Why Does the Vulnerability Scan Tool Detect the Disabled RC4 Vulnerability After WAF Is Connected?
Symptom
When a domain name was connected to WAF, the Cloud Mode - CNAME access was used, and a cipher suite that contains disabled RC4 algorithm was selected. However, the RC4 vulnerability was reported by a third-party vulnerability scanning tool.
Possible Causes
When establishing an HTTPS connection, the modern client declares the target domain name to the server through the Server Name Indication (SNI) extension of the TLS handshake protocol (RFC 6066). WAF matches the TLS policy (including the TLS version and cipher suite) of the corresponding domain name and negotiates with the server using the TLS policy.
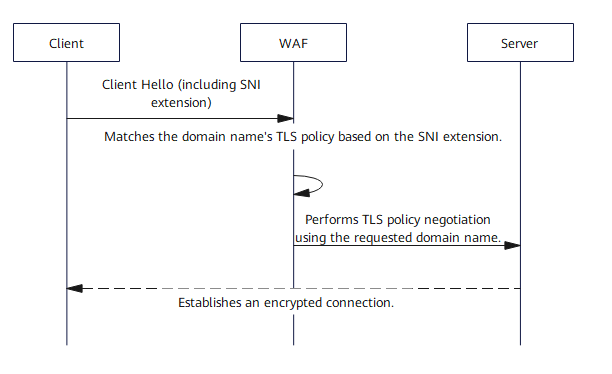
In some special scenarios, for example, when a traditional browser such as Internet Explorer 6 is used or WAF is accessed using an IP address, the client does not carry SNI information and does not support later version cipher suites that are more secure. To be compatible with these scenarios, WAF uses the default certificate for negotiation. The TLS configuration that takes effect is the global policy, which may contain legacy cryptographic algorithms such as RC4.
So, when a third-party vulnerability scanning tool directly scans the WAF IP address, WAF uses the default certificate for TLS negotiation because the client does not submit SNI information. In this situation, the scanning result may show that the disabled RC4 vulnerability exists. In this scenario, if you have selected the cipher suite that does not support RC4 in the domain name access configuration, the RC4 algorithm is not supported when you use the target domain name to access the website.
Solution
No action is required.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





