Accessing a Real-Time Service Through Token-based Authentication
A token specifies certain permissions in a computer system. During token-based authentication, the token is added to requests to get permissions for calling the API.
If a real-time service is in the Running state, it has been deployed successfully. This service provides a standard RESTful API for users to call. You can use token-based authentication to verify your identity when calling a real-time service API.
ModelArts uses tokens for accessing real-time services. Tokens typically last 24 hours. Once expired, you must get a new one. This method suits fast development and testing due to its simplicity, though tokens expire quickly.
Test the real-time service's RESTful API before deploying it to production. Send an inference request using token-based authentication with these steps:
- Method 1: Use GUI-based Software for Inference (Postman). (Postman is recommended for Windows.)
- Method 2: Run the cURL Command to Send an Inference Request. (curl commands are recommended for Linux.)
- Method 3: Use Python to Send an Inference Request.
- Method 4: Use Java to Send an Inference Request.
Constraints
- The size of a request body cannot exceed 12 MB. Otherwise, the request will fail.
- Due to the limitation of API Gateway, the prediction duration of each request does not exceed 40 seconds.
Prerequisites
You have obtained a user token, local path to the inference file, URL of the real-time service, and input parameters of the real-time service.
- For details about how to obtain a user token, see Token-based Authentication. The real-time service APIs generated by ModelArts do not support tokens whose scope is domain. Therefore, you need to obtain the token whose scope is project.
- The local path to the inference file can be an absolute path (for example, D:/test.png for Windows and /opt/data/test.png for Linux) or a relative path (for example, ./test.png).
- You can obtain the service URL and input parameters of a real-time service on the Usage Guides tab page of its service details page.
The API URL is the service URL of the real-time service. If a path is defined for apis in the model configuration file, the URL must be followed by the user-defined path, for example, {URL of the real-time service}/predictions/poetry.
Figure 1 Obtaining the API URL and file prediction input parameters of a real-time service
Method 1: Use GUI-based Software for Inference (Postman)
- Download Postman and install it, or install the Postman Chrome extension. Alternatively, use other software that can send POST requests. Postman 7.24.0 is recommended.
- Open Postman. Figure 2 shows the Postman interface.
- Set parameters on Postman. The following uses image classification as an example.
- Select a POST task and copy the API URL to the POST text box. On the Headers tab page, set Key to X-Auth-Token and Value to the user token.

You can also use the AK and SK to encrypt API calling requests. For details, see Overview of Session Authentication.
Figure 3 Parameter settings
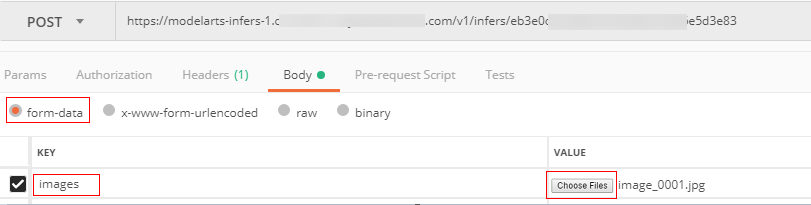
- In the Body tab, file input and text input are available.
- File input
Select form-data. Set KEY to the input parameter of the model, which must be the same as the input parameter of the real-time service. In this example, the KEY is images. Set VALUE to an image to be inferred (only one image can be inferred). See Figure 4.
- Text input
Select raw and then JSON(application/json). Enter the request body in the text box below. An example request body is as follows:
{ "meta": { "uuid": "10eb0091-887f-4839-9929-cbc884f1e20e" }, "data": { "req_data": [ { "sepal_length": 3, "sepal_width": 1, "petal_length": 2.2, "petal_width": 4 } ] } }meta can carry a universally unique identifier (UUID). When you call an API, the system provides a UUID. When the inference result is returned, the UUID is returned to trace the request. If you do not need this function, leave meta blank. data contains a req_data array for one or multiple pieces of input data. The parameters of each piece of data are determined by the model, such as sepal_length and sepal_width in this example.
- File input
- Select a POST task and copy the API URL to the POST text box. On the Headers tab page, set Key to X-Auth-Token and Value to the user token.
