the application teams is essential to maintaining secure, stable service systems while optimizing costs. For O&M, the CCoE team handles routine maintenance of cloud IT infrastructure, including the backbone network, IAM, and compliance audit systems. The application teams manage the routine O&M of applications and their required cloud resources. If there is a service system fault, the CCoE and application teams work together to identify and resolve the issue. In terms of security, the CCoE team manages platform-level protection and centralized security operations. The application teams focus on application-level security, such as preventing SQL injection. Regarding cost management, the CCoE team is responsible for centralized cost management, including centralized cost planning, monitoring, analysis, and optimization, while the application teams add cost tags to cloud resources.
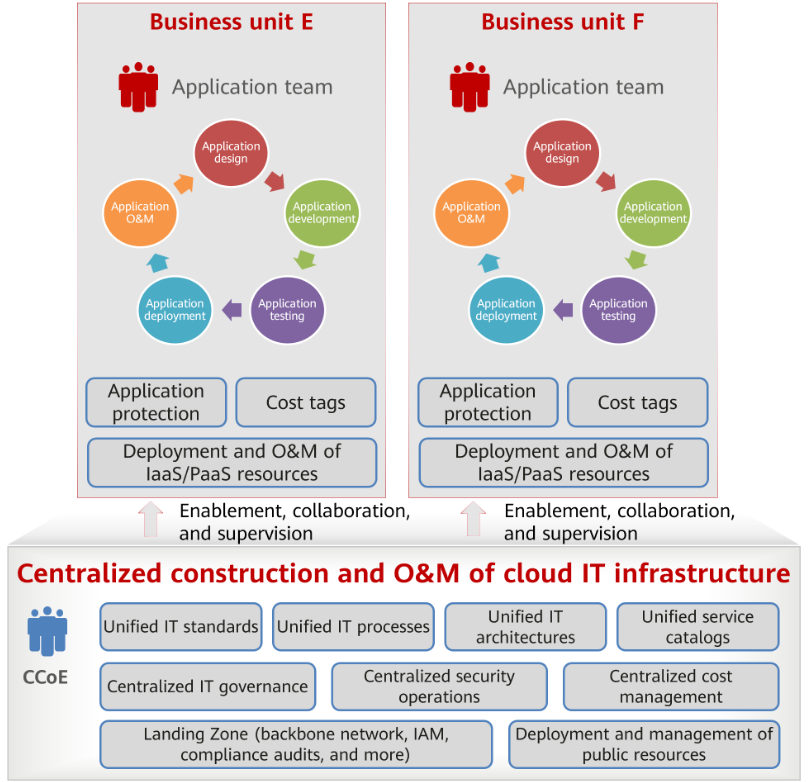
The enablement and collaborative operating model incorporates the advantages of both centralized and decentralized models.
- A balance between centralized control and agility: This model ensures centralized management and unified control and grants business units a degree of autonomy. These features enhance service agility.
- Close collaboration: The CCoE team works hand-in-hand with the application teams within business units, preventing buck-passing and boosting overall operational efficiency.
- Cost optimization: Unified construction of public resources, centralized procurement, and resource integration improve resource utilization and reduce TCO.
- A global view: The CCoE team monitors and analyzes enterprise-wide cloud resource usage, allowing for optimized resource configurations.
The enablement and collaborative operating model also has its disadvantages.
- Complex implementation: Complex IT governance measures must be developed to ensure business units comply with unified IT standards. Alongside this, a unified service catalog must be created and maintained for streamlined operations.
- High capability requirements: Effective implementation demands advanced management expertise and extensive experience in IT governance. CCoE team members must possess higher-level skills and act as advocates, guiding application teams to deploy and manage cloud resources in alignment with best practices.
The enablement and collaborative operating model works well for agile systems, like self-developed digital marketing systems, that need quick updates and fast releases of new features to meet fast-changing market demands. Additionally, this operating model is effective for stable service systems supported by independent application teams with robust IT capabilities.
The three kinds of cloud operating models adhere to different types of service systems and organizational structures. In large enterprises, these kinds of models often coexist, working together to facilitate agile iteration while ensuring secure, stable operations for diverse service systems.
The chosen cloud operating models will significantly influence the application lifecycle management process, which will be elaborated on in the following section.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





