Creating a Service Gateway
Creating a Service Gateway on the Console
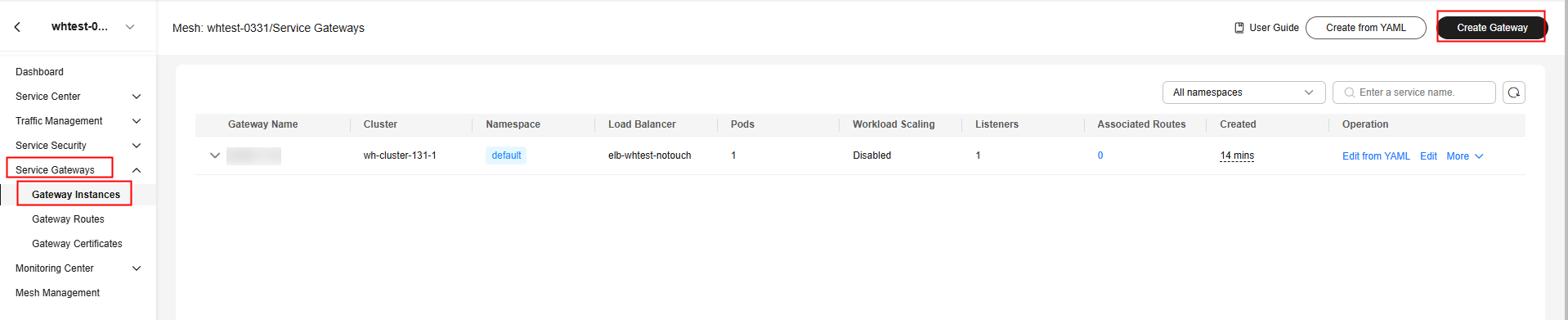
- Log in to the UCS console. In the navigation pane, choose Service Meshes.
- Click the name of the target service mesh to go to its details page.
- In the navigation pane, choose Service Gateways > Gateway Instances.
- In the upper right corner, click Create Gateway.
- Configure parameters.
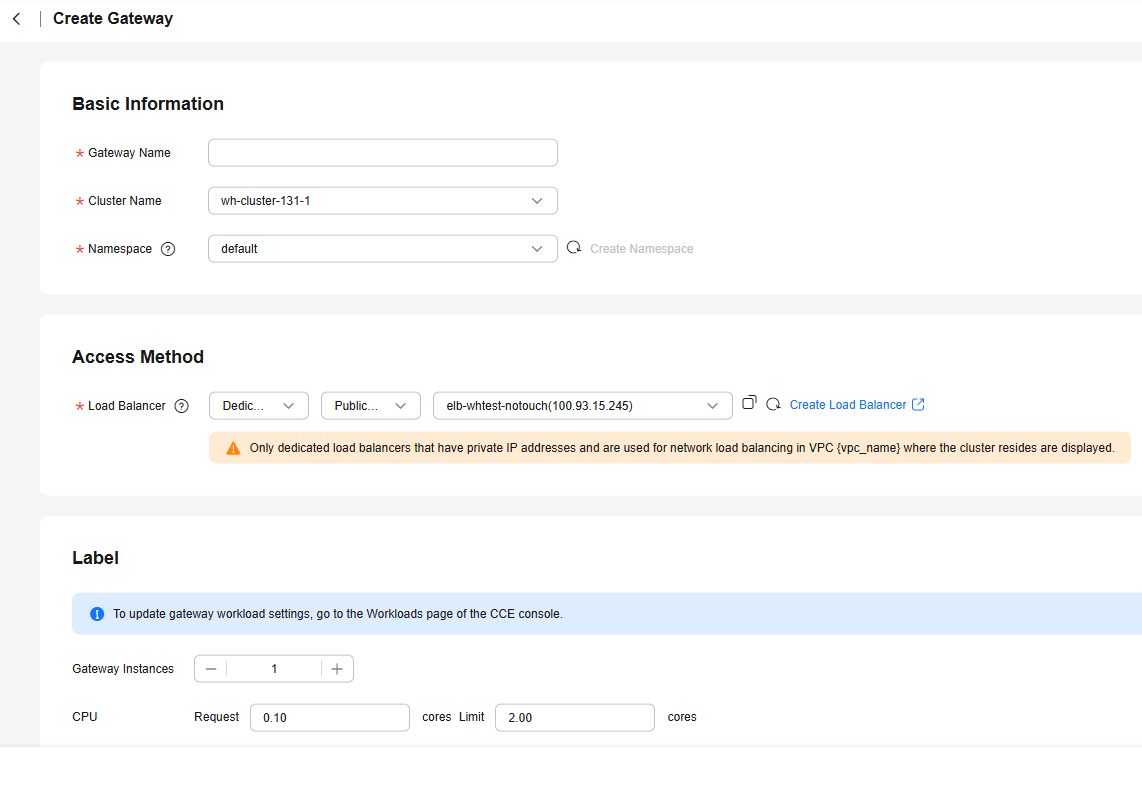
- Basic Information
- Gateway Name: Enter 4 to 59 characters starting with a lowercase letter and ending with a lowercase letter or digit. Only lowercase letters, digits, and hyphens (-) are allowed.