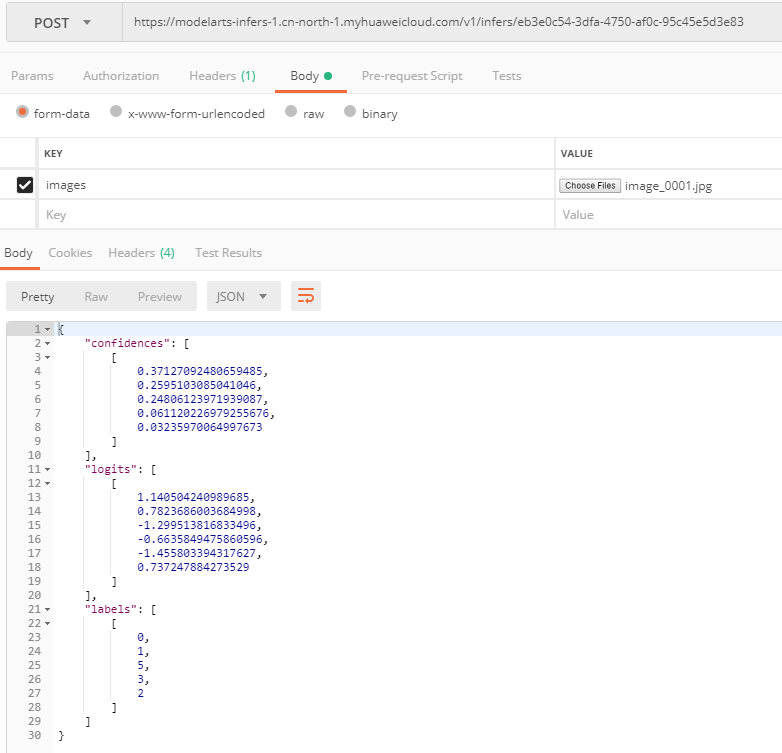
- After setting the parameters, click send to send the request. The result will be displayed in Response.
- Inference result using file input: Figure 5 shows an example. The field values in the return result vary with the model.
- Inference result using text input: Figure 6 shows an example. The request body contains meta and data. If the request contains uuid, uuid will be returned in the response. Otherwise, uuid is left blank. data contains a resp_data array for the inference results of one or multiple pieces of input data. The parameters of each result are determined by the model, for example, sepal_length and predictresult in this example.
Method 2: Run the cURL Command to Send an Inference Request
The command for sending inference requests can be input as a file or text.
- File input
curl -kv -F 'images=@Image path' -H 'X-Auth-Token:Token value' -X POST Real-time service URL
- -k indicates that SSL websites can be accessed without using a security certificate.
- -F indicates file input. In this example, the parameter name is images, which can be changed as required. The image storage path follows @.
- -H indicates the header of a POST command. X-Auth-Token is the header key, which is fixed. Token value indicates the user token.
- POST is followed by the API URL of the real-time service.
The following is an example of the cURL command for inference with file input:
curl -kv -F 'images=@/home/data/test.png' -H 'X-Auth-Token:MIISkAY***80T9wHQ==' -X POST https://modelarts-infers-1.xxx/v1/infers/eb3e0c54-3dfa-4750-af0c-95c45e5d3e83
- Text input
curl -kv -d '{"data":{"req_data":[{"sepal_length":3,"sepal_width":1,"petal_length":2.2,"petal_width":4}]}}' -H 'X-Auth-Token:MIISkAY***80T9wHQ==' -H 'Content-type: application/json' -X POST https://modelarts-infers-1.xxx/v1/infers/eb3e0c54-3dfa-4750-af0c-95c45e5d3e83-d indicates the text input of the request body.
Method 3: Use Python to Send an Inference Request
- Download the Python SDK and configure it in the development tool. For details, see Integrating the Python SDK for API request signing.
- Create a request body for inference.
- File input
# coding=utf-8 import requests if __name__ == '__main__': # Config url, token and file path. url = "URL of the real-time service" token = "User token" file_path = "Local path to the inference file" # Send request. headers = { 'X-Auth-Token': token } files = { 'images': open(file_path, 'rb') } resp = requests.post(url, headers=headers, files=files) # Print result. print(resp.status_code) print(resp.text)The files name is determined by the input parameter of the real-time service. The parameter name must be the same as that of the input parameter of the file type. The input parameter images obtained in Prerequisites is an example.
