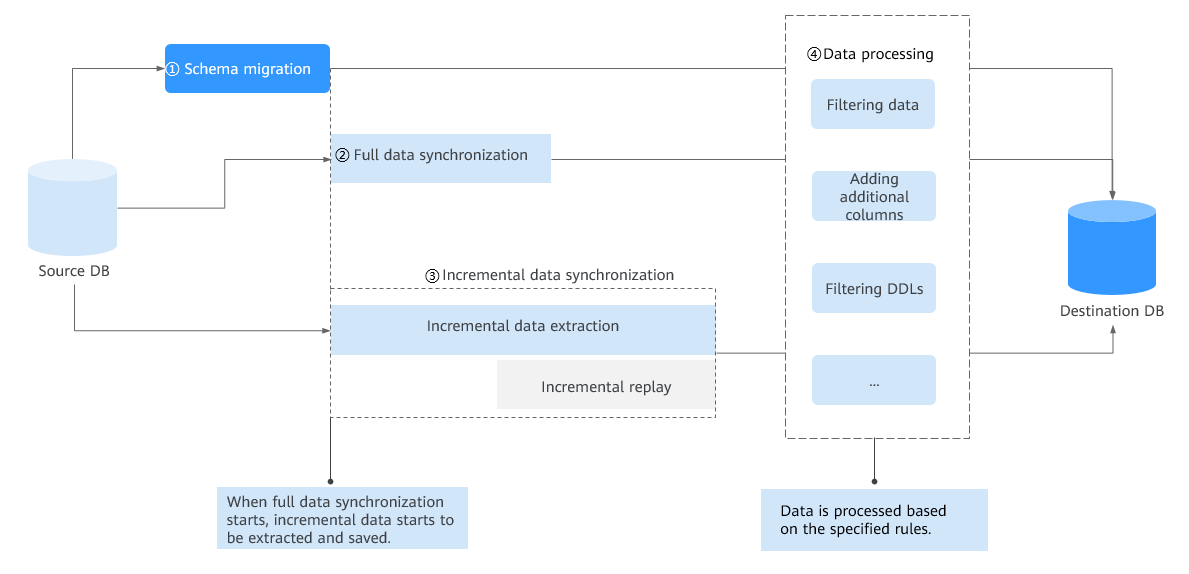
Synchronization Overview
Real-time synchronization refers to the real-time flow of key service data from sources to destinations while consistency of data can be ensured.
It is different from migration. Migration means moving your overall database from one platform to another. Synchronization refers to the continuous flow of data between different services.
You can use real-time synchronization in many scenarios such as real-time analysis, report system, and data warehouse environment.
Real-time synchronization is mainly used for synchronizing tables and data. It can meet various requirements, such as many-to-one, one-to-many synchronization, dynamic addition and deletion of tables, and synchronization between tables with different names.
Supported Database Types
The following table lists the source database and destination database types supported by DRS in real-time synchronization.
|
Source DB |
Destination DB Type |
Synchronization Mode |
Related Documents |
|---|---|---|---|
|
RDS for MySQL |
Incremental Full+Incremental |
From MySQL to MySQL (To the cloud) |
|
RDS for MySQL |
|
Incremental Full+Incremental |
From MySQL to MySQL (Out of the cloud) |
|
RDS for PostgreSQL |
Incremental Full Full+Incremental |
|
|
DDM |
RDS for MySQL |
Incremental Full Full+Incremental |
From DDM to MySQL (To the cloud) |
|
Incremental Full Full+Incremental |
From DDM to MySQL (Out of the cloud) |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





