Configuring a Pipeline Build Task
- Scenario 1: If a software package is generated using Jenkins, for example, a JAR package, use the software package deployment scenario in the script. During deployment, the built software package is uploaded to the OBS bucket and the CAE component is upgraded.
- Scenario 2: If an image package is generated using Jenkins, use the image deployment scenario in the script. During deployment, the built image package is uploaded to the SWR image repository and the CAE component is upgraded.
This section uses the scenario where the instance in Configuring a Pipeline Script is a JAR package as an example.
Creating a GitLab Credential
Use the account and password with the GitLab code repository permission to create a credential in Jenkins for pulling GitLab code.
- Enter http://{IP address of the Linux VM where Jenkins is installed}:8080 in the address box of the browser to log in to Jenkins.
- Choose Manage Jenkins > Configure System. In Configuration, select Gitlab.
- Click Add under Credentials and select Jenkins.
- Configure the GitLab account password and click Add to save the configuration.
- Choose Manage Jenkins > Manage Credentials to view the configured credentials.
The unique ID is used in Configuring a Pipeline Script.
Creating a Pipeline Task
- Enter http://{IP address of the Linux VM where Jenkins is installed}:8080 in the address box of the browser to log in to Jenkins.
- Click New Item.
- Enter the task name, for example, test-demo, select Pipeline, and click OK.
Configuring a Build Trigger
There are two build methods:
- In Jenkins, click Build Now on the right of the task to trigger the pipeline task.
- After the code is submitted through GitLab, the Jenkins build is automatically triggered. In this mode, you can also manually trigger the build.
The second method is used as an example.
- Configure the Jenkins build trigger.
- Select Build when a change is pushed to GitLab, save the GitLab webhook URL (required when configuring GitLab webhook), and click Advanced in the lower right corner.
- Select Filter branches by regex and configure the build task to be triggered after the specified branch is changed. In the example, the branch name is main. Click Generate to generate a secret token and save it. The token will be used for configuring GitLab webhook.
- Configure GitLab webhook.
- Log in to GitLab and go to the code repository. In this example, the repository name is test-demo.
- Choose Settings > Webhooks, and set URL and Secret token to the GitLab webhook URL and secret token obtained in 1.
Figure 1 Webhooks configuration
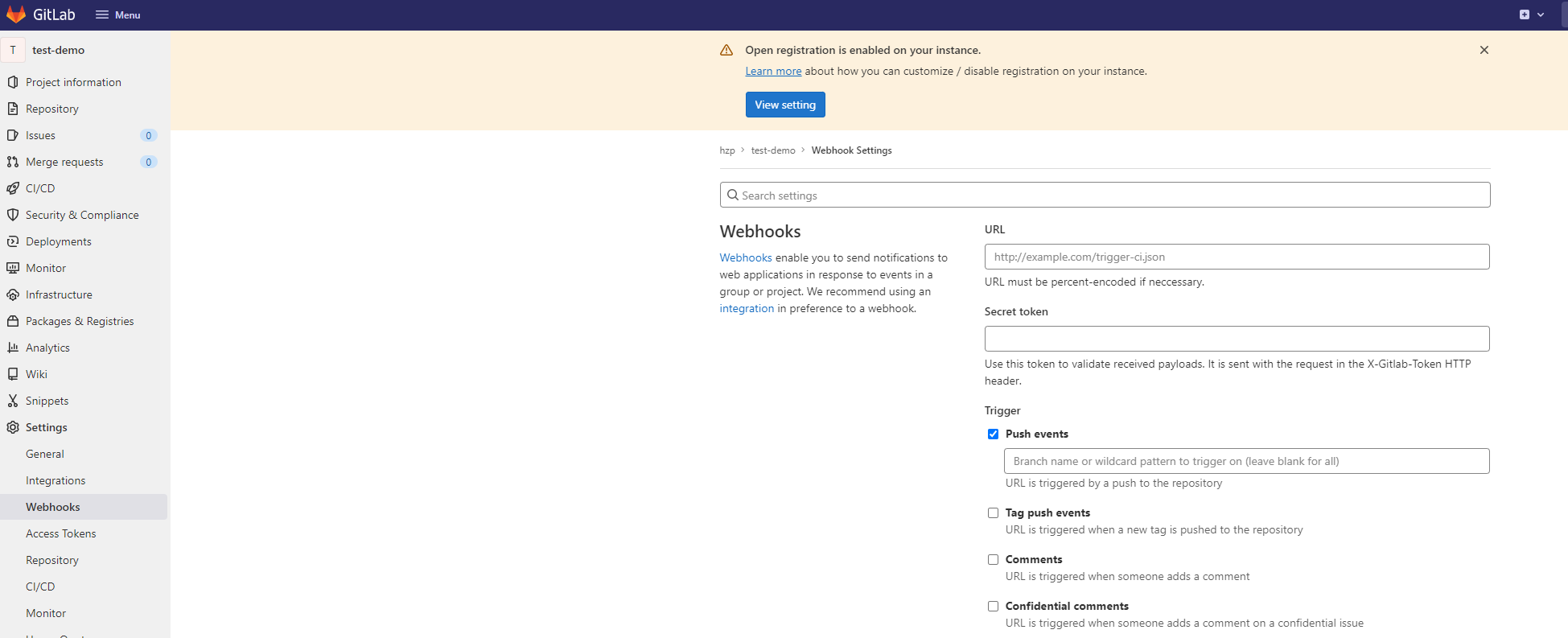
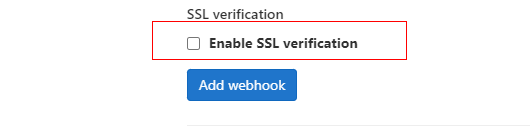
- Deselect Enable SSL verification for SSL verification and click Add webhook.