- Text input (JSON)
The following is an example of the request body for reading the local inference file and performing Base64 encoding:
# coding=utf-8 import base64 import requests if __name__ == '__main__': # Config url, token and file path url = "URL of the real-time service" token = "User token" file_path = "Local path to the inference file" with open(file_path, "rb") as file: base64_data = base64.b64encode(file.read()).decode("utf-8") # Set body,then send request headers = { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'X-Auth-Token': token } body = { 'image': base64_data } resp = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=body) # Print result print(resp.status_code) print(resp.text)The body name is determined by the input parameter of the real-time service. The parameter name must be the same as that of the input parameter of the string type. The input parameter images obtained in Prerequisites is an example. The value of base64_data in body is of the string type.
- File input
Method 4: Use Java to Send an Inference Request
- Download the Java SDK and configure it in the development tool. For details, see Integrating the Java SDK for API request signing.
- (Optional) If the input of the inference request is in the file format, the Java project depends on the httpmime module.
- Add httpmime-x.x.x.jar to the libs folder. Figure 7 shows a complete Java dependency library.
You are advised to use httpmime-x.x.x.jar 4.5 or later. Download httpmime-x.x.x.jar from https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.httpcomponents/httpmime.
- After httpmime-x.x.x.jar is added, add httpmime information to the .classpath file of the Java project as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <classpath> <classpathentry kind="con" path="org.eclipse.jdt.launching.JRE_CONTAINER"/> <classpathentry kind="src" path="src"/> <classpathentry kind="lib" path="libs/commons-codec-1.11.jar"/> <classpathentry kind="lib" path="libs/commons-logging-1.2.jar"/> <classpathentry kind="lib" path="libs/httpclient-4.5.13.jar"/> <classpathentry kind="lib" path="libs/httpcore-4.4.13.jar"/> <classpathentry kind="lib" path="libs/httpmime-x.x.x.jar"/> <classpathentry kind="lib" path="libs/java-sdk-core-3.1.2.jar"/> <classpathentry kind="lib" path="libs/okhttp-3.14.9.jar"/> <classpathentry kind="lib" path="libs/okio-1.17.2.jar"/> <classpathentry kind="output" path="bin"/> </classpath>
- Add httpmime-x.x.x.jar to the libs folder. Figure 7 shows a complete Java dependency library.
- Create a Java request body for inference.
- File input
A sample Java request body is as follows:
// Package name of the demo. package com.apig.sdk.demo; import org.apache.http.Consts; import org.apache.http.HttpEntity; import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse; import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost; import org.apache.http.entity.ContentType; import org.apache.http.entity.mime.MultipartEntityBuilder; import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients; import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils; import java.io.File; public class MyTokenFile { public static void main(String[] args) { // Config url, token and filePath String url = "URL of the real-time service"; String token = "User token"; String filePath = "Local path to the inference file"; try { // Create post HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(url); // Add header parameters httpPost.setHeader("X-Auth-Token", token); // Add a body if you have specified the PUT or POST method. Special characters, such as the double quotation mark ("), contained in the body must be escaped. File file = new File(filePath); HttpEntity entity = MultipartEntityBuilder.create().addBinaryBody("images", file).setContentType(ContentType.MULTIPART_FORM_DATA).setCharset(Consts.UTF_8).build(); httpPost.setEntity(entity); // Send post CloseableHttpResponse response = HttpClients.createDefault().execute(httpPost); // Print result System.out.println(response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()); System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity())); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }The addBinaryBody name is determined by the input parameter of the real-time service. The parameter name must be the same as that of the input parameter of the file type. The file images obtained in Prerequisites is used as an example.
- Text input (JSON)
The following is an example of the request body for reading the local inference file and performing Base64 encoding:
// Package name of the demo. package com.apig.sdk.demo; import org.apache.http.HttpHeaders; import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse; import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost; import org.apache.http.entity.StringEntity; import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients; import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils; public class MyTokenTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // Config url, token and body String url = "URL of the real-time service"; String token = "User token"; String body = "{}"; try { // Create post HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(url); // Add header parameters httpPost.setHeader(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE, "application/json"); httpPost.setHeader("X-Auth-Token", token); // Special characters, such as the double quotation mark ("), contained in the body must be escaped. httpPost.setEntity(new StringEntity(body)); // Send post. CloseableHttpResponse response = HttpClients.createDefault().execute(httpPost); // Print result System.out.println(response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()); System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity())); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }body is determined by the text format. JSON is used as an example.
- File input
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot