Requirement Management Process
Overview
Raw requirements are usually abstract and vague. They need to be analyzed and broken down into minimum-level units that can be delivered in sprints.
In Scrum projects, requirements can be managed in the four-layer hierarchy: , as shown in the following figure.
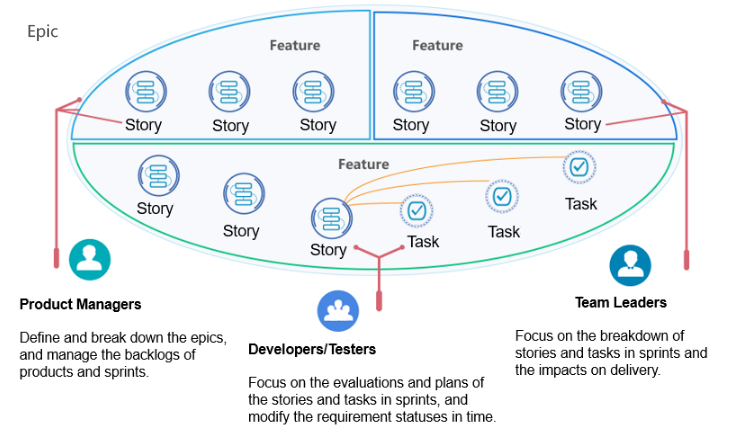
An abstract and vague epic is divided into multiple features which are further broken down into stories. A story, also called user story, is a minimum deliverable unit that is written from the customers' perspective and complies with the INVEST principle. This means that a story should be independent, negotiable, valuable, estimable, small, and testable. After the breakdown, stories are scheduled into one or more sprints based on the manpower of the development team and the estimated finished time of the epic.
This method ensures continuous delivery by producing runnable software in every sprint and offering it to users for testing. The development team can then collect user feedback, apply changes accordingly in the next sprint, and finally deliver a product that meets the requirements of users and achieves business success.
Table 1 describes the work item types used by Scrum projects.
Introduction
Scrum is an incremental, iterative, and agile software development method. It enables continuous delivery through sprints, which are cycles of closed-loop software development from user requirements management to user feedback implementation.
Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective are the major activities for simple but efficient project management. The management process is as follows.
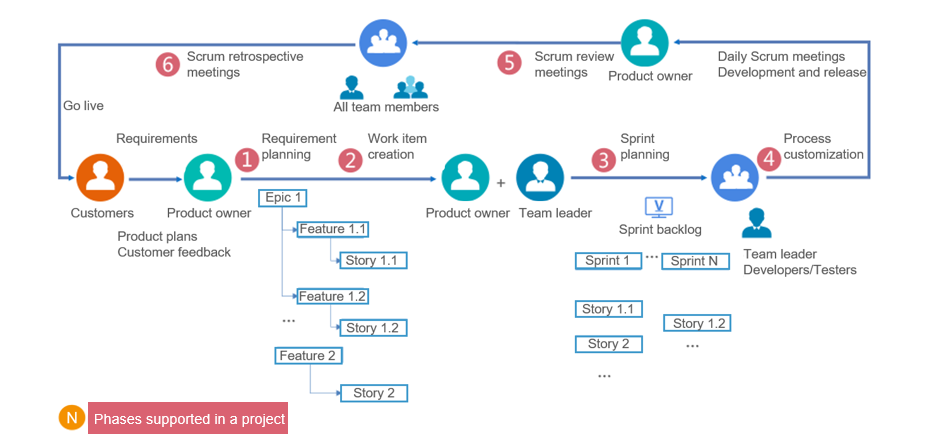
Typical Sprint Process in a Scrum Project
The procedure can be reused for continuous planning and delivery in each sprint management. The following figure shows the Scrum development and project management process.
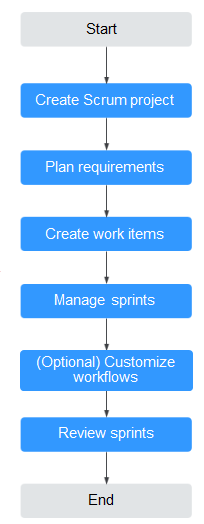
|
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Create Scrum project |
For details, see Creating a CodeArts Project. After a project is created, you can configure common settings. You can invite other users to join a created Kanban project as required. For details about how to add members, see Adding Members to a CodeArts Project. |
|
Plan requirement |
Plan requirements using mind maps or Gantt charts based on the project breakdown needs. For details, see Creating a Mind Map and Creating a Gantt Chart. |
|
Create work item |
Create work items after the requirements are planned. For details, see Creating Work Items, Creating a Work Item in a Mind Map, and Creating a Work Item in a Gantt Chart. |
|
Manage sprint |
Plan and manage sprints. For details, see Configuring a Sprint Plan. |
|
(Optional) Customize workflow |
Customize the workflows as required. For details, see Configuring Common Settings. |
|
Organize sprint retrospective |
Review the sprints for improvements. For details, see Tracking the Project Progress. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