Figure 2 Configuration completed
Configuring a Pipeline Script
A pipeline script is a build command that runs during build. For details about script parameters, see Table 1.
|
Parameter |
Mandatory |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
git_url |
Yes |
String |
Address of the GitLab code repository. |
|
credentials_id |
Yes |
String |
GitLab credential ID configured using the account password. For details, see Creating a GitLab Credential. |
|
branch_name |
Yes |
String |
Name of the GitLab code repository branch. |
|
maven |
Yes |
String |
Path of the executable file for Maven installation, for example, /root/app/maven/apache-maven-3.8.6/bin/mvn. |
|
deploy_shell |
Yes |
String |
Path for storing the deploy.sh script on the VM where Jenkins is located, for example, /root/jar/deploy.sh. For details, see deploy.sh Description. |
|
build_target_name |
Yes |
String |
Build product name: software package name or image name:version number. This parameter is transferred when the script is executed. In the software package deployment scenario, the value is the software package name. In the image deployment scenario, the value is the built image name:version number. |
- After the build trigger is configured, select Pipeline script from the drop-down list on the Pipeline tab.
- Configure the pipeline script. In the example, the JAR package build scenario is used. The script is as follows:
node { // Define the code repository address. def git_url = 'http://100.**.**.207:8090/test/test-demo.git' // GitLab credential ID. def credentials_id = '133b7c9a-eb6a-4484-84b3-c3509ed63df8' // Name of the GitLab code repository branch. def branch_name = 'main' // Path of the executable file for installing Maven. def maven = '/root/app/maven/apache-maven-3.8.6/bin/mvn' // Path for storing the deploy.sh script. You need to set the execute permission on the path. def deploy_shell = '/root/jar/deploy.sh' // (Mandatory) Build product name: software package name or image name. This parameter is transferred when the script is executed. def build_target_name = "cae-demo-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar" stage('Clone sources') { git branch: branch_name, credentialsId: credentials_id, url: git_url } stage('Build') { //Build a JAR package. sh "'$maven' clean package -Dmaven.test.failure.ignore=true" } stage('deploy') { // Execute the script and use the build product to upgrade the CAE component. The timeout interval is 5 minutes. sh "timeout 300s '$deploy_shell' '$build_target_name'" } }
- During pipeline script running, deploy.sh is invoked. For details about the script, see deploy.sh Description.
- Set deploy.sh as an executable file.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





