Configuring an ISO File as a Local Image Source
Context
When you install software on a Linux ECS, the network may be disconnected or resources on the network may be invalid, resulting in software installation failures. In this case, you can configure an ISO file as a local image source to install the software.
Package Managers
Before configuring a local source, you need to determine the package manager to be used. Generally, there are three types of package managers: yum, apt, and zypper.
- yum is for RHEL-based OSs: RHEL, CentOS, EulerOS, and Fedora.
- apt is for Debian and Ubuntu.
- zypper is for SUSE and openSUSE.
Configure a Local Image Source
Configure a local image source by following the instructions in yum, apt, or zypper.
- yum
- Upload the ISO file to the ECS. Run the following command to mount the file to the /mnt directory:
mount XXX.iso /mnt
- Enter the /etc/yum.repo.d directory where the yum configuration file is stored and back up all .repo files. Then, create a new .repo configuration file, for example local.repo. Add the following information to the local.repo file:
[rhel-local] name=local baseurl=file:///mnt enabled=1 gpgcheck=0
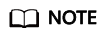
The /mnt directory specified in the configuration file must be the same as the mounting directory of the ISO file.
- Clear yum.
- Generate a new cache.
- Upload the ISO file to the ECS. Run the following command to mount the file to the /mnt directory:
- apt
- zypper
- Upload the ISO file to the ECS.
- Add the ISO file as the source.
sudo zypper addrepo iso:/?iso=/media/SOFTWARE/openSUSE-11.4-DVD-i586.iso DVDISO
In the preceding command:
- /media/SOFTWARE/openSUSE-11.4-DVD-i586.iso is the location of the ISO file.
- DVDISO is the source alias.
- Check whether the source is successfully added.
- Refresh the source.
Examples
The operations in Configure a Local Image Source may be different depending on the OS version. Basically, you need to add a source and refresh it. Debian 10.1.0 and CentOS 8.0 are used as examples to describe how to add a local source.
- Debian 10.1.0
Run cat /etc/apt/sources.list to check whether the sources.list file contains a default cdrom source.
Figure 1 Viewing the source
The source directs to the CD-ROM drive /dev/cdrom. Debian 10.1.0 provides a soft link to link the CD-ROM drive to /media/cdrom.
Figure 2 Checking the media directory
Therefore, mount the ISO file to /media/cdrom.
- CentOS 8.0
- Mount the ISO file to the /mnt directory.
- Rename all source files except CentOS-Media.repo in the /etc/yum.repo.d directory as .bak files or move them to another directory.
- Modify the CentOS-Media.repo file.
Figure 3 Modifying the CentOS-Media.repo file
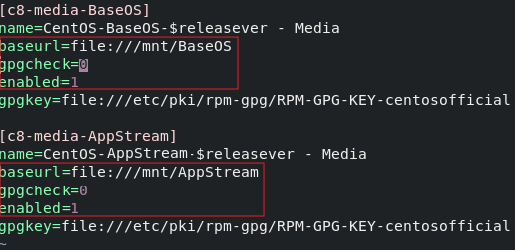
The modifications in the red box are as follows:
- Set baseurl to file:///mnt/BaseOS and file:///mnt/AppStream. mnt is the mounting directory of the ISO file. Delete invalid paths from the default configuration, or a checksum error will occur.
- Change the value of gpgcheck to 0, indicating that the check is not performed.
- Change the value of enabled to 1 for the configurations to take effect.
- Clear yum and generate a new cache.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