- Cluster Name: Select a cluster that has been connected to the service mesh. The workloads of the service mesh will be deployed in this cluster.
- Namespace: Select a service mesh namespace. If the namespace of the cluster is not synchronized to the service mesh, click Create Namespace, select the namespace, and click OK.
- Access Method
- Load Balancer: Select a load balancer for network access.
- Select an existing load balancer from the load balancer list. There are dedicated and shared load balancers. For shared load balancers, only these in the VPC where the cluster resides are displayed. For dedicated load balancers, they must have private IP addresses and are used for network load balancing in the VPC where the cluster resides.
- Click Create Load Balancer and select the required load balancer specifications.
- Load Balancer: Select a load balancer for network access.
- Label
- Gateway Instances: Configure the number of pods for the gateway workload. The default value is 1. Enter a value from 0 to 100.
- CPU request: Enter the minimum number of CPU cores required by a container. The default value is 0.10. CPU limit: Enter the maximum number of CPU cores available for a container. To avoid system faults resulting from excessive use of container resources, do not leave Limit unspecified.
- Memory request: Enter the minimum amount of memory required by a container. The default value is 128. Memory limit: Enter the maximum amount of memory available for a container. When the memory usage exceeds the memory limit, the container will be terminated.
- Listener
- Listener Name: Enter 4 to 59 characters starting with a lowercase letter and ending with a lowercase letter or digit. Only lowercase letters, digits, and hyphens (-) are allowed.
- Protocol: Select HTTP, TCP, TLS, or HTTPS.
- Port: Enter a value from 1 to 65535. Ensure that the port is not occupied by the listener of the selected load balancer.
- (Optional) Service Domain Name: Enter a domain name. The value can start with the wildcard (*). A domain name prefixed with the wildcard is interpreted as a suffix match. For example, *.example.com matches test.example.com and foo.test.example.com, but not example.com.
- Basic Information
- Click OK.

When a gateway is created, pods and a LoadBalancer Service are created automatically. Do not schedule the pods to a node running CentOS 7.6 or Huawei Cloud EulerOS 1.1, or the pods cannot be started. In clusters v1.22 or later, the pods of the gateway workload depend on ip_unprivileged_port_start of the kernel. You can run ls -l /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_unprivileged_port_start to check whether ip_unprivileged_port_start is supported. If it is not supported, the pods cannot be started.
To configure the gateway to allow HTTP traffic over port 801, take the following steps to create a service gateway using YAML.
Creating a Service Gateway Using YAML
- Log in to the UCS console. In the navigation pane, choose Service Meshes.
- Click the name of the target service mesh to go to its details page.
- In the navigation pane, choose Service Gateways > Gateway Instances.
- In the upper right corner, click Create from YAML.
- Create a load balancer with the port set to 801 to process only HTTP traffic. (You can configure the parameters based on site requirements.)
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: Gateway metadata: annotations: gateway.asm/cluster-name: cluster-test # Mandatory. Select the cluster where the pods of the gateway workload and LoadBalancer Service are created. gateway.asm/gateway-deployment-replicas: "2" # Optional. Specify the number of pods for the gateway workload. gateway.asm/gateway-deployment-resources: '{"requests":{"cpu":"100m","memory":"128Mi"},"limits":{"cpu":"2000m","memory":"1024Mi"}}' # Optional. Configure the CPU and memory quotas for the gateway workload. kubernetes.io/elb.class: union # Mandatory. Specify the load balancer type. The value can be union (shared load balancer) or performance (dedicated load balancer). kubernetes.io/elb.id: 73febb1c-b191-4fd9-832e-138b2657d3b1 # Mandatory. Specify the load balancer ID. name: gateway namespace: whtest spec: gatewayClassName: istio listeners: - name: default hostname: "*.example.com" # Optional. port: 801 # 1-65535 protocol: HTTP allowedRoutes: # Optional. Specify the namespaces whose route rules can be associated with the gateway. If this field is not specified, only the route rules of the same namespace can be associated with the gateway. namespaces: from: All # Select All, Same, or Selector.
