OPS06-01 Establishing an Observability System
Observability is a concept in system theory, which refers to whether the status of a system can be observed and reproduced by external systems. As cloud native and microservice architecture evolve, IT systems have higher demands for observability. Observability is how much you learn about the internal state or condition of a complex system by understanding its external output. A system that is highly observable allows for quicker and more accurate identification of issue root causes without extra testing or coding.
- Risk level
High
- Key strategies
The observability system is built on the deterministic recovery proposition, determining the construction of deterministic recovery capabilities and SLOs achievement. The observability system plays a key role in the recovery duration of some faults. As shown in the following figure, the average MTTR duration consists of the average discovery duration, average demarcation duration, and average handling duration. The observability system determines the discovery duration and demarcation duration. In an event, the shorter the MTTR duration, the higher the possibility of achieving the overall SLO.
MTTR = Average discovery duration + Average demarcation duration + Average handling duration
- Design suggestions
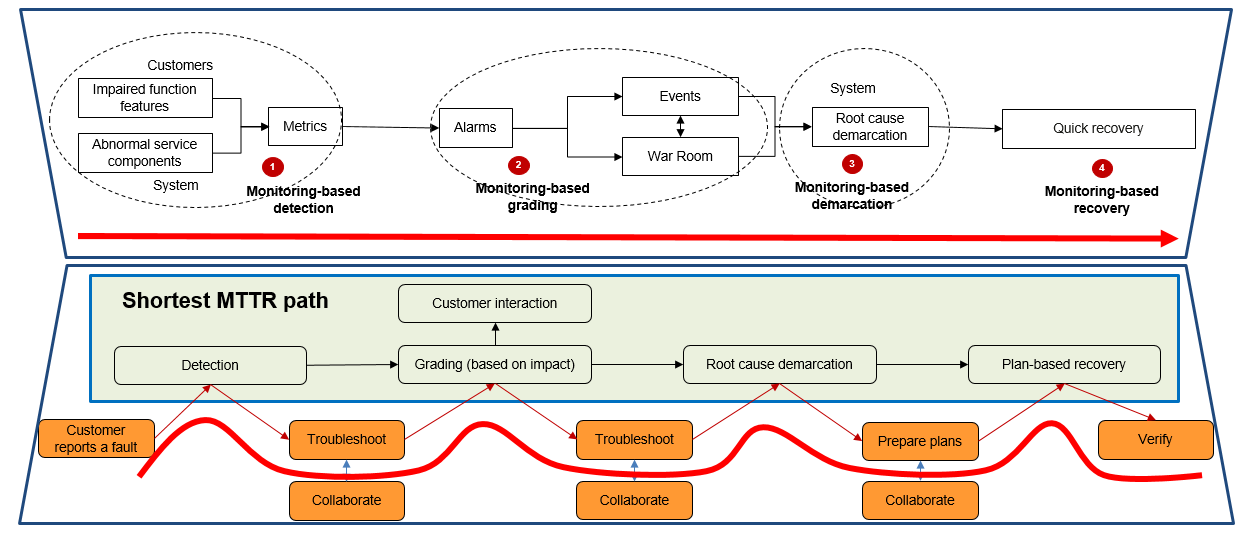
The core design logic of the MTTR-oriented observability system is to identify the shortest recovery path. As shown in the following figure, in the fault recovery MTTR logic, when a service fault happens, it is detected, graded, and analyzed before being pinpointed, located, and fixed. These steps are mostly done manually. To shorten the time, monitoring-based detection, grading, and demarcation must be enabled. If this design can be achieved, the shortest path of MTTR can be formed.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