The following are example YAML files of other protocol gateways.
HTTPS Gateway
Example YAML for creating an HTTPS gateway with TLS termination enabled:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
annotations:
gateway.asm/cluster-name: cluster-test # Mandatory. Select the cluster where the pods of the gateway workload and LoadBalancer Service are created.
gateway.asm/gateway-deployment-replicas: "2" # Optional. Specify the number of pods for the gateway workload.
gateway.asm/gateway-deployment-resources: '{"requests":{"cpu":"100m","memory":"128Mi"},"limits":{"cpu":"2000m","memory":"1024Mi"}}' # Optional. Configure the CPU and memory quotas for the gateway workload.
kubernetes.io/elb.class: union # Mandatory. Specify the load balancer type. The value can be union (shared load balancer) or performance (dedicated load balancer).
kubernetes.io/elb.id: 73febb1c-b191-4fd9-832e-138b2657d3b1 # Mandatory. Specify the load balancer ID.
name: https-gateway
namespace: whtest
spec:
gatewayClassName: istio
listeners:
- name: https
hostnames: ["httpbin.example.com", "httpbin2.example.com"] #Mandatory. If the certificate contains only one domain name, use hostname: "httpbin.example.com".
port: 443
protocol: HTTPS
allowedRoutes: # Optional. Specify the namespaces whose route rules can be associated with the gateway. If this field is not specified, only the route rules of the same namespace can be associated with the gateway.
namespaces:
from: All # Select All, Same, or Selector.
tls:
mode: Terminate
certificateRefs:
- name: httpbin-credential # Mandatory. You need to create a gateway certificate in the same namespace in advance.
TLS Gateway
Example YAML for creating a TLS gateway with TLS termination disabled:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
annotations:
gateway.asm/cluster-name: cluster-test # Mandatory. Select the cluster where the pods of the gateway workload and LoadBalancer Service are created.
gateway.asm/gateway-deployment-replicas: "2" # Optional. Specify the number of pods for the gateway workload.
gateway.asm/gateway-deployment-resources: '{"requests":{"cpu":"100m","memory":"128Mi"},"limits":{"cpu":"2000m","memory":"1024Mi"}}' # Optional. Configure the CPU and memory quotas for the gateway workload.
kubernetes.io/elb.class: union # Mandatory. Specify the load balancer type. The value can be union (shared load balancer) or performance (dedicated load balancer).
kubernetes.io/elb.id: 73febb1c-b191-4fd9-832e-138b2657d3b1 # Mandatory. Specify the load balancer ID.
name: tls-gateway
namespace: whtest
spec:
gatewayClassName: istio
listeners:
- name: tls
hostnames: ["httpbin.example.com", "httpbin2.example.com"] #Mandatory. If the certificate contains only one domain name, use hostname: "httpbin.example.com".
port: 9443
protocol: TLS
allowedRoutes: # Optional. Specify the namespaces whose route rules can be associated with the gateway. If this field is not specified, only the route rules of the same namespace can be associated with the gateway.
namespaces:
from: All # Select All, Same, or Selector.
tls:
mode: Passthrough
TCP Gateway
Example YAML for creating a TCP gateway:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
annotations:
gateway.asm/cluster-name: cluster-test # Mandatory. Select the cluster where the pods of the gateway workload and LoadBalancer Service are created.
gateway.asm/gateway-deployment-replicas: "2" # Optional. Specify the number of pods for the gateway workload.
gateway.asm/gateway-deployment-resources: '{"requests":{"cpu":"100m","memory":"128Mi"},"limits":{"cpu":"2000m","memory":"1024Mi"}}' # Optional. Configure the CPU and memory quotas for the gateway workload.
kubernetes.io/elb.class: union # Mandatory. Specify the load balancer type. The value can be union (shared load balancer) or performance (dedicated load balancer).
kubernetes.io/elb.id: 73febb1c-b191-4fd9-832e-138b2657d3b1 # Mandatory. Specify the load balancer ID.
name: tcp-gateway
namespace: whtest
spec:
gatewayClassName: istio
listeners:
- name: tcp
port: 8899
protocol: TCP
allowedRoutes: # Optional. Specify the namespaces whose route rules can be associated with the gateway. If this field is not specified, only the route rules of the same namespace can be associated with the gateway.
namespaces:
from: All # Select All, Same, or Selector.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





